Posts Tagged ‘Moris Farhi’
PEN Journey 42: From Copenhagen to Dakar to Guadalajara and in Between
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.

Royal Danish Library extension in Copenhagen, dubbed the Black Diamond (Photo by © User:Colin / Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=66870365)
Arriving in Copenhagen in early September 2006, I walked along the waterfront, dodged bicycles and shared coffee and conversation with longtime colleague Niels Barfoed, former President of Danish PEN who had briefly succeeded me as Writers in Prison Chair and was an eminent Danish journalist and writer. We met at the new waterfront extension of the Royal Danish Library, dubbed the Black Diamond because of its imposing black granite cladding and irregular angles. Niels would be moderating a public meeting on Freedom of Expression in the Arab World.
PEN International’s base was broadening in the Middle East and in Africa, both regions where active centers for writers were fragile, but potentially important havens. Danish PEN was hosting a conference with a dozen writers from the Arab-speaking world, including representatives from Egypt, Morocco, Jordan, Palestinian PEN, Tunisia, Lebanon and invited writers from Iraq and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), along with Danish and Norwegian PEN members and International PEN represented by Centers Coordinator Peter Firkin and myself.
The Copenhagen conference had been initiated in part as a response to the Danish cartoons controversy earlier in the year and also as an opportunity to develop PEN’s work and presence in the Middle East. PEN had a few centers in the region and interest from writers in Jordan, Iraq, Kuwait, and Bahrain to form additional PEN centers and a desire to revive PEN Lebanon. Developing PEN centers in these areas was challenging given the politics and conflicts on the ground.
Ekbal Baraka, President Egyptian PEN (left) and Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, PEN International Secretary (right) meeting in Cairo, 2006
The Copenhagen meetings explored common fields of interest among Western and Arab writers, networking among Arab writers and ways in which PEN could assist. Women writers in the Arab world had particular challenges, a discussion led by Egyptian PEN President Ekbal Baraka. Ekbal later became Chair of PEN International’s Women Writers Committee. Algerian PEN and International PEN board member Mohamed Magani offered to host a subsequent meeting in Algiers the following fall, along with a conference on translation. A public event in the evening showcased the work of the visiting writers.
On the final day the public conference on Freedom of Expression in the Arab World moderated by Niels included discussions on Networking in the Cause for Freedom of Media and Opinion and featured renowned Tunisian journalist and human rights campaigner Sihem Bensedrine. A discussion on Access to Information: Implications to Development was addressed by Jordanian journalist Daoud Kuttab and Danish columnist and Danish PEN President Anders Jerichow. Lebanese Writer Elias Khoury and Egyptian journalist and commentator Mona Eltahawy concluded the conference in a discussion on Publication and Powerplay in the Middle East.
The days together resulted in a loose network of these and other Arab writers and eventually led to the opening of additional PEN centers and work in the Middle East. PEN currently has Bahrain, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, and Palestinian centers as well as the Egyptian, Algerian and Moroccan Centers.
******

Anna Politkovskaya, Russian journalist assassinated, 2006
A few weeks after the Copenhagen conference, my phone rang early on Saturday morning October 7, 2006 at my home in Washington, DC. Sara Whyatt, PEN International’s Writers in Prison Committee Director, was on the line. She called to tell me that Anna Politkovskaya, Russian journalist, PEN member who’d visited PEN Congresses and meetings, who’d worked for years reporting on Chechnya—had been assassinated. The report was that Anna had been shot that morning in the elevator of her apartment building in Moscow.
For seven years Anna had been one of the few reporting on the war in Chechnya despite intimidation and violence. She had been arrested by the Russian military and suffered a mock execution; she’d been poisoned while flying from Moscow to the Beslan school hostage crisis and had to turn back to get medical treatment. She had survived many dangerous encounters. But now she had been killed.
The killing of Anna Politkovskaya swept through the news media around the world as well as through the PEN world. We were stunned and deeply saddened and then began our protests and calls for investigation, along with human rights organizations worldwide. PEN honored Anna at its subsequent Congress and meetings and annually held an Anna Politkovskaya lecture on the anniversary of her death to commemorate her fortitude and inspiration.
The work in PEN was a helix of hope and pain and sorrow and hope again.
******

Dakar, Senegal, venue for PEN’s upcoming 73rd World International Congress in 2007
At the end of November Senegalese PEN hosted a meeting with African centers engaged with the planning of PEN’s 73rd Congress to be held in 2007 in Dakar. The meeting included representatives from Egypt, Morocco, Algeria, Guinea, Senegal, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, and Ghana. It was standard practice for International PEN to visit the site of an upcoming Congress to review logistics and budgets and programs in advance, to assist and assure the Congress ran smoothly. The 73rd Congress in Dakar would be only the second time a PEN Center in Africa had hosted a World Congress. In addition to reviewing the facilities at the Meridien hotel by the ocean, the delegation met with the Minister at the Ministry of Culture and Classified Historical Heritage which was supporting the Congress.
At that meeting and throughout the Congress to come, I offered the sentiment I had drafted and memorized in French and still endorse:
“Il n’y a que quelques autres pays dans le monde ou l’ecrivain est plus honore qu’au Senegal.
“There are few countries in the world where the writer is more honored than in Senegal.”
Because Senegal’s founding President Leopold Senghor had been a poet and writer of global distinction, also a Vice President of International PEN, Senegal celebrated literature. “As a national leader, Leopold Senghor left a rich heritage and respect for African culture and writing which we hope to honor by International PEN’s upcoming Congress in Dakar,” I told the Minister.

Karen Efford, PEN Program Officer, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, PEN International Secretary, and Caroline McCormick, PEN International Executive Director, meeting in Dakar. Senegalese PEN members organizing PEN 73rd World Congress included Abdoulaye Racine Senghor, Abdoulaye Fode Ndione, Mamadou Diop Traoré, Seydi Sow, Mbaye Gana Kehe, Alioune Badara Beye, Elie-Charles Moreau, Silcarneyni Gueye, Aissatou Diop
Senegalese PEN hosted our working meetings at its headquarters where the focus was also on regional development. International PEN’s Executive Director Caroline McCormick and Program Officer Karen Efford led a “mapping” or gathering of information with each center on its activities and membership and needs in order to determine how PEN International could assist, especially with fundraising. The Centers also participated in the discussions on the programs and facilities for the July 2007 Congress.
After hours of meetings, we all went to dinner together at the local restaurant. I don’t remember the food, except there were generous plates family style. I remember the atmosphere—the bright blues and reds and yellows in the restaurant, the music, and the laughter after a long day concentrating on budgets, logistics, and translations. The planning meetings were work but also fun with friendships among the writers from the PAN Africa Network with whom I had met on numerous occasions over the past few years.
In my three years as International Secretary, I was impressed by the care of all the host centers for Congresses. The Congress in Senegal would be my last as an officer of International PEN, except for the privilege of attending as a Vice President in the years to come. The operational work and responsibility would be passed on. I had determined not to stand for a second term. I had other responsibilities that had been put on hold for three years, and I had learned it was better to leave a position when everyone wanted you to stay, than to stay too long when people were waiting for you to leave. I needed to return to being a writer and to my family and to the other organizational work I did. So Senegal would be a farewell of sorts for me. It would prove to be a grand occasion, but I am getting ahead of myself…
******
“Does Freedom of Expression Have a Limit?” “Hospitality without Borders.”—those two panels I participated in and moderated at the 2006 Gothenburg Book Fair, Scandinavia’s largest. The International Publishers Association (IPA) and International PEN had been collaborators in selecting the Fair’s theme of Freedom of Expression that year. The Book Fair reflected the Freedom of Expression theme in many of its over 2000 events for the 100,000 visitors. PEN and IPA, along with the International Cities of Refuge Network (ICORN), had an exhibit with a stage where events and seminars took place.
For me, it was a special pleasure to attend the Fair in Sweden where my mentor and predecessor as Writers in Prison Chair Thomas von Vegesack was a respected and now retired publisher. Thomas attended the Book Fair. I noted in my remarks that it was from Thomas I’d learned the difference between having principles and simply talking about principles. Thomas didn’t like “principles,” which meant he didn’t like paradigms of abstractions. Our role—PEN’s role—was pragmatic. It was to help writers in trouble, to be in touch with them and their families so the isolation of imprisonment was broken, to give them support and most of all to figure out where the access was within our PEN centers and within our larger freedom of expression community to pressure governments to spring open the prison doors and also to get protection for writers under death threats. (It was two weeks after the Gothenburg Book Fair that Anna Politkovskaya was assassinated.)
The world had changed since the days Thomas and I had been chair of WiPC. In the late 1980’s and early 1990’s we had all been hopeful that the fall of the Berlin Wall and the fall of the totalitarian governments would ease the situation for writers worldwide, but there were now as many writers as ever under threat. PEN’s casebook listed over 1000. There were more non-state actors. There was also a level of global communication that was only budding in 1993 when Thomas handed over the reins to me. There were new bad guys, and many of the good guys were not as good as they once were. We were in a world where freedom of expression was no longer accepted as an unqualified value.
Yet “the world is still changed by ideas and books, and writers who write them are still the main vehicle for ideas,” I concluded my opening talk.
On the panel “Does Freedom of Expression Have a Limit?” we had no easy answer. We asked if there was a personal and public responsibility to tell the truth, or at least not to lie. And who determined a lie? The responsibility of the writer was to try to find and tell the truth even if truth seemed relative at times. The question arose, who sets the limits on freedom of expression? The State? Society at large? What were those limits and penalties and were they set by fear of attack or violence or censorship?
It was generally agreed that calls for violence such as the killing of another human being set a limit on freedom of expression, especially when this call came from someone who had the power of the state to exercise the threat. An example was the fatwa on Salman Rushdie. The limit should not be on Rushdie but on the Ayatollah and the state that issued the fatwa calling for his death.
Hate speech had a limit when it urged violence as in the case of Radio Rwanda during the genocide against the Tutsis or certain broadcasts during the Balkans wars.
PEN’s Charter contained the elements of the dialectic upon which free societies were based, both the respect for other cultures in an effort to dispel race, class and national hatreds and also a commitment to protect the free and unhampered transmission of thought and ideas.
“And since freedom implies voluntary restraint, members pledge themselves to oppose such evils of a free press as mendacious publication, deliberate falsehood and distortion of facts for political and personal ends,” the PEN Charter concluded.
Democracies flourish only when an exchange of competing, even contradictory, ideas can occur in a battle of ideas, the panel concluded.

Novelist Moris Farhi, former WiPC Chair and PEN Vice President/English PEN
The panel “Hospitality Without Borders,” co-sponsored by ICORN, featured Orhan Pamuk, the Turkish novelist who a month later won the Nobel Prize for Literature, and Moris Farhi, also Turkish but long resident in the UK and member of English PEN. Moris had followed me as Chair of PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee after Niels Barfoed’s brief tenure.

Novelist Orhan Pamuk (Photo credit: © Elena Seibert)
The previous year, Orhan had faced charges of “insulting the Turkish Army and Turkishness” because of his statement in a Swiss newspaper regarding the Armenian genocide and massacre of a million Armenians and 30,000 Kurds in Anatolia in 1919. On the panel Orhan noted how valuable it was for a persecuted writer in his home to know about the possibility of finding refuge in a safe city, even if he didn’t take advantage or was unable to leave his present situation at the time.
Moris, who’d also chaired English PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee, talked about the challenges facing the host city and the community receiving a guest writer. He focused on how to make sure the writer didn’t just disappear from the literary community and the need to focus on translation and publishing strategies for the writer. It was important to help the writer establish new foundations and relationships in a new city.
I recalled the situation of Bangladeshi novelist Taslima Nasreen who had faced death threats and was given asylum in Sweden and awarded the Tucholsky prize. Taslima Nasreen’s was one of the more dramatic cases in my PEN history as she was whisked out of Dhaka in the dark of night and brought to Stockholm by Swedish PEN. That had turned out to be just one stop on a difficult journey into exile.
******
 At the end of 2006, PEN Guadalajara, San Miguel PEN and the Ibero-American Foundation of PEN established a presence for the first time at the 20th Guadalajara Book Fair. The Guadalajara Book Fair was considered the most important publishing event in the Spanish-speaking world, hosting 450,000 visitors and 15,000 book professionals from over 40 countries. Officials of the Guadalajara Book Fair were eager to have a relationship with PEN in order to collaborate and “create and guarantee space in which literature of different languages cohabit supporting the freedom of opinion with words as vehicle of understanding between different nations and cultures,” according to the Coordinator of the Festival events.
At the end of 2006, PEN Guadalajara, San Miguel PEN and the Ibero-American Foundation of PEN established a presence for the first time at the 20th Guadalajara Book Fair. The Guadalajara Book Fair was considered the most important publishing event in the Spanish-speaking world, hosting 450,000 visitors and 15,000 book professionals from over 40 countries. Officials of the Guadalajara Book Fair were eager to have a relationship with PEN in order to collaborate and “create and guarantee space in which literature of different languages cohabit supporting the freedom of opinion with words as vehicle of understanding between different nations and cultures,” according to the Coordinator of the Festival events.
International PEN aspired to have a more robust presence at book fairs globally, but did not yet have the budget or staff. However International PEN supported centers’ activities at book fairs such as at Frankfurt, Gothenburg, and now Guadalajara. I visited the Guadalajara Book Fair as part of this initiative.
PEN Guadalajara and San Miguel and the Ibero-American Foundation of PEN hosted a stand at the Book Fair and offered readings and presentations of books and displayed hundreds of books from PEN members and PEN centers around the globe. On the Book Fair’s program two eminent PEN members, Vice President Nadine Gordimer and former PEN International President Mario Vargas Llosa were featured. Nadine Gordimer participated in a Literary Salon and later had dinner with PEN members. I have no notes from that dinner, but I have fond memories of the outside restaurant in the evening and the hospitality of Guadalajara and San Miguel PEN and the graciousness of Nadine Gordimer.

Photo Left: Meeting at 2006 Guadalajara Book Fair: María Elena Ruiz Cruz, Víctor Sahuatoba, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, Lucina Kathmann, Luis Mario Cerda, Martha Cerda, Moisés Zamora. Photo Right: At dinner: Moisés Zamora, Nadine Gordimer, Martha Cerda, and Joanne Leedom-Ackerman
Martha Cerda, President of Guadalajara PEN, PEN Vice President Lucina Kathmann of San Miguel PEN and I met with Book Fair officials and assured that PEN would have a presence and partnership with the Guadalajara Book Fair in the years to come through its Latin American centers.
The visit to Guadalajara also offered the opportunity to meet with members from several Latin American PEN centers in a preliminary focus on the region and on the “mapping” International PEN would undertake of resources, programs and needs of the Latin American PEN centers before the 2008 Congress in the region.
******
At the end of 2006 PEN’s long time staff member Jane Spender retired. Jane had worked with Peter Day on the PEN International Magazine as an editor; she’d been administrative assistant to the Administrative Secretary Elizabeth Paterson and then became the Administrative Director when Elisabeth retired. She had taken on the role of International PEN Program Director when PEN hired an Executive Director. We all relied on Jane’s intelligence, good humor and patience. Jane and I had spent hours—too many hours we both agreed—toiling over just the right word on several documents. I was especially going to miss working with Jane; I have kept the friendship to this day. To celebrate the past and send her off with good wishes for the future, we surprised her by giving her a bicycle which I rode across the office and presented to her. Friends from International PEN and English PEN all gathered in PEN’s new offices on High Holborn. PEN is about people, and Jane was one of the stalwart ones.

Jane Spender retirement party at PEN offices, 2006. L to R: Sara Whyatt, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, Jane Spender, Caroline McCormack, Karen Efford, Terry Carlbom, Ursula Setzer, Josephine Pullen-Thompson, Francis King, Peter Day, Gilly Vincent, Jane Spender, Nawal, Karen Efford, Elizabeth Paterson
Next Installment: PEN Journey 43: Turkey and China—One Step Forward, Two Steps Backward
PEN Journey 24: Moscow—Face Off/Face Down: Blinis and Bombs—Welcome to the 21st Century
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.
“Contrary to our tradition, this year’s PEN Congress is being held in a country in which a massive, genocidal military and paramilitary operation is under way. Besides mass murder, the crimes perpetrated against the civil population of Chechnya include deportation, rape, torture, destruction and theft of personal property as well as the systematic looting and destruction of the material bases of Chechnyan culture and civilization. At the same time, freedom of information has been severely curtailed, and the official propaganda plays on xenophobic and even racist ethnic stereotypes…” So began a Declaration from the 67th World Congress of International PEN voted by the Assembly of Delegates in May, 2000.

Program for PEN International 67th World Congress, Moscow
The decision to hold the International PEN Congress in Moscow was a controversial one, resulting in some members refusing to attend because of Russia’s prosecution of the war in Chechnya and the concern that holding a Congress in Moscow would give the government an appearance of approval. However, PEN’s Secretariat with the new Executive Committee concluded that the long-planned millennial Congress also presented the opportunity for International PEN to show solidarity with Russian PEN which had been outspoken both on the war and on behalf of Russian journalists and writers under pressure.
“The writers of Russia, united under the auspices of the Russian Centre of the International PEN Club, are concerned about the escalation of the war in Chechnya which is becoming a threat to not only peaceful residents of Grozny-city but also to the national security of Russia. The ultimatum announced to women, children and old people of the Chechen capital makes them hostages of both terrorists and federal forces. It is hard to believe that in this situation the Russian authorities are going to use the same methods as terrorists. We are very aware how hard it is to cut the tight Chechen knot, but in any case innocent people do not have to become victims of the decisions taken…” Russian PEN sent this appeal earlier to the acting President of the Russian Federation, Vladimir Putin.
Russian PEN members, including President Andrei Bitov, had signed the appeal. Russian PEN’s General Secretary Alexander (Sascha) Tkachenko noted at the Congress that it was essential to call on all those involved—Russian and Chechen—to cease their brutalities. Sascha himself had regularly stood up to the Russian government. He championed the cases of imprisoned writers Alexandr Nikitin and Grigory Pasko, both of whom had recently been freed after trials. Pasko, who was a journalist and former Russian Naval officer, had been arrested and accused of espionage for his publication of environmental problems in the Sea of Japan. Nikitin, a Naval officer, had been charged with stealing state secrets by contributing to a report that revealed the sinking of Russian nuclear submarines and the dangers these decaying submarines posed to the environment.
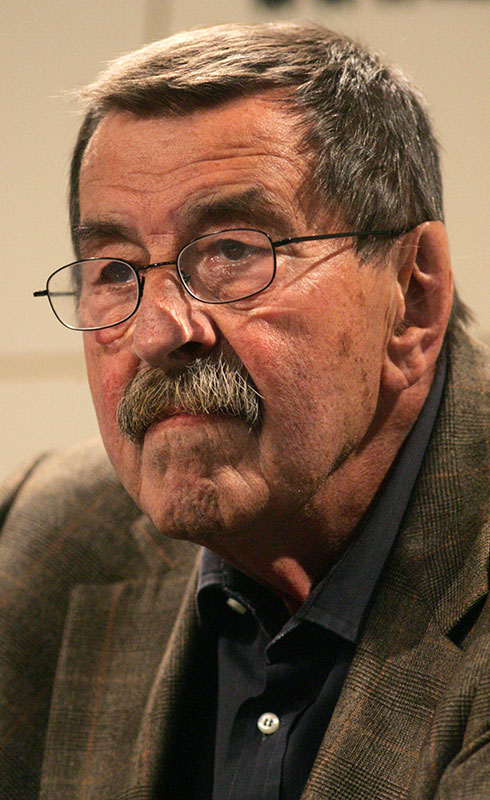

German novelist Günter Grass talk opened PEN’s 67th Congress
The freedom and the openings which many embraced after the break-up of the Soviet Union in the early 1990’s were beginning to close down and restrictions tighten. At the Moscow Congress Pasko expressed his gratitude for everything PEN had done to obtain his freedom. He urged the Assembly to focus on environmental problems. But he warned that the structure of the current Russian government had grown out of the KGB, and he feared nothing good would come for free speech or the environment.
In the opening address of the Congress German novelist Günter Grass, who won the Nobel Prize for Literature the previous year, recounted the many times in the past century that writers had called attention to the abuses and genocides which governments had tried to hide. “At least literature does achieve this—it does not turn a blind eye; it does not forget; it does break the silence,” Grass concluded.
The Congress theme “Freedom of Criticism. Criticism of Freedom…”seemed a particularly UNESCO title, with a focus on how freedom is exercised, noting that freedom unrestrained by morality can lead to a license for corruption, brigandage, state terrorism, censorship and the wanton murder of those who dare to speak out. “That freedom is a double-edged sword is a fact long appreciated in free societies. It is what prompted Voltaire to place a limitation upon it, when it interfered with the freedom of another,” one Congress description noted.
Thus framed, the panels and the work of PEN’s committees proceeded. Many wondered how able PEN members would be to criticize openly as we met both formally and in cafes sharing conversation and meals of blinis and caviar. There was no incident nor interference that I recall at the Moscow Congress nor at the subsequent programs in St. Petersburg, but we were all aware that repercussions could follow after we left. Over time Putin’s government did close down the space for NGO’s with Russian PEN as one of the early targets. (Future blog post.)
The Moscow Congress itself proved an opportunity to celebrate Russian literature and other literature as well as to conduct the work of PEN’s committees which met in halls named after Tolstoy, Pushkin, and Chekov. Many writers from over 70 PEN centers were visiting Moscow for the first time since the Soviet Union broke apart. Since my first trip in 1991 shortly after the coup attempt (PEN Journey 8), the city had changed. Western hotels, restaurants and stores had moved in; certain citizens had amassed wealth; others had lost jobs and security. It was a city of contrasts with children on the street begging, but begging by playing violins. A wealthy new group crowded the lobbies of western hotels and department stores.
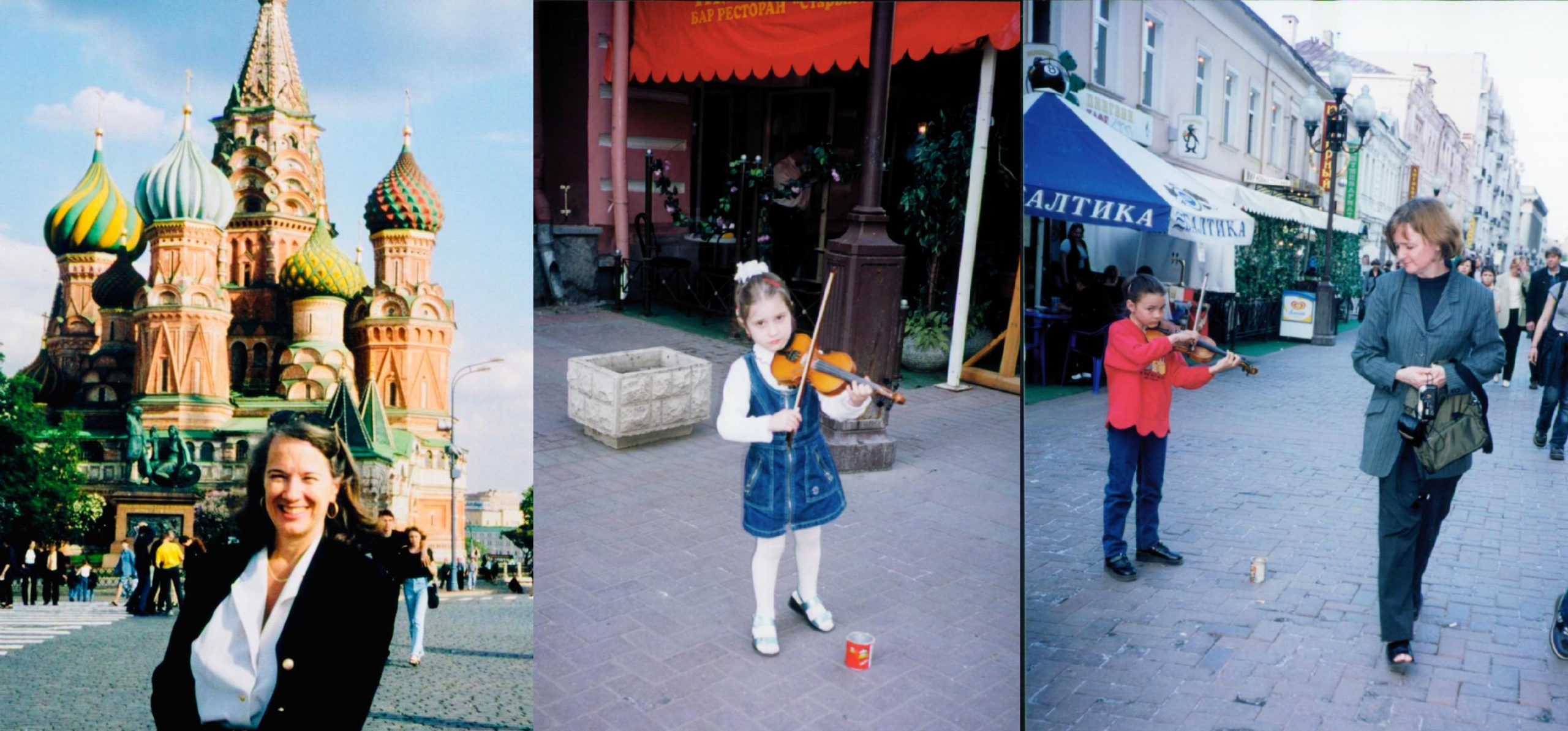

On the streets at PEN Congress in Moscow May, 2000: L: Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, PEN Vice President; R: Sara Whyatt, PEN Writers in Prison Committee Program Director
In a message to the Congress Andrei Bitov wrote:

Full text of Russian PEN President Andrei Bitov’s message to PEN delegates
I always believed…that I would meet my old age in the USSR under Brezhnev, much though I disliked the idea. I could not allow myself to dream (or I would have been driven to despair) that I would be lucky enough to travel around the world more or less without restriction, that my works would be published without being censored, published with no delay and in their entirety, however hastily written.
Under Brezhnev one could not think of joining the PEN Club—that “reactionary bourgeois, anti-Soviet, etc., organization”! (It turned out only recently that Gorky, Pilniak and Voinovich had all dreamt of such a grouping…)
One could certainly never have imagined its World Congress being held in Moscow!
But fifteen years have elapsed since that time, long enough to see many people grow old and die and another generation come into the world and reach their youth. That is the History none of us, either here or in the wider world, could imagine…
We should not rail at the century that has gone, nor at the passing year—we should hope that they have taught us much. However, judging by events in Russia and in the rest of the world, it is obvious that we have not drawn any sensible conclusions from our experience…
In one tiny drop of the substance of the World Congress is reflected the entire universe, the problems it faces reflect, as in a distorting mirror, world political problems…
We are responsible for each day of our lives, not for the future.
Thank you for having the determination (and courage) to come to Russia at this particular time.
PEN’s business at the Assembly of Delegates included the International Secretary Terry Carlbom’s report on PEN’s relationship with UNESCO as the only global organization representing literature associated with UNESCO and a preliminary notice about a multi-year strategic plan under development. Business also included the election of the International President. Homero Aridjis was standing for a second term, and former International Secretary Alexander Blokh of Russian origin had returned to this PEN Congress for the first time since he’d stepped down as International Secretary in 1998, (PEN Journey 20) and he was also running for President. I was asked to chair the Assembly for the election, including during a stir that arose when Alex wasn’t present to speak for his candidature. He’d left the meeting early for an appointment, mistakenly thinking he would speak in the afternoon. However, there was no afternoon session, and controversy arose over whether the election should be postponed so he could speak. I ruled that he would be the first item on the morning agenda and then the election would proceed as scheduled. Homero Aridjis won a second term; Alexander Blokh continued to serve PEN for many years as a Vice President and President of French PEN.
Also at the Congress Martha Cerda (Guadalajara Center) succeeded Lucina Kathmann as Chair of the Women Writers’ Committee; Veno Taufer (Slovene PEN) succeeded Boris Novak, who’d opposed holding the Congress in Moscow and had stepped down as chair of the Writers for Peace Committee, and Eugene Schoulgin (Swedish PEN) was confirmed as the new Writers in Prison Committee Chair.
In his farewell comments as WiPC chair Moris Farhi quoted Günter Grass’s address that literature always breaks the silence. Moris added that by breaking the silence, by telling the truth and exposing wrong-doing, literature also defied fear and embraced courage. The members of International PEN had witnessed this defiance of fear and the manifestation of courage time and again. Moris noted among those with courage were Grigory Pasko, Alexander Tkachenko and our colleague Boris Novak.
The Moscow Congress saw the return of delegates from Chinese PEN after a decade-long absence post Tiananmen Square. Two resolutions on China were presented, one calling for the release of dissident writers imprisoned in China and another protesting the long prison terms for writers in Tibet. The Chinese delegate objected to both resolutions, arguing first that Tibet shouldn’t be singled out as though it were not part of China. He also said that the Chinese people and Chinese writers cared for human rights after centuries of feudal society, but the West emphasized individual rights and values while the Chinese valued collective human rights and obligations to the family and society. The Chinese believed that human rights in a given country were related to the social system, the level of economic development and historical and cultural traditions of that country, and they encompassed the right to development and subsistence. A country of more than 1.2 billion people had to find food and clothing. It was impossible for one pattern to solve all existing problems. The Cold War had ended, but its influence remained with those who believed their values, their concept of human rights, their position were the only correct ones in the world. Dialogue was the only way to resolve the differences of view, a dialogue based on equality and mutual respect.
Hands shot up seeking to respond. At least 25 delegates at the Assembly spoke, welcoming the return of the Chinese delegates to the PEN Congress, but most taking exception to the argument of the relativity of human rights in PEN’s work. The first to speak was Eric Lax of PEN Center USA West who said he appreciated the speaker’s comments but wanted to add that the PEN Charter, to which all members subscribed, was very clear that freedom to write was a basic tenant of the organization and that information should pass unimpeded without restriction. Some questioned the way the resolution was written. Alexander Tkachenko of Russian PEN said he felt PEN should be understanding of people living under a regime about which the rest of PEN knew little. It was up to the Assembly to decide whether to support the resolution; they needn’t accept the Chinese delegate’s opinion, but they should respect it. He didn’t want the Chinese to be missing from PEN for another ten years. PEN should be tolerant of those for whom it was extremely dangerous to discuss such questions. The Assembly applauded. A small amendment was made to the resolutions, both of which passed with large majorities, though not unanimously.
The following year the Independent Chinese PEN Center (ICPC) came into being, a center of independent writers and democracy activists inside and outside of China. One of the founding members and the second president of ICPC (2003-2007) was writer Liu Xiaobo, on whose behalf PEN worked twice when he was imprisoned after Tiananmen Square and again when he was arrested in 2009. Liu Xiaobo was the first Chinese citizen to win the Nobel Prize for Peace in 2010, but he was incarcerated in a Chinese jail, and he died in custody in 2017.

Next Installment: PEN Journey 25: War and more War: Retreat to London
PEN Journey 23: Nepal—WIPC Crossing the Bridge Between People
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.
As I write these PEN Journeys, memory differs with each one. I sit and think, pulling up whatever memories I have. Some are visual; some are of activities, some of the twists and turns in PEN itself; many are of friends, a few of incidents; others come from concurrent parts of my life such as moving to London with my family and connecting to work at International PEN headquarters (PEN Journey 5), or scaling the Berlin Wall just after Germany reunited (PEN Journey 4), or visiting Russia shortly after the coup attempt (PEN Journey 8).
I have paper documentation for most of PEN’s events, not because I was an archivist in the making but more of a packrat who was too busy to sort through papers after a congress or conference and so set the files in a drawer. I am not even accounting for all the emails and digital files that began to accumulate in the late 1990’s and 2000’s. In my recounting, I am only now entering that period when the internet and email were burgeoning. For some of the Journeys I have photographs, but my picture-taking was random in retrospect, probably reflecting my role at the time. The more work I had, the fewer pictures. There were no iPhones or Android phones during these earlier years so I had to have a camera at hand. In certain years I have no photographic record of PEN though some may yet turn up in the recesses of my basement. There are, however, always pictures in my head.
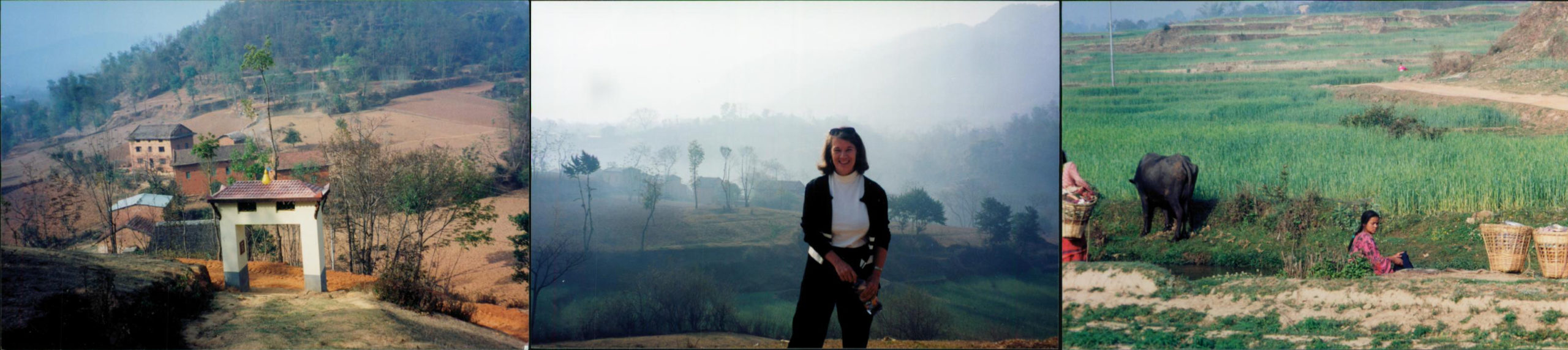
For the Writers in Prison Committee’s (WiPC) third biannual meeting in Katmandu, Nepal in the spring of 2000, I have lots of pictures. We were celebrating the 40th anniversary of International PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee. As ex-chair, I helped with the conference, but the burden of the meeting wasn’t mine so I was also out with camera in hand. In my head I still carry the landscape of Nepal—the hills outside Katmandu with the haze over mountains in the distance, the woman in a red sari walking up the hill carrying bundles of sticks, the gentle landscape and the harsh conditions.
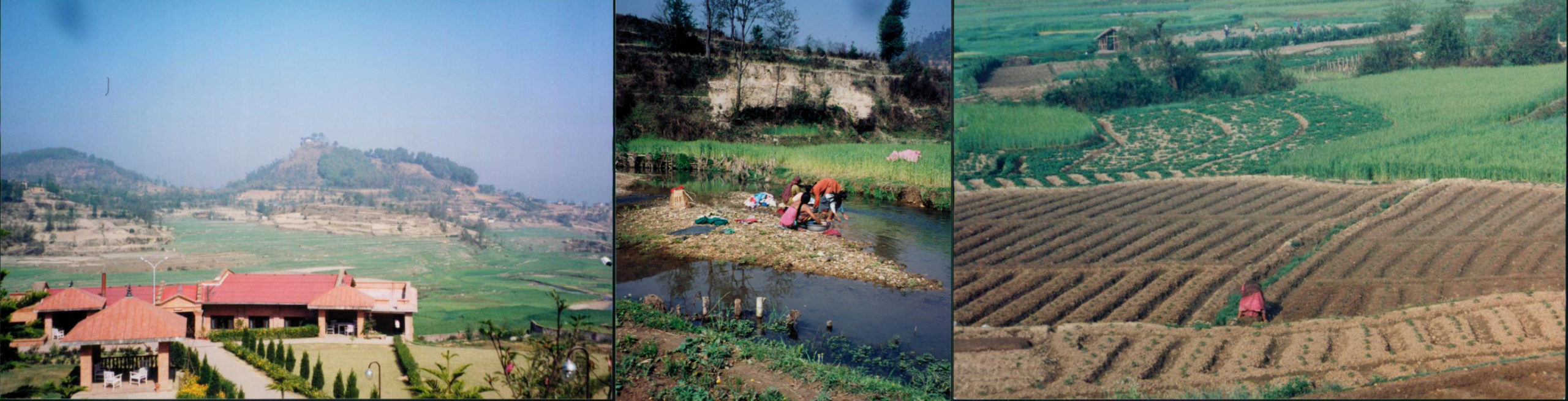

Landscape in hills and fields outside Katmandu, Nepal at Writers in Prison Committee Conference, April 2000
I arrived a few days early to visit schools and women’s education projects relating to other work I did, some as a board member of Save the Children. By the time I joined the PEN Conference, I had already fallen in a soft love with the country and its people, the old—sometimes centuries old—and the new culture: Katmandu with its rickshaws and bustling streets and vibrant colors and the hills outside where farmers still farmed with oxen plowing the fields and children high in the hills crowded into village schools and women learning to read in makeshift community libraries. And there was the nation’s complicated governing system with a privileged royal family which only a year later would be massacred by one of its own and in the hills a Maoist insurgency developing which threatened the government and population for years to come. Nepal was as dramatic a place as the landscape it occupied.
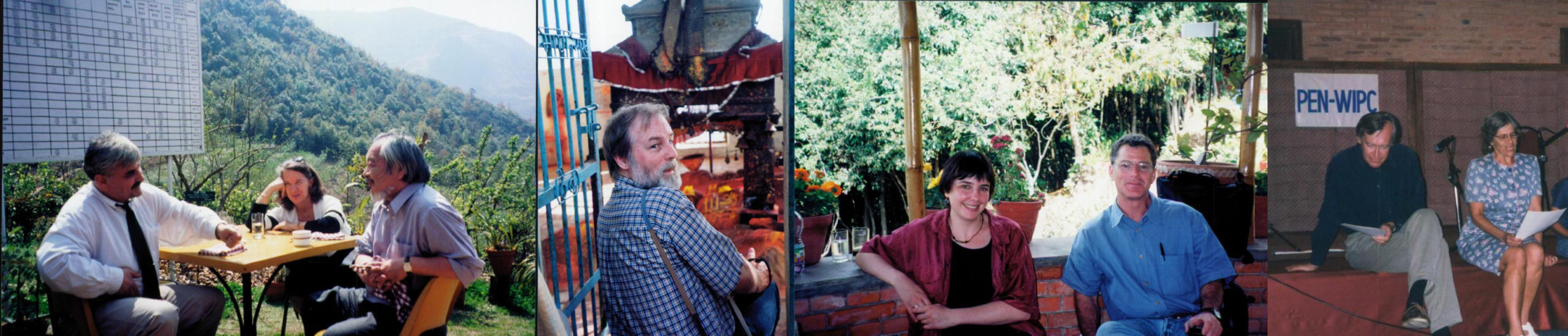

At work and rest at WiPC Conference. L to R: Alexander (Sascha) Tkachenko (Russian PEN), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (American PEN/PEN Int’l), Mitsakazu Shiboah (Japan PEN), Jens Lohman (Danish PEN), Cathy McCann (Asia researcher PEN Int’l), Larry Siems (American PEN), Eugene Schoulgin (Norweigan PEN), Lucina Kathman (San Miguel Allende PEN)
At PEN’s WiPC conference, 43 writers gathered from 25 countries representing every continent except Africa where the costs had limited attendance. Before the meeting WiPC chair Moris Farhi and I and the WiPC staff met to identify areas of work that needed review and possible restructuring. From a survey of the centers we developed discussion points which were circulated before the meeting. Since the fall of the communist states, PEN had seen a growth in membership, an increase in freedom of expression work by the centers, and an expanded use of email and the internet. The innovation in communications was having an impact on the way PEN did its work and challenged old methodologies such as letter-writing campaigns.
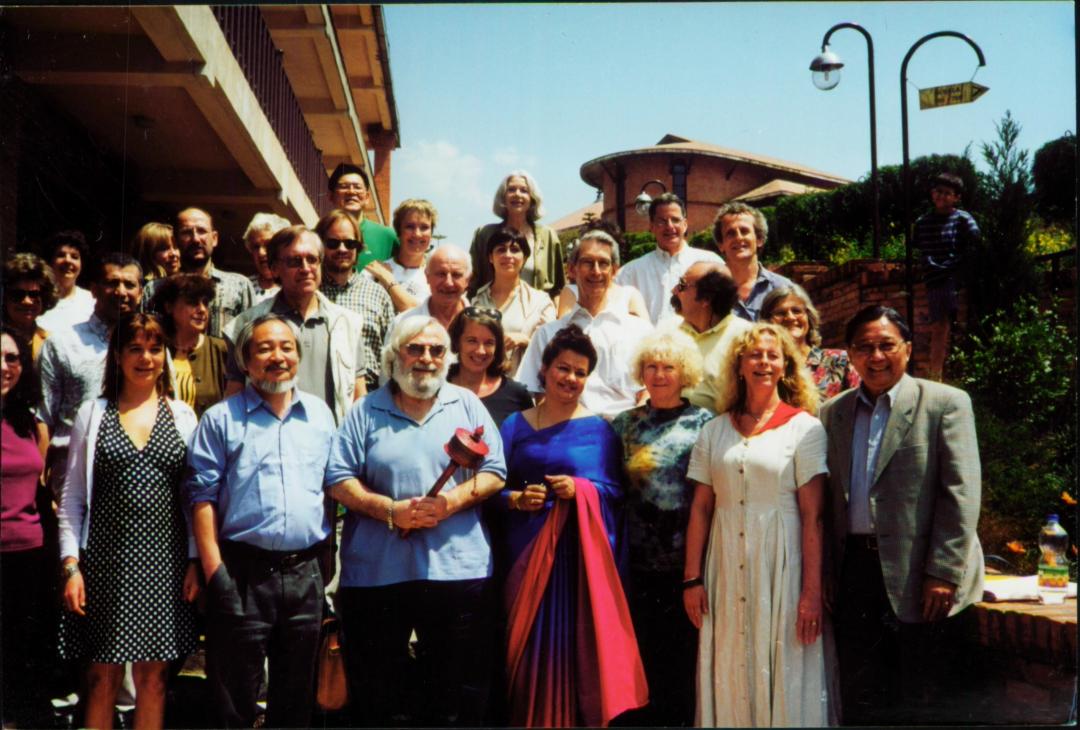

Delegates at PEN Writers in Prison Committee Conference, Nepal, 2000. In center WiPC Chair Moris Farhi holding local prayer wheel.
The agenda developed included workshops on the use of the internet, on PEN’s WiPC case list and newsletter, on PEN’s commitment to journalists in peril as compared to writers who had no other organization to protect them. We considered crisis situations and the changing nature of repression, including nongovernment and non-custodial forms of repression, WiPC relations with international organizations, the role of PEN’s Congress, the role of regional centers and networks, the value of PEN missions to other countries, and always, the discussion on how to fund the work and how to assure those finances included funds to bring delegates from every region to future meetings.
Looking back at the program, it appears exhaustive (or exhausting), though I don’t recall it as tedious or overwhelming. With each workshop, the group developed a summary of the situation and recommendations. For example, a recommendation was to post on PEN’s website, accessible to everyone, the information on the RAN special actions. The RAN (Rapid Action Network) itself was a relatively new tool which was sent out over the internet for immediate action on certain PEN cases. It was also agreed and recommended in another workshop that journalists should continue to be part of PEN’s campaigns and that PEN should collaborate more closely with journalists’ organizations.
Reading through the minutes and recommendations of the four-day meeting, I am impressed by the professionalism of the work of the WiPC staff, small as it was, just Sara Whyatt, Program Director and Cathy McCann, Asia researcher.
At the Nepal conference a new WiPC chair—Eugene Schoulgin from Swedish PEN was elected to take over from Moris Farhi after PEN’s Congress in Moscow the following month.
As well as workshops and discussions, we were entertained by local groups and also entertained ourselves with song and dance in the evening as we had at the first WiPC conference in Helsingør (PEN Journey 17).
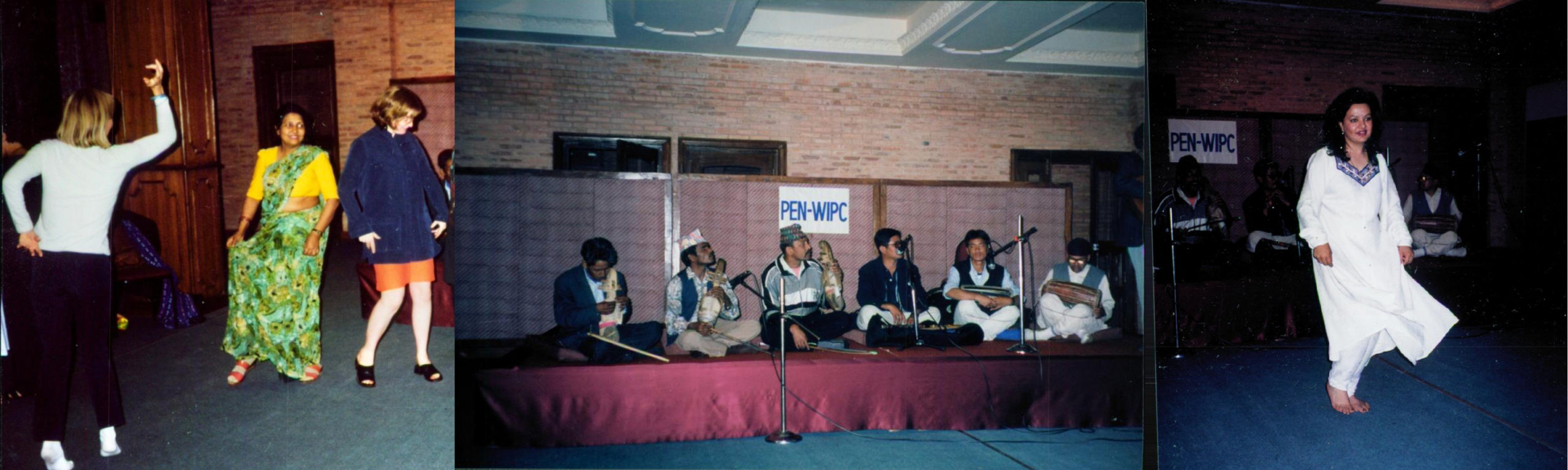

After working days at WiPC Conference, music and dancing, including local Nepal PEN members and Sara Whyatt (WiPC Program Director) in orange skirt on left and on right Archana Singh Karki (Nepal PEN) in white; local musicians in middle.
On the last day UNESCO sponsored a panel The Culture of Peace: Censorship and the Writer which PEN Nepal President Greta Rana introduced, observing that censorship led to violence and that 47 journalists in South Asia were currently imprisoned for addressing free expression issues. Sara Whyatt in her introduction of the printed talks noted that free expression was inextricably entwined with the promotion of peace for without voices to challenge dictatorships and warmongers, peace would be an even rarer commodity than it was.
Because I don’t need copyright permission to reprint my talk, I take the liberty of sharing it below. Other panelists included Ratna Sarumpaet, an Indonesian script writer whose play about the plight of women laborers led to her imprisonment; Kunda Dixit, a Nepali journalist who spoke about the role of the free media in ensuring objectivity in times of pressure from political and corporate interests; Shahid Nadeem, a Pakistani playwright long exiled in England, who told of returning to Pakistan where critical voices were still seen as a threat; WiPC Chair Moris Farhi who noted that xenophobia and religious fanaticism were increasingly dangerous elements; Rajeev Rajbhandari, a Nepali internet expert, who argued it was not the content of the internet that was problematic but the uses of its new technology; Romesh Gumesekere, a Sri Lankan author and poet, who identified illiteracy as an encumbrance to the promotion of free expression; and myself whose talk below began with the poem of the renowned Turkish poet Nâzım Hikmet:
The prisoner Halil
closed his book.
He breathed on his glasses, wiped them clean,
gazed out at the orchards,
and said:
“I don’t know if you are like me,
Suleyman,
But coming down the Bosporus on the ferry, say
making the turn at Kandilli,
and suddenly seeing Istanbul there,
or one of those sparkling nights
of Kalamish Bay
filled with stars and the rustle of water,
or the boundless daylight
in the fields outside Topkapi
or a woman’s sweet face glimpsed on a streetcar,
or even the yellow geranium I grew in a tin can
in the Sivas prison—
I mean, whenever I meet
with natural beauty,
I know once again
human life today
must be changed . . .”
—Nâzım Hikmet, Human Landscapes
In 1938 Turkish poet Nâzım Hikmet (1902–63) was sent to prison, charged with “inciting the army to revolt,” convicted on the sole evidence that military cadets were reading his poems. He was sentenced to 28 years but was released 12 years later in 1950. His “novel” in verse, Human Landscapes from My Country, was written in prison, featuring Halil, a political prisoner, scholar, and poet who was going blind….
Today in Istanbul journalist Nadire Mater is charged with “insulting the army” for her book Mehmet’s Book, a collection of interviews with soldiers who have served in the conflict with the Kurds in the Southeast of Turkey. Nadire Mater and her publisher will be in court in early May to face charges, which could bring them at least six years in prison.
I’d like to read a brief passage from one of the interviews in Mehmet’s Book:
These friends coming from the West didn’t really know any Kurds, because they don’t know any they couldn’t really understand very well. What should be said about this? They are not familiar, and not being familiar, they act according to the government’s opinion…They’ve adapted to what they hear and read. I would explain to these friends that the other side is human, that the politics of the government is wrong.
We all of course adapt to what we hear and read. That is why it is so important that we have the opportunity to consider many points of view. The reality we carry in our heads and in our hearts shapes us as individuals and governs us as nations. Writers are the ones who produce what people read. The writer bears both the responsibility and the liability for his words and the realities they evoke. The writer can be a positive instrument for change as Hikmet saw the need, or as we have seen in the past decade in the Balkans, the writer can inflame animosities. The writer is not always the hero, but at his or her best, the writer can build bridges, reporting on and imagining not only himself, but those who are not him, illumining he humanity that connects us.
Peace between people relies on such bridges. The nature of a bridge is to span the space between points. The pilings of a bridge absorb the tension as one crosses over the space. However, censorship undermines, even destroys the pilings. The censor would allow only a limited view of reality, and by disallowing other views, the censor cuts away at the pilings necessary to build the bridge between him and the so-called enemy.
Censorship takes many forms. Whether it be brutal killings as in Iraq, death threats as in Peru and Colombia, long term prison sentences as in Burma and China or shorter terms as in Cuba or endless court cases as in Turkey where writers say the judicial process itself is punishment, the effect of censorship is to weaken or even tear down the bridge and to freeze up the imagination that envisions this bridge.
Fortunately, however, the imagination is a nimble and wily companion. It is also the natural enemy of the tyrant. While a man or woman can be censored, threatened, even put behind bars, his ability to think and imagine other worlds can defy and even eventually triumph over the most ruthless tyranny. I still remember reading and hearing the testimony of writers in prison in the Western Sahara in the early 1990’s when they were forced to live in subhuman conditions. They spoke about how they used their ration of soap to write poetry on their trousers, used coffee grounds to write on any scrap of paper they could find in the prison yard. They then memorized each other’s verses to stay alive and sane. The prison guards told them they might as well forget the outside world for they would die in prison. But they could imagine another world, and they lived in their imaginations, and those outside prison imagined them and worked on their behalf. Ultimately they were freed.
In the work PEN does for writers we have observed tragedies, but we have also witnessed the resiliency of writers and the power of ideas to find their way.
I have always found instructive the story of the Zimbabwean novelist Solomon M Mutswairo. Writing in the 1950’s Mutswairo knew the implication of his message and the sting of the British censor so he cast his story in the ancient kingdom of his people. The political content went unrecognized by the British, who in an expansive mood in 1956 published his novel Feso as the first novel in the Shona language. The Shona people, however, understood the story of protest against oppression. When the British finally realized what they had published, they came to arrest Mutswairo, who happened to be teaching in the U.S. at the time. He protested from afar. But how can you arrest me when you are the ones who published my book! Feso later became a rallying cry for independence.
Today with the move towards democracy around the world, fewer countries routinely throw writers in prison, but PEN still monitors cases of writers in over 80 countries, including Nepal. In many countries the struggle towards democracy has not yet yielded the full freedom of expression, including a free press, that is essential.
Freedom of expression is an engine and a safety valve in strong working democracies for that is how the population both expresses itself and gains information and different points of view in order to make decisions.
Historically democracies have not gone to war with each other. Since we are considering a “culture of peace” in this panel, we do well to pay attention to the freedom of expression on which strong democracies are built. With imagination one may envision the bridge to peace; the writer may articulate the vision but it is up to us all to walk across that bridge. Let us hope its pilings are secure.

Next Installment: PEN Journey 24: Moscow—Face Off /Face Down: Blinis and Bombs—Welcome to the 21st Century
PEN Journey 21: Helsinki—PEN Reshapes Itself
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.
In the old days, at least my old days, the Vice Presidents of PEN International sat in a phalanx on a stage while the Assembly of Delegates conducted business—revered writers, mostly white older men, along with the President, International Secretary and Treasurer of PEN in the center. If the Assembly business wore on, it was not unusual to see one or two of them nodding off. The role of the Vice Presidents was to provide continuity—many had been former PEN Presidents—to provide wisdom, contacts and gravitas. The designation was for life.
But times were changing. For instance, I had recently been elected a Vice President. I was a woman. I’d served PEN in several positions, including president of my center, founding board member of the International PEN Foundation and International Writers in Prison chair; I was a writer, though not of international renown, and at the time I was relatively young. I had been nominated by English PEN whose General Secretary thought it was high time more women sat on that stage. I didn’t relish sitting on a stage, but I was honored to hold the position. The Helsinki Congress in 1998 was the first when Vice President was the only role I had. I don’t recall if there was a stage at that Assembly. The fun was that I didn’t have to do anything. I could float between committee meetings, offer comments when relevant, wisdom if I had any and be called upon for whatever insight or experience or task might serve. (Traditionally the Congress organizers paid for the Vice Presidents’ registration and hotel, but from the start I chose to cover my expenses as a way of contributing to PEN. The expense of Vice Presidents attending was growing more and more difficult for the host centers; on the other hand many Vice Presidents wouldn’t be able to attend otherwise.)

Program for 65th PEN International Congress in Helsinki, Finland
At the 65th PEN Helsinki Congress held at the Marina Conference Center on the waterfront, a short walk from the city center, delegates and PEN members from 70 centers around the world gathered. The Congress’ theme was Freedom and Indifference. My memories are of meals on the water with colleagues, of eating fish and mussels and walking among old and very new buildings, visiting the architecturally stunning Contemporary Art Museum and other cultural excursions I often didn’t have time to attend when chairing the Writers in Prison Committee.
At the Congress I could even sit in on a few of the literary sessions which included abstract topics such as Where Does Indifference End and Tolerance Begin?—The Role of the Intellectual in Contemporary Society; Eurocentrism and the Global Village; The Cultural Gap Between East and West; The Ambivalence of Otherness: Identity and Difference; Crime Literature Portraying the Society; On Cultural Creolisation (mixture) and Borderlands. I confess reading those topics now stirs memories of sleepy academic afternoons, but the writers presenting included some of the engaged and engaging writers of the day, including Wole Soyinka, Caryl Phillips, Andrei Bitov and many Finnish and Scandinavian writers such as Sweden’s Agneta Pleijel.
At the Congress I still concentrated on the work of the Writers in Prison Committee which former Iranian prisoner Faraj Sarkohi attended. The year before he had been a main case for PEN, imprisoned and tortured and threatened with execution. In introducing his presence to the Assembly of Delegates, PEN President Homero Aridjis noted that PEN members could take satisfaction in having played an important role in obtaining his release. Sarkohi had managed to get a passport and was now living in Europe where he’d resumed his literary and journalistic activities.
Moris Farhi, the new WiPC Chair, introduced Sarkohi to the General Assembly of Delegates where Sarkohi said he owed his life and freedom to the international movement initiated by PEN both in the London headquarters and in the PEN centers around the world. For the first time in 20 years the Iranian government had been forced to release someone they had wanted to kill, he said. His release demonstrated to other writers in Iran that release was possible even if the government wanted to execute them. Sarkohi had briefly spoken with another PEN main case in prison who told him he was no longer worried, knowing now about the international support he was receiving.
Sarkohi explained that writers were considered by the despots in Tehran to be guilty because they worked with words, because they tried to discover and express in words different aspects of truth. It was believed writers made magic, he said. Everyone knew the magical power inherent in words so the writers were arrested. The government forced them to deny themselves, to accept false charges, and in this way they killed writers mentally. When a writer was forced by physical and mental torture to deny himself, his ideas and his work, his power of creation died, and he was killed as a writer. When Sarkohi was in solitary confinement, he remembered the way in which those suspected of magic were treated in the Middle Ages. People were arrested and burned and told “If you live, your magic powers are proved and we kill you. If you die, it is established that you do not have magic powers.’—but you were dead anyway. Writers were regarded as the new practitioners of magic in this century and that treatment by tyrants and despots was that of the Middle Ages.
Sarkohi described how he and colleagues who were still in prison had issued a new Charter, inspired by the PEN Charter, in which they protested censorship, both by the government, self-censorship and by the public such as groups which beat up a writer in the street. The Charter also demanded the right for writers to organize an association, something not permitted in Iran. He worried now about the fate of his colleagues in Iran because five years ago when writers published a Charter and sent the text abroad, the government had reacted and killed a famous translator and dumped his body in the street and murdered a famous poet in his home.
Sarkohi noted that German PEN and other PEN centers had prepared a resolution for the Congress making it clear to the Iranian government that International PEN was watching the fate of Iranian writers so they would know before they arrested or killed someone that Iranian writers were supported. He believed that support let all the world see that writers were not alone.

L to R: Mansur Rajih from Yemen, one of the first ICORN guests in subsequent years, and Iranian writer Faraj Sarkohi, former WiPC main case at PEN International’s 65th Congress in Helsinki, Finland, 1998
While the Helsinki Congress focused on the traditional work of PEN and its Committees, it was also a watershed Congress addressing the structure and governance of PEN. The Ad Hoc Committee, elected at the previous congress in Edinburgh (see PEN Journey 20), had examined the draft of revised Regulations and Rules and presented a final draft for the Assembly’s adoption. The revised Regulations and Rules were the product of two years’ work and consultations among centers. These were the first amendments to the Regulations of PEN since 1988 and the first major revision since 1979.
International PEN’s reform to provide more democratic decision-making, more communication between the International and the Centers and more transparency was not an entirely smooth transition and reflected a larger global trend at the time among the 100+ nationalities represented in PEN.
At the Congress a new International Secretary—Terry Carlbom from Swedish PEN—was elected as the only candidate, Peter Day, editor of PEN International magazine, having stepped down from consideration because of health reasons. The former International Secretary Alexandre Blokh, who had served for 16 years, didn’t attend the Congress, but was elected a Vice President and returned to subsequent Congresses.
Marian Botsford Fraser of PEN Canada, representing the Ad Hoc Committee, presented the new proposed Rules and Regulations, noting that they were “the nuts and bolts or the strings and hammers of a piano or the engine of a car or mother board of a computer. In any case their workings were unfamiliar to most writers,” she said. “It was as if we had been asked to rebuild the engine of a 1979 Audi, a vehicle renowned for the complexity of its construction. Frankly I can think of only one more difficult assignment for nine writers and that would have been to collaborate on the writing of a novel.”
She noted that the Committee of nine was a diverse collection of individuals with the wisdom that democracy sometimes magically bestowed upon its practitioners. The Edinburgh Assembly had chosen a group of people who represented the linguistic, cultural and geographic diversity of PEN and who brought to the table individually and collectively their commitment to the history and the future of PEN, their desire to remain true to the spirit of the Charter of PEN and to the identity of PEN as first and foremost an organization of writers working together to protect language, literature and the fundamental human right of freedom of expression. “We brought to the process different and strongly held views on how to make the regulations that we were charged with drafting embody those principles, how to create a structure that would become the foundation for the future of this organization,” she said.
She thanked certain Ad Hoc members, who in fact did seem to have some knowledge of the workings of a 1979 Audi and added special thanks to Administrative Director Jane Spender “who took the whole mess of scribbled bits of paper, half sentences, cryptic clauses, clearly articulated ideas and sometimes incoherent good intentions back to London, and through another process of consultation and discussion and writing and rewriting was able to turn all of this into two documents that were sent to all Centers as Draft Regulations and Rules.” Homero Aridjis, the new International PEN President, also participated in this task along with the Ad Hoc Committee.
As I read through the minutes of the Helsinki Assembly, I recalled the tensions that arose, particularly around single words such as “a-political”—after all we were an organization of writers where words and translation of words mattered—and around events that had happened off stage. Changing the way a 77-year old organization worked was perhaps more like shifting from an Audi into an SUV which could hold more people, handle more difficult terrain but also consumed more fuel and energy. But metaphors aside, after debate and discussion, agreement was ultimately achieved.
The most important change was the move to form an Executive Committee that would be the main implementing body for International PEN, a step agreed by most all Centers who chose to participate in the process. Instead of government by a small executive of the President, International Secretary and Treasurer between the Assembly of Delegates’ meetings, an Executive Committee of seven members drawn from the centers around the globe and elected for three-year terms (and up to six years) would operate along with the three executives of PEN. The election for the first Executive Committee was to take place at the 1999 Congress in Warsaw. Until then the Ad Hoc Committee would continue to function and also act as a Selection Committee to assure qualified candidates were put forward.
Details of this new structure were modified over the next twenty years. The Selection Committee evolved into an elected Search Committee to assure qualified candidates were proposed for the various offices and to gather their required papers. The Search Committee was not set up to be a guardian council or an arbiter of candidates, but a facilitator for the process. In 2005 an Executive Director was added to the equation. As with any organization, PEN keeps growing and changing, but the essential structure to broaden and democratize governance of this global organization was set in place in 1998 in Helsinki. I’m not sure what vehicle I would compare PEN to these days, probably not a finely tuned Audi, but it continues to drive.
As for Vice Presidents, that office was not changed during this watershed period of reform, but over time, PEN changed the role of Vice Presidents and designated the ex-Presidents as Presidents Emeritus instead and divided the Vice Presidents into two equal categories with twelve in each: those elected for “service to PEN” and those designated for “service to literature;” the later included internationally renowned writers and Nobel laureates such as Nadine Gordimer, Toni Morrison, Svetlana Alexievich, Orhan Pamuk, Margaret Atwood, Ngũgĩ wa Thiong’o, J.M. Coetzee.
When I became International Secretary (2004-2007), the Executive Committee (now called the Board) and I proposed, and the Assembly agreed, that Vice Presidents’ terms should be limited, at least in the category of service to PEN—ten years or sometimes twenty—then most would move to emeritus status. It took another ten years before this change was implemented.
These are arcane details but illustrate PEN as an organization striving to keep those experienced engaged at the same time keep the organization unencumbered so it can grow and bring in new ideas and talent. It is a vehicle constantly re-tooling with the Charter as its base and a body of creative members whose greatest talents are not necessarily in rules and regulations yet who respect their necessity. Vice Presidents Emeritus, as I now am, are invited to the Congresses and show up and are still sought out for the bit of history we know and for the bits of wisdom we might offer from our experience and for continuity. We knew PEN in the days of the Audi, though even then it was perhaps not so finely tuned, I think, but it got from here to there across the globe as it still does.
Next Installment: PEN Journey 22: Warsaw—Farewell to the 20th Century
PEN Journey 20: Edinburgh—PEN on the Move, Changes Ahead
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest
I begin with the memories…
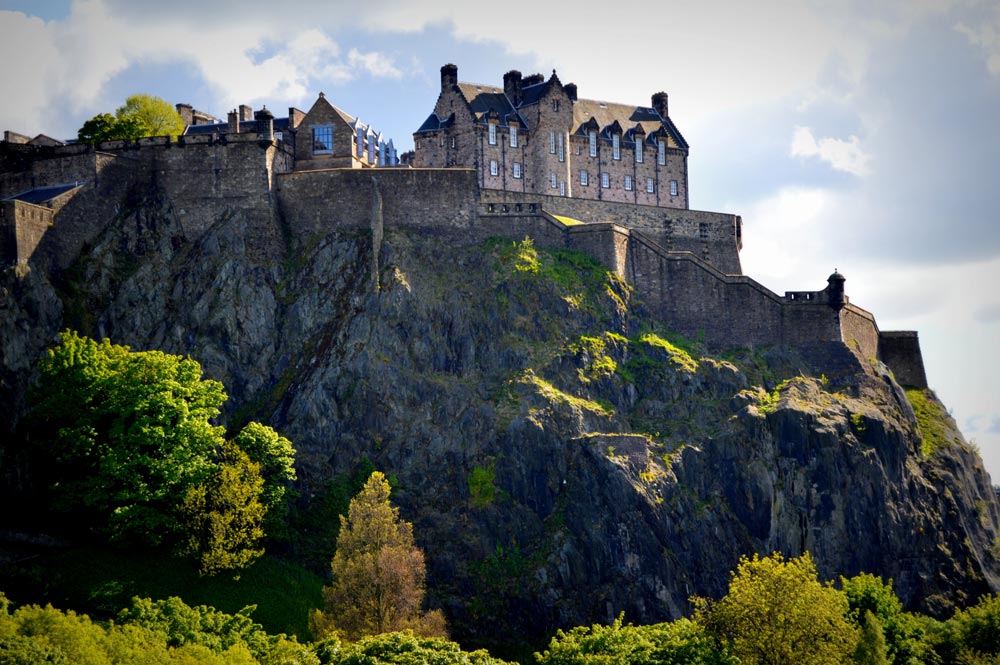

Castle Rock and Edinburgh Castle in Edinburgh, Scotland
—the imposing walls around Castle Rock which stands above the city of Edinburgh and dates back to the Iron Age,
—the 12th century castle/fortress inside,
—the Old Parliament building,
—the New Parliament building where we sat in high-backed theater-style seats in an arena,
—the dorm room residence inside Pollack Halls where we stayed at Edinburgh University near the city center, beside an extinct volcano,
—the receptions at Parliament House and Signet Library and the City Arts Center where there was never quite enough food for the overly hungry delegates who descended upon the platters,
—the UNESCO seminars on women and literature, including my paper The Power of Penelope,
—and elections, so many elections and speeches—three candidates for Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC) Chair, seven candidates for International PEN President, nine Ad Hoc Committee members as precursors to a new governing board for International PEN.
These were the first contested elections I remembered in International PEN. A wider democracy was spreading with ballots and speeches. I also remember the tension and the occasional flares of anger, and the effort to hold us all together and ultimately the confident results and the determination to move forward in unity. International PEN President Ronald Harwood warned that while PEN badly needed to democratize “power” so it wasn’t too centralized, residing in the hands of a few, the delegates should not make the struggle personal and should go forward with a sense of humor. We were an organization of writers, not the government of the world, he admonished, warning members not to confuse bureaucracy with democracy.
—I remember the trip to Glasgow where a few of us had a stimulating visit and tea at the home of James Kelman (Booker Prize winner How Late It Was, How Late) who had been with us in the protests in Turkey a few months before (see PEN Journey 19) and the old Mercedes tucked in the garage in the working class neighborhood.
—And the Edinburgh International Festival, including the Edinburgh Book Festival, happening simultaneously all around us.
—And finally the exquisite August light in Scotland.

Program for 1997 PEN International Congress
I begin with memory then plunge into the minutes and documents of the 64th PEN Congress August, 1997 when delegates from 77 PEN centers around the world gathered. The Congress theme Identity and Diversity posed the questions:
In the contemporary world there are intense pressures, political or commercial, deliberate or unconscious, towards an imposed uniformity. One example is the effect on language. Indigenous languages, which embody particular traditions and experience, are in many countries under threat of displacement and extinction. These tendencies are inimical to literature which depends on its local personality for its color and effectiveness even when it achieves universal significance.
On the other hand, we live in an inter-dependent world where peace, prosperity and ultimately even survival, require co-operation. This international co-operation may be assisted by the use of a few languages which are widely understood. International exchange of the appropriate kind can also bring cultural enrichment.
How can these apparently contradictory objectives of diversity and co-operation be reconciled? Does literature have a role in this respect?
As with most abstract themes and questions, there is no simple answer, but the theme was a pivot, in this case both in the literary sessions and inadvertently in the business of PEN as the organization sought to restructure itself. Because this was my last congress as Chair of the Writers in Prison Committee, the work of that Committee absorbed my focus. My two reports—one the official printed International PEN Writers in Prison Committee report and the other an address to the Congress—observed, and in a fashion related, to this theme:
[Written report:]

PEN Writers in Prison Committee Report, 1997
Tension between the individual and the state underlies the work of PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee. In some countries constitutions and governing principles are set out to protect the individual from the state, but in the majority of countries which PEN monitors where writers are imprisoned, threatened or killed, the state is organized to protect itself from the individual. Whether those countries be totalitarian regimes like China, Myanmar/Burma, Syria, Vietnam, Cuba or democracies like Turkey and South Korea, when the state holds itself superior to the rights of its individual citizens, freedom of expression is seen as a threat to stability rather than a sign of stability.
In 1997 the Writers in Prison Committee has defended individual writers in at least as many of the new and older democracies around the world as in totalitarian states. Since 1990 dozens of nations in Latin America, Africa, Europe, and Asia have restored or initiated multi-party democratic elections. The turn to the democratic process initially freed up restrictions on writers and journalists in many countries. However, after the first flush of these freedoms, after dozens of independent publications sprang up in Argentina, Belarus, Cambodia, Ethiopia, Russia, Sierra Leone, Zambia, etc., tensions mounted between the individual voice and the state. Restrictions and press laws followed, and writers once again found themselves facing prison terms on such charges as “insulting the President”, “writing derogatory statements against the government and government officials”, and “seditious libel.”
In some states like Sierra Leone harsh restrictions on the media preceded coups and the loss of democracy. Reporting restrictions and brief detentions of journalists enforced by the crumbling Mobutu government in Zaire (now Congo), did not serve to protect it from its eventual collapse. Earlier this year the political crackdown in Belarus was preceded by severe censorship and curtailment of publications. The collapse of the government in Albania was followed by severe restrictions on publications and attacks and death threats on journalists and writers.
When a coup occurs and democracy fails, the consequences for free expression are usually disastrous as has been seen in Nigeria where journalists continue to serve lengthy prison terms and are arbitrarily detained, sometimes for months without charge. Another instance of a threat to freedom of expression in Nigeria is that of PEN member and Nobel laureate Wole Soyinka who is among 12 dissidents charged in Nigeria this year with the capital offense of treason. Soyinka remains free outside the country but is certain to be imprisoned if he returns.
Pressure on writers and the media continued or increased in many new and old democracies, including Algeria, Argentina, Bosnia, Cameroon, Croatia, Ethiopia, Egypt, Indonesia, Kyrgystan, Mexico, the Palestinian authority, Turkey, Uganda and Zambia. Pressures took the form of legislation which required publications to obtain government licenses and approval and/or required journalists to have state-approved credentials. Pressure also took the form of arrest, arbitrary detention and death threats…
When democracy fails, there are hosts of reasons embedded in history and politics. Curtailment of free expression is not necessarily the precipitating cause, and curtailment of free expression does not always lead to failure of democracy. However, repression of the written word and of the writer remains at the very least a symptom and often a warning light that political failure lies ahead…
The report goes on to outline situations of individuals under threat. Reading these reports is reading a political history of the time, told through the circumstances of individual writers. One of the highlighted cases at the Congress in 1997 was that of Iranian writer Faraj Sarkohi who’d signed a petition calling for freedom of expression, along with 134 other Iranian writers. Sarkohi had been kidnapped by the Iranian secret service while on his way to visit family in Germany; he was tortured and threatened with execution. Because of the worldwide protests by PEN and others, he was eventually released the following year and sent into exile.
Visiting the WiPC meeting in Edinburgh, Egyptian professor Nasr Hamed Abu-Zeid, a leading liberal theologian on Islam, told his story of being declared an apostate for his research and forced to divorce his wife, also an academic. They had fled Egypt where apostates could be killed. Şanar Yurdatapan, the Turkish activist who’d organized the Gathering in Istanbul for Freedom of Expression which many of us attended earlier that spring, had just been released from prison and also spoke to the meeting. The cases of Sarkohi and Abu-Zeid and Şanar were among 700 on the WiPC records.
[Address to Assembly of Delegates:]
After four years chairing International PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee, I’ve come to appreciate the simplicity of the Committee’s mandate and the complexity of its execution. To defend the individual’s right to free expression is to defend not only the essence of literature but also a cornerstone of free society. Our defense begins with the individual writer, but inevitably we are caught in the movements of politics and history where individuals struggle to shape, divert or oppose the tides. One of the most significant developments in the past few years has been the expansion of multi-party democracies across the globe, a development that at first glance would signal progress for free expression. However, from our work we have seen that democracy takes more than a polling booth and a list of candidates on a ballot to come to fulfillment. Freedom of the written word is essential for a democracy to work over the long term, and attacks on this freedom usually foreshadow larger repression and even the failure of the democracy itself.
This year PEN has seen repressive laws enacted and/or writers arrested and killed in the new and old democracies of Albania, Algeria, Argentina, Belarus, Bosnia, Cambodia, Cameroon, Croatia, Ethiopia, Egypt, Indonesia, Kyrgyzstan, Mexico, Russia, Palestinian territory, Peru, Sierra Leone, South Korea, Turkey, Zambia. Many governments have passed or tried to pass laws to bring publications under their control through licensing and government-approved credentials. These laws have been followed by the arrest of writers.
Repression remains the most severe in totalitarian states such as China, Cuba, Iran, Myanmar (Burma), Nigeria, Syria, Vietnam. China continues to imprison more writers for longer periods of time—over 70 individuals, many serving 10-20 years—than any other country. Many of the writers who were imprisoned during Tiananmen Square have been released in the past two years, but others have taken their place. The Writers in Prison Committee is watching with great concern legislation which could lead to restrictions on writers in Hong Kong as China takes over. The Committee is also following closely the continued repression in Myanmar (Burma) where prison conditions remain harsh and at least 25 writers remain behind bars, many with sentences exceeding ten years…
Many of the cases in Africa this year came from new democracies struggling with issues of free expression, including Cameroon, Ethiopia, Uganda, and Zambia. The military dictatorship of Sani Abacha in Nigeria continued to occupy the focus of many PEN centres who worked on behalf of writers still in prison. Protests from a number of PEN centres assisted in the release of two Nigerian writers…Our Committee heard a statement from PEN main case Koigi wa Wamwere from Kenya, where riots have broken out after calls for democratic reform. Centres around the world have lobbied for his release, and he is now out on medical bail, and the Writers in Prison Committee has assisted his return to Norway where he is living. He sent a message thanking PEN for its work on his behalf. He writes, “When dictators arrest writers, they guard them with more guns and soldiers than they guard enemy armies in captivity. Dictators fear ideas and writers more than they fear guerrilla armies. Afterall they know that without ideas even guerrilla armies would wither away and die…”
In Latin America PEN continued to protest this year the imprisonment and detention of writers in Cuba. This spring the Writers in Prison Committee issued its report on its Cuba trip last fall, focusing on dissident writers who often had to choose between prison and exile…In Peru, though legislative and judicial reforms have occurred in the last years, at least 11 writers there have reported threats and/or attacks from both governmental and non-governmental sources, and sixty writers and journalists have reported death threats or attacks in Argentina…
The Writers in Prison Committee continues to work closely with freedom of expression organizations around the world, sharing our research and disseminating via the internet so that when a writer is arrested as far away as Tonga, the King of Tonga suddenly found himself receiving faxes from all over the world.
Over the years the political tides have shifted, but members’ work on behalf of individuals and the friendship of writer to writer remain even after the writers are released. This year we saw releases in Cameroon, China, Cote d’Ivoire, Cuba, Indonesia, Iran, Kenya, Kuwait, Maldives, Myanmar (Burma), Nigeria, Peru, and Russia. On occasions we have gotten to meet and know the individuals personally. This year when the Nigerian government picked up Ladi Olorunyomi, the Writers in Prison Committee was quickly alerted. A number of us had had the opportunity to meet with her husband Dapo, a prominent editor and dissident now living in exile in the United States. Isabelle Stockton, our Africa researcher and I spoke in the morning, and she called him to gather more details. When I phoned him later in the day, he said, “I was going to call you, but before I could, PEN was already calling me.” As soon as we determined that Ladi Olorunyomi had not been charged with a crime, had no access to lawyers and was not allowed to see her family, we put out a Rapid Action to our centres and shared the information with other freedom of expression organizations all around the globe. During her almost two months in captivity we were able to monitor the case, share information, and hear with great relief when this writer and mother was finally released.
Dapo, who had secretly fled Nigeria a year earlier lest he be imprisoned, wrote PEN, “Thank you for everything! I am very grateful, but I lack the words, appropriate enough to convey my gratitude…to our good friends at PEN International.”
The business of PEN throughout the year and at the annual Congress also included the work of the Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee, Women’s Committee, Peace Committee, the growing activity of the Exile Network and the literary sessions. The UNESCO seminars on Women’s Cultural Identity linked to the seminars on Literature and Democracy at the Guadalajara Congress the year before. In many parts of the world women still did not have full democratic rights. Significantly, in Latin America only 10% of books published were by women, and in Africa it was as few as 2%. But I must leave others to elaborate these activities.
At the 64th Congress results of the many elections yielded the next group of leaders who would take the organization into the last years of the 20th Century and into the transformation of governance. At the Congress Ronald Harwood was elected a Vice President as I had been at the previous Congress and as such we stayed connected and in the wings for the changes ahead.
Election results of the 64th PEN Congress:

Homero Aridjis
Seven candidates stood for the presidency from Europe, Africa and the Americas though one dropped out. Homero Aridjis of Mexico, well-known poet, journalist and diplomat, was elected the next President of International PEN.

Moris Farhi
Novelist Moris Farhi, former chair of English PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee, was elected chair of the WiPC. The two runner-ups Louise Gareau-Des Bois (Quebec PEN) and Marian Botsford Fraser (PEN Canada) agreed to serve for a year as Vice Chairs. In 2009 Marian Botsford Fraser was elected chair of WiPC and served till 2015.
The new Ad Hoc Committee elected at the Congress included Marian Botsford Fraser (Canada), Takashi Moriyama (Japan), Boris Novak (Slovenia), Carles Torner (Catalonia), Jacob Gammelgaard (Denmark), Vincent Magombe (Africa Writers Abroad), Gloria Guardia (Colombia), Gordon McLauchlan (New Zealand) and Monika van Paemel (Belgium). This committee was charged with considering all the restructuring proposals and preparing a draft for discussion and adoption by the Assembly of /Delegates at the 1998 Helsinki Congress. The Ad Hoc Committee was also tasked as a Nominating Committee to search for a new International Secretary. Alexander Blokh, re-elected for another year as International Secretary, planned to step down at the 1998 Helsinki Congress. Little did I know nor aspire to take on that role six years later.
New PEN Centers voted in at the Edinburgh Congress included Cuban Writers in Exile, Somali-speaking Center, Sardinian PEN Center, and a reconstituted Mexican PEN Center.

PEN International’s Writer in Prison Centre to Centre newsletter, July, 1997
Next Installment: PEN Journey 21: Helsinki–PEN Reshapes Itself
PEN Journey 17: Gathering in Helsingør
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.
What I remember most about the gathering of colleagues from 28 countries—31 PEN centers—51 of us in all at the first Writers in Prison Committee conference in 1996 was the seriousness of purpose and intellect during the day and the fun and talent in the evenings.
Hosted by Danish PEN, writers from every continent gathered at a university in Helsingør—known in English as Elsinore, the home of Shakespeare’s Hamlet—where we met in workshops and ensemble during the day to shape and refine our work on behalf of writers and freedom of expression around the world. But in the evening we were at a small university in a small city without transportation or distraction so we entertained ourselves. Each delegate displayed talents—from poetry reading to song to dance to musical performances.
As Chair of the WiPC gathering, I’d brought none of my own writing to read and was left to exhibit meager other talent which consisted of playing a few opening bars of Für Elise on the piano and whistling tunes with my far more talented Danish and Russian colleagues. Archana Singh Karki from Nepal in flowing red dress entertained with her graceful dance; Siobhan Dowd, our Irish former WiPC director and Freedom of Expression director at American PEN, silenced us with her soulful Irish folk songs, sung acapella; Sascha, Russian PEN’s General Secretary, not only whistled robustly but recited his poetry, which I was told I should be glad I didn’t understand with its bawdy content; Sam Mbure from Kenya and Turkish/English novelist Moris Farhi also read and recited work. PEN International President Ronald Harwood joined the discussions in the day and was audience in the evening. I don’t recall if Ronnie offered his own work, but we all bonded in our mission and in our support for the talent in the room.

Entertainment in the evening: From the top left—Jens Lohman (Danish PEN), Alexander (Sascha) Tkachenko (Russian PEN), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (Chair of WiPC)in a whistling song; Rajvinder Singh (German PEN, East) accompanying Archana Singh Karki (Nepal PEN) in dance; Siobhan Dowd (at piano—English & American PEN) with Moris Farhi (reading—English PEN); Sam Mbure (reciting—Kenyan PEN); Niels Barfoed (reading—Danish PEN)
During the three days, we fine-tuned our methods of working on and campaigning for our main cases, those writers who were imprisoned, attacked or threatened because of their writing, often their nonviolent voice of protest against authoritarian regimes. We considered PEN’s decision-making on borderline cases such as those which included drug charges, advocacy of violence, pornography, hate speech, terrorism. These were not categories we normally took on as cases. We discussed when we might take up such a case or assign them to investigation or judicial concern. We laid the groundwork for more joint actions among centers and other organizations such as the U.N., OSCE and IFEX, the International Freedom of Expression Exchange.

Round Table of the WiPC conference which included delegates from PEN centers in Switzerland, Jerusalem, Denmark, England, Mexico, Portugal, America, Norway, Czech Republic, Ghana, Canada, Australia (Melbourne and Sydney), Portugal, Finland, Nepal, Scotland, Malawi, Kenya, Ghana, Croatia, Slovakia, Sweden, Spain, Austria, Japan, Germany, Russia, Poland, Netherlands
With PEN’s WiPC staff Sara Whyatt and Mandy Garner, we set out a campaign calendar for the year, beginning with Turkey in May; China in June; Myanmar in July; Guatemala in September; Vietnam in October; Nigeria in November; Human Rights Day focus in December; Cuba in January; Rushdie and Fatwa and Iran in February; United Nations Commission on Human Rights lobbying in February/March and a return to China during the Chinese New Year in February/March; International Women’s Day in March and World Press Freedom Day in May. This campaign calendar meant that the London office would send information each month related to these foci, and PEN centers would plan programs if the campaign fit their work and the cases they had taken on.
We discussed the elements of successful missions to troubled areas and what future missions should be considered. In 1997 PEN International and Danish PEN sent representatives on a quiet mission to Cuba. We also strategized on the effect of writers observing trials in certain countries, particularly in Turkey.
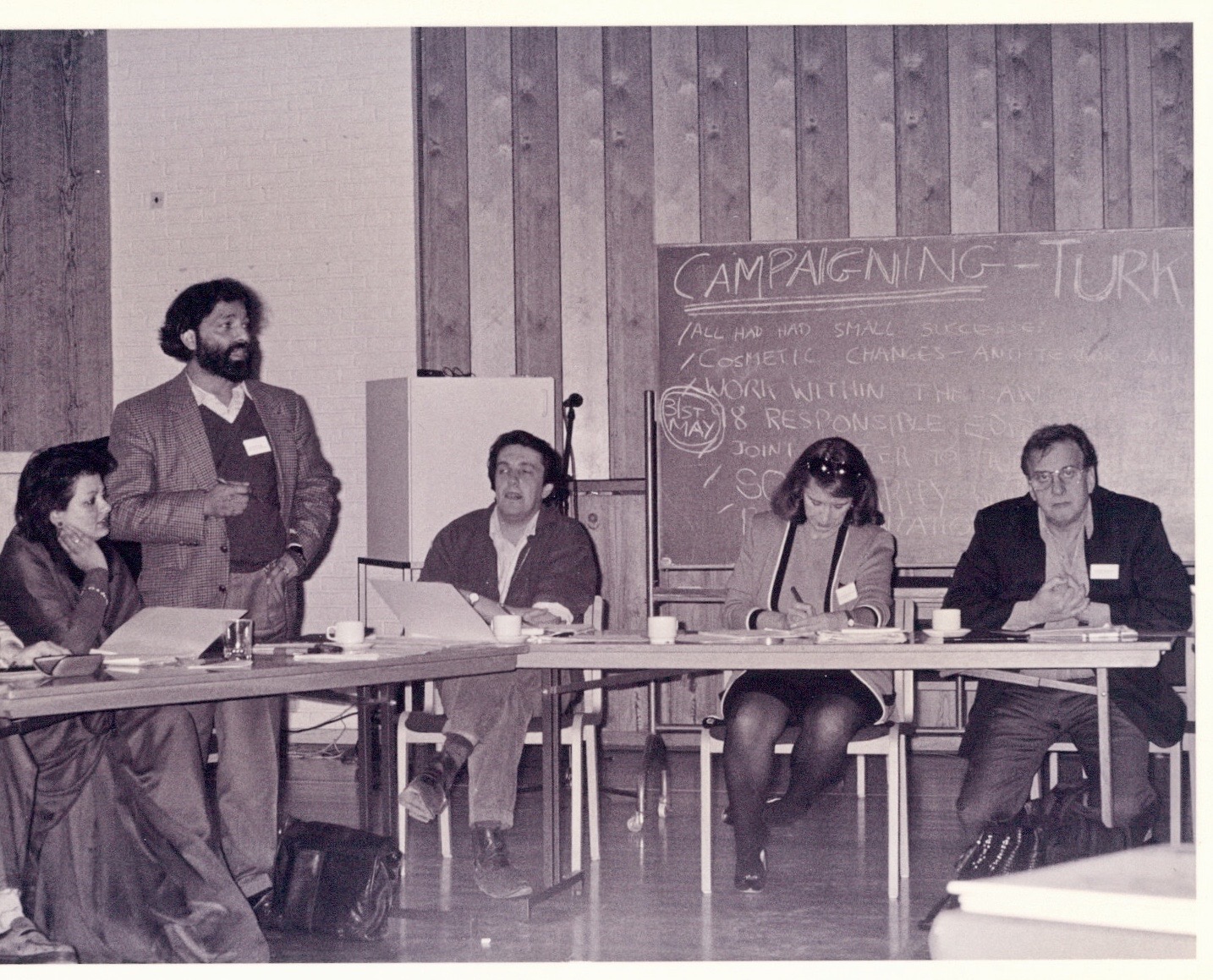

Working session on Turkey Campaign at at WiPC conference: L to R: Archana Singh Karki (Nepal PEN), Rajvinder Singh (German PEN, East), Robin Jones (WIPC staff), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (WiPC Chair), Ronald Harwood (PEN International President)
During the conference a request came for members of PEN to sign on individually and en mass as publishers of a book in Turkey which republished an article by the famed Turkish novelist Yaşar Kemal, along with articles by other Turkish writers who were in prison because of their writing. Kemal had recently been charged because of an article he’d published in the German magazine Der Spiegel about the Kurds. The organizer in Turkey had gathered hundreds of Turkish writers, publishers, artists, and actors to sign on as publishers. They wanted to present the book and the list of hundreds of publishers to challenge the courts to bring charges against everyone. Many of us agreed to participate. This act launched a campaign in Turkey and a mission later in 1997. (Blog to come.) The independent Turkish Freedom of Expression Initiative has since gathered biennially for the last 23 years. For this kind of joint action PEN was primed to cooperate.
Finally in Helsingør the Writers in Prison Committee took a step towards opening up the election process for the WiPC Chair. My term was due to expire at the fall 1996 Congress in Guadalajara. We decided to select a nominating committee from members to find candidate(s) for the next chair rather than have the post appointed by the Secretariat in London. That process was later replicated in other elections in PEN and is standard procedure today.

Workshop: From left includes: Neils Barfoed (Danish PEN), Lady Diamond (Ghana PEN), Moris Farhi (English PEN), Sara Whyatt (WiPC Programme Director), Mandy Garner (WiPC researcher), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (WiPC Chair at front)
Helsingør was a fitting venue for the first WiPC Conference, not only because of its literary credentials with the Kronborg Castle where most of Shakespeare’s Hamlet takes place, but also because of its historic legacy in World War II. Helsingør was one of the most important transport points for the rescue of Denmark’s Jews. A few days before Hitler had ordered that the Danish Jews were to be arrested and deported to concentration camps October 2, 1943, one of the Nazi diplomatic attaches who’d received word in advance shared the information with the Jewish community leaders. Using the name Elsinore Sewing Club, the Jewish leaders communicated with the population, and the Danes moved the Jews away from Copenhagen to Helsingør, just two miles across the straights to neutral Sweden. The Danish citizens hid their fellow Jewish citizens until they could get onto fishing boats, pleasure boats and ferry boats and escape over a period of three nights. The Danes managed to smuggle the majority of its Jewish citizens—over 7200 Jews and 680 non-Jews—across the water to safety.
Next Installment: PEN Journey 18: Picasso Club and Other Transitions in Guadalajara
PEN Journey 5: PEN in London, Early 1990’s
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey might be of interest.
I moved to London where International PEN is headquartered in January 1990 from Los Angeles. I came with my husband and my 9 and 11-year old sons who rarely wore long sleeves, let alone coats or jackets. A few weeks into our resettlement, London spun in its first major tornado of the decade with hail and winds whipping at hurricane force and cars and trees toppled and a few rooftops airborne. The weather was highly unusual for London. Our family, who was still in temporary housing, took the unwelcome weather as a welcome of sorts, signaling that we might just be in for an adventure. Did you see that roof flying…!
There were still complaints: only four television channels, movies strictly restricted by age and when you did get into a theater, you had assigned seats, milk that went bad in a day, delivered on the stoop in glass bottles, a refrigerator that barely held enough food for a day, appliances that came without plugs…And where was the sun?
Yet the magic of the city quickly affected us all. My youngest son discovered the best skateboarders lived in London, and London (and England) was full of history and castles, and my oldest son, who was soon moved ahead a grade in school because he was highly talented in math, met students from all over the world in his class at the American School, a few of whom talked and imagined in his orbit. He was put on the rugby team to help socialize and the following year on the wrestling team, where he eventually, as an adult and by then dual citizen, wrestled for Great Britain in the Olympics.
For me, finding home in London meant connecting with PEN, both International PEN and English PEN. Writers can be members of more than one PEN center, though can vote with only one center. I’d begun my PEN journey in Los Angeles at PEN Los Angeles Center (changed to PEN USA West). When my second book was published, I also joined PEN American Center, based in New York, and now in London. I joined English PEN, the oldest and the original PEN center since the organization was founded by British writers in 1921. International PEN and English PEN had separate offices, but the Administrative Secretary of International PEN and the General Secretary of English PEN were longtime friends and actually lived next door to each other in Fulham. The two organizations worked independently, yet closely together.

Early on I visited International PEN’s office, headquartered in Covent Garden on King Street in the Africa Centre. To get to the office at the front of the house, you had to go through the Africa Book Shop on the first floor. PEN had two rooms with several desks in the larger room with papers stacked everywhere. There was a filing cabinet and a photocopier and just enough space to squeeze between to get to the desk looking onto the street.
International PEN was kept functioning by the stalwart and efficient Elizabeth Paterson, who I don’t recall getting angry at anyone even as the work piled on and people around the world in PEN centers asked more and more of her, including the smart, demanding International Secretary Alexander Blokh. Alex flew in every month, usually from Paris, and displaced the Writers in Prison Committee’s small staff from the second office in order to conduct the business of PEN around the world. Alex was a former UNESCO official, and at that time UNESCO was one of International PEN’s major funders. When UNESCO was formed, according to Alex, it established organizations for the various arts, but when it came to literature, it recognized that PEN already existed, and so its outreach and funding funneled through PEN. Over the years PEN has grown more and more independent of UNESCO support.
Elizabeth, with her quiet intelligence and subtle humor, managed to keep International PEN running day to day while Alex developed the literary and cultural programs with the centers and the standing committees—the Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee, the Peace Committee, and the Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC). The WiPC tended to operate more autonomously with its elected chair Swedish publisher Thomas von Vegesack and before him Michael Scammell. When I arrived in London, there was also a petite gray-haired woman Kathleen von Simson, a volunteer who’d helped manage the Writers in Prison Committee work for years. PEN had recently hired a paid Coordinator Siobhan Dowd whose task was to professionalize the human rights work, and Siobhan hired researcher Mandy Garner. The two of them worked in the tiny second room. Siobhan eventually crossed the ocean to head up the Freedom to Write program at American PEN.

Fall 1990. Left to right: Elizabeth Paterson, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, Per Wastberg (former PEN International President), Siobhan Dowd, Bill Barazetti
Also finding space on King Street was the Assistant Treasurer (and later International Treasurer) Bill Barazetti, who at that time was an unsung hero from World War II. It was later publicized that Bill had smuggled hundreds of Jewish children out of Prague with false identity papers he arranged. He was a wiry gray-haired former intelligence officer who’d also interrogated captured German pilots. Alex Blokh, whose pen name was Jean Blot, was an exiled Russian Jew, a lawyer and had also been active in the French Resistance during World War II, and Elizabeth had endured the bombings in London during the War. Though it was 1990 and the Berlin Wall and other barriers which had gone up after World War II were now falling, in the PEN office there was still a feeling of that post-War period, an abstemiousness and a fortitude of the dedicated amateur who knew what sacrifice was and endured no matter what. I couldn’t articulate the atmosphere at the time, but as an American born after the war, grown up in Texas and moving to London from Los Angeles, I felt the contrasts and the constraints. One small incident I remember was when a donation for a baby gift for the newly hired Sara Whyatt was being gathered. I offered £20 for the pot and was told by Elizabeth, “Oh, no, that amount would embarrass her.” The concept of anyone being embarrassed by a pooled £20 contribution silenced me. I put in £10 instead, still considered a large amount. Because I was new and an American, I tried to listen and learn, but I understood expectations and horizons were different.
A generation of my own joined the office in the persons of Jane Spender, a former editor, smart and literary who worked with Elizabeth and later Gilly Vincent, who took on the part time assignment to help with development work for the eventual International PEN Foundation. (see PEN Journey 4) Later Gilly became General Secretary of English PEN. I quickly learned to respect the differences; the American way was not the British way. I remember a fundraising event in which there must have been 20 major English writers featured and attending, and the ticket price was £25. The PEN Foundation netted perhaps £3000 that evening. In New York with that line up of writers, I am confident American PEN would have added at least one, if not two, zeros to the proceeds, but we were in London, and the event was not a glittery affair but more like a large family gathering of literary friends at someone’s home.
PEN International moved its offices in 1991 from Covent Garden to Charterhouse Buildings in Clerkenwell nearer the City of London. The new offices were on the top floor of a bonded warehouse, and I never met anyone who didn’t arrive breathless after climbing the steep four or five flights of stairs. There was no elevator, but there was an outside hoist where PEN could load supplies and mail out the window and drop or raise these to and from the ground, preferably not in the rain. Elizabeth set the door code as the beginning and ending years of World Wars I and II, an 8-digit code everyone could remember. The offices at Charterhouse Buildings were spacious compared to King Street—two large airy rooms, one for the Writers in Prison Committee and one for all the other work of PEN, a spacious entry room used as a meeting area and a smaller private office where the International Secretary could work or small meetings could be held. All the rooms were painted “magnolia”–a creamy white/yellow color. The full-time staff by then was, I think, three, along with four or five part-time staff and volunteers, including Jane Spender, Peter Day, editor of PEN International magazine, Bill Barazetti and later his daughter Kathy and occasional interns.
When Siobhan prepared to leave for the U.S., Thomas asked me to interview candidates with him for her replacement. Between interviews he explained to me his view of England in the constellation of Europe by a story of when a fog settled over the English Channel and the headline in a British paper announced: Continent Isolated. Later, when the Channel Tunnel finally connected Great Britain to France in 1994, I sent Thomas a note and a copy of the headline from a British paper: “You’ll be glad to know, Thomas: Continent No Longer Isolated, the headline read.
Thomas and I agreed on the best candidate, and PEN hired Sara Whyatt as the new Program Director of the Writers in Prison Committee. Sara came to PEN from Amnesty and set about further professionalizing WiPC’s research and advocacy work. Sara and Mandy split up the globe, with Mandy focusing on Latin America and Africa.

Across London in Chelsea, English PEN rented offices from the London Sketch Club on Dilke Street where it held weekly literary programs, a monthly formal dinner, an annual Writers Day Program honoring one writer—Arthur Miller, Graham Greene, and Larry McMurtry were three I recall—and a mid-Summer Party. The literary programs and dinners, held in the Sketchers studio and bar, featured writers such as Michael Ignatieff, Germaine Greer, Michael Holroyd, Jan Morris, Rachael Billington, A.L. Barker, Penelope Lively, Andrew Motion, A.S. Byatt, Margaret Foster, William Boyd, Margaret Drabble, Iris Murdoch, and frequently Antonia Fraser, Harold Pinter and Ronald Harwood, just to name a few.
When I moved to London and joined English PEN, the General Secretary Josephine Pullein-Thompson, a stalwart writer/member, managed the organization and kept it running with minimal staff and with active members. Author of young adult novels, Josephine wrote books about young girls and horses. When I close my eyes, I can hear her gruff voice and see her square face and think of horses. She was pragmatic and no-nonsense and what I think of as the epitome of a certain era of British resolve. She befriended me early, I think, because I was focused on a task—getting charitable status for PEN International which ultimately allowed English PEN to claim the same. It was Josephine years later who nominated me as a Vice President of International PEN.

Members of English PEN were passionate about PEN’s mission to protect and speak up on behalf of writers under threat in oppressive regimes. Among activities, members, including notable British writers such as Ronald Harwood, Harold Pinter, and Antonia Fraser, who were good friends, and Moris Farhi, a Turkish/British novelist with a great beard, great girth and great heart, who later succeed me as Writers in Prison Chair, and dozens of other English PEN members held vigils, often by candlelight. They protested outside embassies of countries where writers were in prison. They got press coverage and ultimately helped secure the release of writers, particularly those in former Commonwealth countries like Malawi.
Malawian poet Jack Mapanje recalled his spirit lifting when he saw the press clippings of Harold Pinter and others protesting outside the Malawi Embassy in London on his behalf. When he was released, he resettled in England and joined English PEN.

Jack Mapanje
Next Installment: Freedom and Beyond…War on the Horizon
