Posts Tagged ‘Niels Barfoed’
PEN Journey 42: From Copenhagen to Dakar to Guadalajara and in Between
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.

Royal Danish Library extension in Copenhagen, dubbed the Black Diamond (Photo by © User:Colin / Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=66870365)
Arriving in Copenhagen in early September 2006, I walked along the waterfront, dodged bicycles and shared coffee and conversation with longtime colleague Niels Barfoed, former President of Danish PEN who had briefly succeeded me as Writers in Prison Chair and was an eminent Danish journalist and writer. We met at the new waterfront extension of the Royal Danish Library, dubbed the Black Diamond because of its imposing black granite cladding and irregular angles. Niels would be moderating a public meeting on Freedom of Expression in the Arab World.
PEN International’s base was broadening in the Middle East and in Africa, both regions where active centers for writers were fragile, but potentially important havens. Danish PEN was hosting a conference with a dozen writers from the Arab-speaking world, including representatives from Egypt, Morocco, Jordan, Palestinian PEN, Tunisia, Lebanon and invited writers from Iraq and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), along with Danish and Norwegian PEN members and International PEN represented by Centers Coordinator Peter Firkin and myself.
The Copenhagen conference had been initiated in part as a response to the Danish cartoons controversy earlier in the year and also as an opportunity to develop PEN’s work and presence in the Middle East. PEN had a few centers in the region and interest from writers in Jordan, Iraq, Kuwait, and Bahrain to form additional PEN centers and a desire to revive PEN Lebanon. Developing PEN centers in these areas was challenging given the politics and conflicts on the ground.
Ekbal Baraka, President Egyptian PEN (left) and Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, PEN International Secretary (right) meeting in Cairo, 2006
The Copenhagen meetings explored common fields of interest among Western and Arab writers, networking among Arab writers and ways in which PEN could assist. Women writers in the Arab world had particular challenges, a discussion led by Egyptian PEN President Ekbal Baraka. Ekbal later became Chair of PEN International’s Women Writers Committee. Algerian PEN and International PEN board member Mohamed Magani offered to host a subsequent meeting in Algiers the following fall, along with a conference on translation. A public event in the evening showcased the work of the visiting writers.
On the final day the public conference on Freedom of Expression in the Arab World moderated by Niels included discussions on Networking in the Cause for Freedom of Media and Opinion and featured renowned Tunisian journalist and human rights campaigner Sihem Bensedrine. A discussion on Access to Information: Implications to Development was addressed by Jordanian journalist Daoud Kuttab and Danish columnist and Danish PEN President Anders Jerichow. Lebanese Writer Elias Khoury and Egyptian journalist and commentator Mona Eltahawy concluded the conference in a discussion on Publication and Powerplay in the Middle East.
The days together resulted in a loose network of these and other Arab writers and eventually led to the opening of additional PEN centers and work in the Middle East. PEN currently has Bahrain, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, and Palestinian centers as well as the Egyptian, Algerian and Moroccan Centers.
******

Anna Politkovskaya, Russian journalist assassinated, 2006
A few weeks after the Copenhagen conference, my phone rang early on Saturday morning October 7, 2006 at my home in Washington, DC. Sara Whyatt, PEN International’s Writers in Prison Committee Director, was on the line. She called to tell me that Anna Politkovskaya, Russian journalist, PEN member who’d visited PEN Congresses and meetings, who’d worked for years reporting on Chechnya—had been assassinated. The report was that Anna had been shot that morning in the elevator of her apartment building in Moscow.
For seven years Anna had been one of the few reporting on the war in Chechnya despite intimidation and violence. She had been arrested by the Russian military and suffered a mock execution; she’d been poisoned while flying from Moscow to the Beslan school hostage crisis and had to turn back to get medical treatment. She had survived many dangerous encounters. But now she had been killed.
The killing of Anna Politkovskaya swept through the news media around the world as well as through the PEN world. We were stunned and deeply saddened and then began our protests and calls for investigation, along with human rights organizations worldwide. PEN honored Anna at its subsequent Congress and meetings and annually held an Anna Politkovskaya lecture on the anniversary of her death to commemorate her fortitude and inspiration.
The work in PEN was a helix of hope and pain and sorrow and hope again.
******

Dakar, Senegal, venue for PEN’s upcoming 73rd World International Congress in 2007
At the end of November Senegalese PEN hosted a meeting with African centers engaged with the planning of PEN’s 73rd Congress to be held in 2007 in Dakar. The meeting included representatives from Egypt, Morocco, Algeria, Guinea, Senegal, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, and Ghana. It was standard practice for International PEN to visit the site of an upcoming Congress to review logistics and budgets and programs in advance, to assist and assure the Congress ran smoothly. The 73rd Congress in Dakar would be only the second time a PEN Center in Africa had hosted a World Congress. In addition to reviewing the facilities at the Meridien hotel by the ocean, the delegation met with the Minister at the Ministry of Culture and Classified Historical Heritage which was supporting the Congress.
At that meeting and throughout the Congress to come, I offered the sentiment I had drafted and memorized in French and still endorse:
“Il n’y a que quelques autres pays dans le monde ou l’ecrivain est plus honore qu’au Senegal.
“There are few countries in the world where the writer is more honored than in Senegal.”
Because Senegal’s founding President Leopold Senghor had been a poet and writer of global distinction, also a Vice President of International PEN, Senegal celebrated literature. “As a national leader, Leopold Senghor left a rich heritage and respect for African culture and writing which we hope to honor by International PEN’s upcoming Congress in Dakar,” I told the Minister.

Karen Efford, PEN Program Officer, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, PEN International Secretary, and Caroline McCormick, PEN International Executive Director, meeting in Dakar. Senegalese PEN members organizing PEN 73rd World Congress included Abdoulaye Racine Senghor, Abdoulaye Fode Ndione, Mamadou Diop Traoré, Seydi Sow, Mbaye Gana Kehe, Alioune Badara Beye, Elie-Charles Moreau, Silcarneyni Gueye, Aissatou Diop
Senegalese PEN hosted our working meetings at its headquarters where the focus was also on regional development. International PEN’s Executive Director Caroline McCormick and Program Officer Karen Efford led a “mapping” or gathering of information with each center on its activities and membership and needs in order to determine how PEN International could assist, especially with fundraising. The Centers also participated in the discussions on the programs and facilities for the July 2007 Congress.
After hours of meetings, we all went to dinner together at the local restaurant. I don’t remember the food, except there were generous plates family style. I remember the atmosphere—the bright blues and reds and yellows in the restaurant, the music, and the laughter after a long day concentrating on budgets, logistics, and translations. The planning meetings were work but also fun with friendships among the writers from the PAN Africa Network with whom I had met on numerous occasions over the past few years.
In my three years as International Secretary, I was impressed by the care of all the host centers for Congresses. The Congress in Senegal would be my last as an officer of International PEN, except for the privilege of attending as a Vice President in the years to come. The operational work and responsibility would be passed on. I had determined not to stand for a second term. I had other responsibilities that had been put on hold for three years, and I had learned it was better to leave a position when everyone wanted you to stay, than to stay too long when people were waiting for you to leave. I needed to return to being a writer and to my family and to the other organizational work I did. So Senegal would be a farewell of sorts for me. It would prove to be a grand occasion, but I am getting ahead of myself…
******
“Does Freedom of Expression Have a Limit?” “Hospitality without Borders.”—those two panels I participated in and moderated at the 2006 Gothenburg Book Fair, Scandinavia’s largest. The International Publishers Association (IPA) and International PEN had been collaborators in selecting the Fair’s theme of Freedom of Expression that year. The Book Fair reflected the Freedom of Expression theme in many of its over 2000 events for the 100,000 visitors. PEN and IPA, along with the International Cities of Refuge Network (ICORN), had an exhibit with a stage where events and seminars took place.
For me, it was a special pleasure to attend the Fair in Sweden where my mentor and predecessor as Writers in Prison Chair Thomas von Vegesack was a respected and now retired publisher. Thomas attended the Book Fair. I noted in my remarks that it was from Thomas I’d learned the difference between having principles and simply talking about principles. Thomas didn’t like “principles,” which meant he didn’t like paradigms of abstractions. Our role—PEN’s role—was pragmatic. It was to help writers in trouble, to be in touch with them and their families so the isolation of imprisonment was broken, to give them support and most of all to figure out where the access was within our PEN centers and within our larger freedom of expression community to pressure governments to spring open the prison doors and also to get protection for writers under death threats. (It was two weeks after the Gothenburg Book Fair that Anna Politkovskaya was assassinated.)
The world had changed since the days Thomas and I had been chair of WiPC. In the late 1980’s and early 1990’s we had all been hopeful that the fall of the Berlin Wall and the fall of the totalitarian governments would ease the situation for writers worldwide, but there were now as many writers as ever under threat. PEN’s casebook listed over 1000. There were more non-state actors. There was also a level of global communication that was only budding in 1993 when Thomas handed over the reins to me. There were new bad guys, and many of the good guys were not as good as they once were. We were in a world where freedom of expression was no longer accepted as an unqualified value.
Yet “the world is still changed by ideas and books, and writers who write them are still the main vehicle for ideas,” I concluded my opening talk.
On the panel “Does Freedom of Expression Have a Limit?” we had no easy answer. We asked if there was a personal and public responsibility to tell the truth, or at least not to lie. And who determined a lie? The responsibility of the writer was to try to find and tell the truth even if truth seemed relative at times. The question arose, who sets the limits on freedom of expression? The State? Society at large? What were those limits and penalties and were they set by fear of attack or violence or censorship?
It was generally agreed that calls for violence such as the killing of another human being set a limit on freedom of expression, especially when this call came from someone who had the power of the state to exercise the threat. An example was the fatwa on Salman Rushdie. The limit should not be on Rushdie but on the Ayatollah and the state that issued the fatwa calling for his death.
Hate speech had a limit when it urged violence as in the case of Radio Rwanda during the genocide against the Tutsis or certain broadcasts during the Balkans wars.
PEN’s Charter contained the elements of the dialectic upon which free societies were based, both the respect for other cultures in an effort to dispel race, class and national hatreds and also a commitment to protect the free and unhampered transmission of thought and ideas.
“And since freedom implies voluntary restraint, members pledge themselves to oppose such evils of a free press as mendacious publication, deliberate falsehood and distortion of facts for political and personal ends,” the PEN Charter concluded.
Democracies flourish only when an exchange of competing, even contradictory, ideas can occur in a battle of ideas, the panel concluded.

Novelist Moris Farhi, former WiPC Chair and PEN Vice President/English PEN
The panel “Hospitality Without Borders,” co-sponsored by ICORN, featured Orhan Pamuk, the Turkish novelist who a month later won the Nobel Prize for Literature, and Moris Farhi, also Turkish but long resident in the UK and member of English PEN. Moris had followed me as Chair of PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee after Niels Barfoed’s brief tenure.

Novelist Orhan Pamuk (Photo credit: © Elena Seibert)
The previous year, Orhan had faced charges of “insulting the Turkish Army and Turkishness” because of his statement in a Swiss newspaper regarding the Armenian genocide and massacre of a million Armenians and 30,000 Kurds in Anatolia in 1919. On the panel Orhan noted how valuable it was for a persecuted writer in his home to know about the possibility of finding refuge in a safe city, even if he didn’t take advantage or was unable to leave his present situation at the time.
Moris, who’d also chaired English PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee, talked about the challenges facing the host city and the community receiving a guest writer. He focused on how to make sure the writer didn’t just disappear from the literary community and the need to focus on translation and publishing strategies for the writer. It was important to help the writer establish new foundations and relationships in a new city.
I recalled the situation of Bangladeshi novelist Taslima Nasreen who had faced death threats and was given asylum in Sweden and awarded the Tucholsky prize. Taslima Nasreen’s was one of the more dramatic cases in my PEN history as she was whisked out of Dhaka in the dark of night and brought to Stockholm by Swedish PEN. That had turned out to be just one stop on a difficult journey into exile.
******
 At the end of 2006, PEN Guadalajara, San Miguel PEN and the Ibero-American Foundation of PEN established a presence for the first time at the 20th Guadalajara Book Fair. The Guadalajara Book Fair was considered the most important publishing event in the Spanish-speaking world, hosting 450,000 visitors and 15,000 book professionals from over 40 countries. Officials of the Guadalajara Book Fair were eager to have a relationship with PEN in order to collaborate and “create and guarantee space in which literature of different languages cohabit supporting the freedom of opinion with words as vehicle of understanding between different nations and cultures,” according to the Coordinator of the Festival events.
At the end of 2006, PEN Guadalajara, San Miguel PEN and the Ibero-American Foundation of PEN established a presence for the first time at the 20th Guadalajara Book Fair. The Guadalajara Book Fair was considered the most important publishing event in the Spanish-speaking world, hosting 450,000 visitors and 15,000 book professionals from over 40 countries. Officials of the Guadalajara Book Fair were eager to have a relationship with PEN in order to collaborate and “create and guarantee space in which literature of different languages cohabit supporting the freedom of opinion with words as vehicle of understanding between different nations and cultures,” according to the Coordinator of the Festival events.
International PEN aspired to have a more robust presence at book fairs globally, but did not yet have the budget or staff. However International PEN supported centers’ activities at book fairs such as at Frankfurt, Gothenburg, and now Guadalajara. I visited the Guadalajara Book Fair as part of this initiative.
PEN Guadalajara and San Miguel and the Ibero-American Foundation of PEN hosted a stand at the Book Fair and offered readings and presentations of books and displayed hundreds of books from PEN members and PEN centers around the globe. On the Book Fair’s program two eminent PEN members, Vice President Nadine Gordimer and former PEN International President Mario Vargas Llosa were featured. Nadine Gordimer participated in a Literary Salon and later had dinner with PEN members. I have no notes from that dinner, but I have fond memories of the outside restaurant in the evening and the hospitality of Guadalajara and San Miguel PEN and the graciousness of Nadine Gordimer.

Photo Left: Meeting at 2006 Guadalajara Book Fair: María Elena Ruiz Cruz, Víctor Sahuatoba, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, Lucina Kathmann, Luis Mario Cerda, Martha Cerda, Moisés Zamora. Photo Right: At dinner: Moisés Zamora, Nadine Gordimer, Martha Cerda, and Joanne Leedom-Ackerman
Martha Cerda, President of Guadalajara PEN, PEN Vice President Lucina Kathmann of San Miguel PEN and I met with Book Fair officials and assured that PEN would have a presence and partnership with the Guadalajara Book Fair in the years to come through its Latin American centers.
The visit to Guadalajara also offered the opportunity to meet with members from several Latin American PEN centers in a preliminary focus on the region and on the “mapping” International PEN would undertake of resources, programs and needs of the Latin American PEN centers before the 2008 Congress in the region.
******
At the end of 2006 PEN’s long time staff member Jane Spender retired. Jane had worked with Peter Day on the PEN International Magazine as an editor; she’d been administrative assistant to the Administrative Secretary Elizabeth Paterson and then became the Administrative Director when Elisabeth retired. She had taken on the role of International PEN Program Director when PEN hired an Executive Director. We all relied on Jane’s intelligence, good humor and patience. Jane and I had spent hours—too many hours we both agreed—toiling over just the right word on several documents. I was especially going to miss working with Jane; I have kept the friendship to this day. To celebrate the past and send her off with good wishes for the future, we surprised her by giving her a bicycle which I rode across the office and presented to her. Friends from International PEN and English PEN all gathered in PEN’s new offices on High Holborn. PEN is about people, and Jane was one of the stalwart ones.

Jane Spender retirement party at PEN offices, 2006. L to R: Sara Whyatt, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, Jane Spender, Caroline McCormack, Karen Efford, Terry Carlbom, Ursula Setzer, Josephine Pullen-Thompson, Francis King, Peter Day, Gilly Vincent, Jane Spender, Nawal, Karen Efford, Elizabeth Paterson
Next Installment: PEN Journey 43: Turkey and China—One Step Forward, Two Steps Backward
PEN Journey 18: Picasso Club and Other Transitions in Guadalajara
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.
PEN perches on a three-legged stool. One leg is literature—the work of writers around the world. The other leg is freedom of expression—the defense of writers, particularly those in authoritarian regimes. The third leg is community—the fellowship among writers from over 100 countries sharing, appreciating, translating. PEN began as a loose network of clubs after World War I and grew quickly. The governance of the organization has evolved and at times set the three legs of the stool at odd angles to each other. One such occasion was at the Guadalajara Congress in 1996 as PEN celebrated its 75th anniversary.
My file for that Congress, whose theme was “Literature and Democracy,” bulges with documents and papers and programs in duplicates and triplicates. I don’t know why it is so much larger than the other files. In retrospect, the 1996 Congress was an inflection point, a turn in the road. Maybe I was collecting evidence.

Program from PEN International 63rd Congress in Guadalajara, Mexico
At the Congress I was handing over the reins of the Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC), having finished my term, at least that was my intent. Ronald Harwood was doing the same as President of PEN International, at least that was his intent. Elizabeth Paterson was retiring after 28 years as Administrative Secretary of PEN, and WiPC researcher Mandy Garner was also moving on. PEN was navigating transitions, some planned, but others with a momentum of their own.
For the global context of that time, I reported as Chair of WiPC to the Congress:
“…two political phenomena have emerged, both perhaps linked to the end of the Cold War. First, we have seen conflicts erupting not so much between nations as within nations. This phenomenon, though not new, has offered particular challenges for the writer. Dozens of writers have been killed in conflicts in Algeria, Bosnia, Rwanda, Chechnya. In a number of counties with internal conflicts, including Peru, India, and Turkey, governments have used Anti-Terror Laws to arrest writers who write about the opposing parties.
“Another phenomenon is the increasing number of countries turning to the democratic process for government. The end of the Cold War saw the fall of many totalitarian regimes. Since 1990 over 50 countries have, at least on paper, turned to democracy to select their governments. However, democracy has not always settled so easily into place. One of the indispensable elements of a working democracy is freedom of expression, and this freedom has often been curtailed. Because PEN’s mandate is to protect the free flow of ideas and the freedom of writers to write, to criticize and to protest, PEN’s mission is as compelling today with newly emerging democracies as it was during the Cold War era. In country after country—from Albania, Algeria, Azerbaijan, Cambodia, Cote d’Ivoire, Croatia, Egypt, Ethiopia, Romania, Tajikistan, Zambia—writers can be and have been arrested on such charges as “disseminating false propaganda,” “insulting the President,” and “publishing false news.” The Writers in Prison Committee’s protests and work for these writers is fundamental in a larger political process that is unfolding…
“…Whenever one might feel despair for the way human beings can treat one another, the despair can be lifted by noting the caring of the writers who work for each other. The members of the new Ghana PEN have adopted a writer in Peru; Mexican members and Swedish members work for Turkish writers; Polish, Slovak, Nepalese, French and many other members work on behalf of imprisoned Vietnamese writers. Canadian writers are working on behalf of their Nigerian colleagues, an American writer writes in Portuguese to an Indonesian imprisoned writer; English and German writers have been in long-term correspondence with an imprisoned writer in South Korea. Danish writers are working for an imprisoned writer in Yemen; Norwegian, Finish, Austrian and Czech writers are protesting on behalf of Chinese writers; Australian and Catalan writers work for imprisoned colleagues in Myanmar/Burma…”
These corridors of concern linked men and women around the world in defense of each other and of freedom of expression. The Writers in Prison Committee was a place everyone came together to focus on PEN’s mission. Discussion on resolutions and actions began there and were taken to the full Assembly of Delegates.
That year resolutions passed and action was taken on cases in: Algeria where seven writers had been killed and many more threatened and arrested; the Dominican Republic where intolerance was growing and a writer had disappeared; Turkey where 50 writers were imprisoned and 100 others sentenced to prison; Indonesia where writers had been arrested and imprisoned and the famed writer Pramoedya Ananta Toer was under town-arrest and where in East Timor writers had been killed and leader and poet Alexandre (Xanana Gusmao) was in prison and sentenced to death; Iran where writers were disappeared, tortured and imprisoned; Central Asian Republics, particularly Tajikistan, where at least 29 journalists had been murdered in the last four years; China where dozens of writers were serving long prison sentences or were sentenced to re-education camps; Cuba where journalists were imprisoned and harassed; Mexico where journalists were killed, disappeared and threatened; Vietnam where writers were serving lengthy prison terms; and Nigeria where Ken Saro Wiwa had been hanged the year before and other writers were in prison.
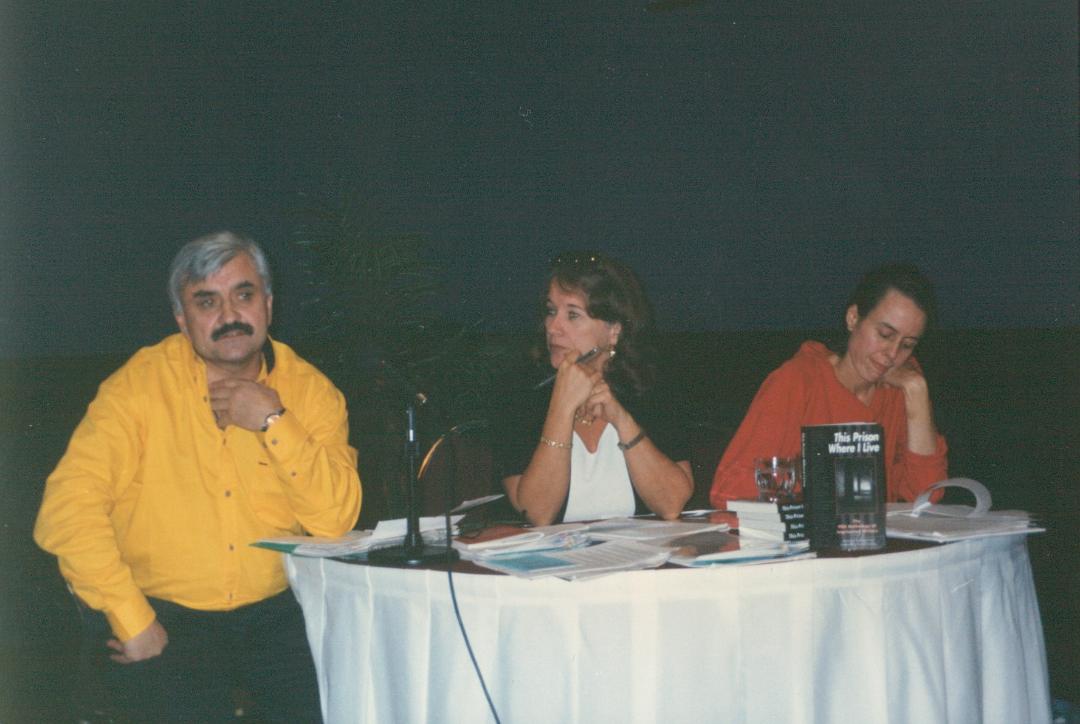

Writers in Prison Committee at Guadalajara Congress, 1996. L to R: Alexander Tkachenko (Russian PEN), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (WiPC Chair), Mandy Garner (WiPC researcher)
At the WiPC meeting there was a report on PEN’s quiet mission to Cuba where writers were hoping the system would open up after the global changes in 1989. Writers there said they were in a goldfish bowl but never sure how big the bowl was from day to day, and those arrested often faced a choice between long prison sentences and exile. The WiPC meeting also heard from the sister of Myrna Mack, a Guatemalan anthropologist who had been killed and was one of the significant leaders of the worldwide movement against impunity. We also launched the anthology This Prison Where I Live of writings from PEN cases over the years.
In addition to the Writers in Prison Committee, the Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee, the Peace Committee and the Women’s Committee met in the early days of the Guadalajara Congress. Literary sessions focused on the Congress theme with programs on Literature of Old and New Democracies and Post-Communist Democracies.

Picasso Club neckties: Top l to r: Michael Scammel (International PEN Vice President), Carles Torner (Catalan PEN), Isidor Consul (Chair PEN Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee)
Also during those first days of the Congress, a group of members were meeting off site to launch a process to reshape the governance of PEN. For as long as anyone could remember, the International Secretary and President had been the sole decision-makers between Congresses where the Assembly of Delegates voted on issues. Many felt this system no longer allowed sufficient democratic expression for a worldwide organization.
I was friends with many of those meeting, but the WiPC staff and I kept out of the off-site gatherings. We felt we needed to keep the WiPC a neutral place where everyone came together. One morning the men in that group entered the Assembly of Delegates all wearing the same Picasso print necktie, “a figure twisted like a pretzel,” one member described later, ties bought at the Picasso restaurant where they had met. The group had felt shut out of discussions, and now were coming forward together. It was like a declaration of revolution. “For heaven sakes, take off the ties!” I recall someone saying, and the ties gradually were folded into pockets, but a revolution had begun.
Two Spontaneous Resolutions were introduced to the Assembly:
Spontaneous Resolution 1 On PEN’s Structure Submitted by the Swedish Centre, seconded by the Canadian Centre, and supported by the American, Bangladeshi, Catalan, Danish, Finnish, Japanese, Kenyan, Melbourne, Nepalese, Norwegian, San Miguel de Allende, Slovakian, Swiss German and USA West Centers.
Resolutions II on P.E.N’s Structure, submitted by the same centres.
“Taking into consideration the debate on P.E.N.’s composition, development and structure, held in Guadalajara on Sunday, November 10th, 1996, on the occasion of P.E.N.’s 75th anniversary;
Convinced of the need to enhance its democratic structure and facilitate wider international participation;
Resolves to request one P.E.N. Centre to elaborate the draft of a revised version of the current regulations, in cooperation and consultation with all the other Centres, as well as the International President and Secretary….”
After discussion and debate, it was agreed that PEN centers should send their suggestions for reform of the Constitution to the Japanese Centre, and Japanese PEN would coordinate and forward them to the International Headquarters and to all Centres so that the Centres could consider and vote on them at the 1997 Edinburgh Congress. One of these proposals, which was presented in Guadalajara by the Spanish-speaking Centres, was that Spanish should be made the third official language of PEN if financing could be raised.

Delegates at Writers in Prison Committee meeting PEN 63rd Congress in Guadalajara, 1996
PEN had its own democratic elections on the Congress agenda with a vote for the new International President. There was only one candidate put forward by the International Secretary and his PEN Center, a respected poet from Romania, a woman, who would have been the first woman President of PEN. She herself had lived under a repressive regime, but she had not been very involved in the international organization, and she had not been part of the discussion to reform PEN’s governance. When she spoke to the issue, questioning the need and the process, there was in the lunch conversations and in the corridors afterwards, pushback and a questioning of her suitability as President.
The next morning she withdrew her candidature. She said that it had become clear that the organization was undergoing a transformation and she felt she was the wrong person to be president at such a time of change. It seemed to her that PEN was in process of being transformed from an organization of writers into something less. She had been motivated by her dream of PEN, not as an organization with bureaucratic structures and competing pressure groups, but as a place where the writers of the world came together. She was a writer from Eastern Europe who had had great problems under successive dictatorships. From this perspective she had had an image of PEN as something extraordinary. It was true that she had confused PEN with the Writers in Prison Committee, she said. It was PEN which had spoken out when she was forbidden to publish. The work of the Writers in Prison Committee remained very important to her. What troubled her was the discovery of pressure groups who appeared to be fighting for a power which in her eyes had no existence. The only power which writers possessed was the power of their books and the fear of those in power that the truth told in those books would outlive their tyrannies.
Many members applauded her withdrawal speech. It articulated the pressure and tension in the 75-year-old organization which lived on ideals but also had to increasingly function in the competitive world of nongovernmental organizations with budgets and boards and democratic processes, an organization that needed to calibrate, modernize and keep all its members engaged.
Ronald Harwood agreed to serve another year as President. The International Secretary was reelected. Some members noted quietly that regulations required he face election every year now because of his age.
My replacement as Chair of the Writers in Prison Committee was unanimously elected. The former President of Danish PEN, Niels Barfoed was a respected writer and longtime PEN member, who as a young boy had circumvented the Nazis as a courier with banned literature from his older brother who was in the Resistance. The WiPC had chosen a nominating committee to assure qualified candidate(s) were nominated. I left Guadalajara satisfied that the new WiPC process had come up with such a well-qualified Chair. I commiserated with Ronnie, thanking him for taking on another term though it meant his own writing would be curtailed. I was elected as a Vice President of PEN International and left Guadalajara happy to be returning to my own work. However, a few months later Niels fell ill and resigned, and I too was back as Chair of the Writers in Prison Committee. Ronnie and I served a fourth year together.
At the end of the Congress, I went to the airport with Alexandre Blokh, the longtime International Secretary. It had been a difficult Congress for him. He questioned whether he had stayed on too long. At the Edinburgh Congress in 1997 new governance and regulations were proposed, and at the 1998 Congress in Helsinki Alex stepped down after 16 years. PEN International was on its way to having an international board and more democratic governance which presented its own challenges as the organization proceeded towards the 21st Century.

PEN International Writers in Prison Committee bimonthly newsletter, July and September, 1996
Next Installment: PEN Journey 19: Prison, Police and Courts in Turkey—Freedom of Expression Initiative