Posts Tagged ‘freedom of expression’
The Journey of Liu Xiaobo: From Dark Horse to Nobel Laureate
The Journey of Liu Xiaobo: From Dark Horse to Nobel Laureate, published April 1 by Potomac Books (The University of Nebraska Press) tracks the life and ideas of the scholar, poet and activist who has been called the Nelson Mandela of China. It has been my privilege to edit this volume, along with colleagues of Liu’s. Below is my editor’s note to introduce this book which I hope readers will embrace to celebrate Liu Xiaobo’s life and legacy. (Essay reprinted with permission of Potomac Books.)
“Freedom of expression is the foundation of human rights, the source of humanity, and the mother of truth.”—Liu Xiaobo, I Have No Enemies: My Final Statement

Available at Potomac Books, Politics and Prose, Barnes and Noble, Amazon, Powells, and Indiebound
Editor’s Note
Joanne Leedom-Ackerman
A zoo in China placed a big hairy Tibetan mastiff in a cage and tried to pass if off as an African lion. But a boy and his mother heard the animal bark, not roar. As news spread, the zoo’s visitors grew angry. “The zoo is absolutely trying to cheat us. They are trying to disguise dogs as lions!” declared the mother.1
In 2009 the Chinese government put Liu Xiaobo, celebrated poet, essayist, critic, activist, and thinker into a cage, labeled him “enemy of the state,” charged him with “inciting subversion of state power,” and sentenced him to eleven years’ imprisonment. Liu Xiaobo was not an enemy, but he was a “lion” the state feared. He challenged orthodoxy and conventional thinking in literature, which he wrote and taught, and authoritarian politics, which he protested and tried to help reshape. His insistence on individual liberty in more than a thousand essays and eighteen books, his relentless pursuit of ideas, including as a drafter and organizer of Charter 08, which set out a democratic vision for China through nonviolent change, and finally his last statement, “I have no enemies and no hatred,” threatened the Chinese Communist Party and government in a way few other citizens had.
Dr. Liu Xiaobo was the first Chinese citizen to win the Nobel Prize for Peace, in 2010, but he was in prison, was not allowed to attend the ceremony, and died in custody in July 2017.
When news of Liu Xiaobo’s death reached the world and in particular the writers and democracy activists who knew him, writers began to write. Tributes and analyses poured in, many sent to the Independent Chinese PEN Center (ICPC), a gathering of writers inside and outside of Mainland China that Liu helped found and served as president. The Journey of Liu Xiaobo traces Liu’s history and the path of liberalism in China and is perhaps the largest gathering of Chinese democracy activists’ writing in one volume. Because of length restrictions, some tributes are listed only by authors’ names in the appendix.
A Chinese edition was published in 2017 as Collected Writings in Commemoration of Liu Xiaobo by Democratic China and the Institute for China’s Democratic Transition. It is hoped that this revised and expanded English edition, organized according to phases of Liu’s life and development, will find an even wider audience and offer insight into the person—his ideas, his loves, and his legacy. Some have suggested that because of Liu Xiaobo’s death and the economic and political ascendency of the current Chinese regime, Liu’s legacy has been reduced to a void. I would recommend that those who claim such consider the longer arc of history. The same was said of visionaries in Eastern Europe when earlier protests were crushed in Poland, East Germany, and elsewhere; the same was said of early martyrs in South Africa, where repression eventually led to widespread civic resistance and in other countries where civilians have challenged repressive systems. Liu Xiaobo was committed to nonviolent engagement and political change. Though he no longer walks the earth, his ideas and writings endure. History will unfold this story. In the meantime the essays in this volume recount one man’s journey and commitment to the struggle for the individual’s right to freedom.2
Societies move forward and are changed by ideas, by leaders, and ultimately by their citizens. None of these essays show Liu Xiaobo aspiring to personal power. But those in power worried about this man of ideas and this activist who set ideas into motion. He didn’t need to roar like a lion to garner the world’s attention and respect. By his life and his death he holds those in power to account.
Notes
———————————————————————————————————————
- Michael Bristow, “China ‘Dog-Lion’: Henan Zoo Mastiff Poses as Africa Cat,” BBC News, August 15, 2013, https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-china-23714896..
- In these collected essays, a number of writers express concern about the fate of Liu Xiaobo’s beloved wife, poet and artist Liu Xia, who spent years under house arrest. Since the writing of these articles, Liu Xia has been allowed to go to Germany for medical treatment. As of 2019 she resides in Berlin.
PEN Journey 21: Helsinki—PEN Reshapes Itself
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.
In the old days, at least my old days, the Vice Presidents of PEN International sat in a phalanx on a stage while the Assembly of Delegates conducted business—revered writers, mostly white older men, along with the President, International Secretary and Treasurer of PEN in the center. If the Assembly business wore on, it was not unusual to see one or two of them nodding off. The role of the Vice Presidents was to provide continuity—many had been former PEN Presidents—to provide wisdom, contacts and gravitas. The designation was for life.
But times were changing. For instance, I had recently been elected a Vice President. I was a woman. I’d served PEN in several positions, including president of my center, founding board member of the International PEN Foundation and International Writers in Prison chair; I was a writer, though not of international renown, and at the time I was relatively young. I had been nominated by English PEN whose General Secretary thought it was high time more women sat on that stage. I didn’t relish sitting on a stage, but I was honored to hold the position. The Helsinki Congress in 1998 was the first when Vice President was the only role I had. I don’t recall if there was a stage at that Assembly. The fun was that I didn’t have to do anything. I could float between committee meetings, offer comments when relevant, wisdom if I had any and be called upon for whatever insight or experience or task might serve. (Traditionally the Congress organizers paid for the Vice Presidents’ registration and hotel, but from the start I chose to cover my expenses as a way of contributing to PEN. The expense of Vice Presidents attending was growing more and more difficult for the host centers; on the other hand many Vice Presidents wouldn’t be able to attend otherwise.)

Program for 65th PEN International Congress in Helsinki, Finland
At the 65th PEN Helsinki Congress held at the Marina Conference Center on the waterfront, a short walk from the city center, delegates and PEN members from 70 centers around the world gathered. The Congress’ theme was Freedom and Indifference. My memories are of meals on the water with colleagues, of eating fish and mussels and walking among old and very new buildings, visiting the architecturally stunning Contemporary Art Museum and other cultural excursions I often didn’t have time to attend when chairing the Writers in Prison Committee.
At the Congress I could even sit in on a few of the literary sessions which included abstract topics such as Where Does Indifference End and Tolerance Begin?—The Role of the Intellectual in Contemporary Society; Eurocentrism and the Global Village; The Cultural Gap Between East and West; The Ambivalence of Otherness: Identity and Difference; Crime Literature Portraying the Society; On Cultural Creolisation (mixture) and Borderlands. I confess reading those topics now stirs memories of sleepy academic afternoons, but the writers presenting included some of the engaged and engaging writers of the day, including Wole Soyinka, Caryl Phillips, Andrei Bitov and many Finnish and Scandinavian writers such as Sweden’s Agneta Pleijel.
At the Congress I still concentrated on the work of the Writers in Prison Committee which former Iranian prisoner Faraj Sarkohi attended. The year before he had been a main case for PEN, imprisoned and tortured and threatened with execution. In introducing his presence to the Assembly of Delegates, PEN President Homero Aridjis noted that PEN members could take satisfaction in having played an important role in obtaining his release. Sarkohi had managed to get a passport and was now living in Europe where he’d resumed his literary and journalistic activities.
Moris Farhi, the new WiPC Chair, introduced Sarkohi to the General Assembly of Delegates where Sarkohi said he owed his life and freedom to the international movement initiated by PEN both in the London headquarters and in the PEN centers around the world. For the first time in 20 years the Iranian government had been forced to release someone they had wanted to kill, he said. His release demonstrated to other writers in Iran that release was possible even if the government wanted to execute them. Sarkohi had briefly spoken with another PEN main case in prison who told him he was no longer worried, knowing now about the international support he was receiving.
Sarkohi explained that writers were considered by the despots in Tehran to be guilty because they worked with words, because they tried to discover and express in words different aspects of truth. It was believed writers made magic, he said. Everyone knew the magical power inherent in words so the writers were arrested. The government forced them to deny themselves, to accept false charges, and in this way they killed writers mentally. When a writer was forced by physical and mental torture to deny himself, his ideas and his work, his power of creation died, and he was killed as a writer. When Sarkohi was in solitary confinement, he remembered the way in which those suspected of magic were treated in the Middle Ages. People were arrested and burned and told “If you live, your magic powers are proved and we kill you. If you die, it is established that you do not have magic powers.’—but you were dead anyway. Writers were regarded as the new practitioners of magic in this century and that treatment by tyrants and despots was that of the Middle Ages.
Sarkohi described how he and colleagues who were still in prison had issued a new Charter, inspired by the PEN Charter, in which they protested censorship, both by the government, self-censorship and by the public such as groups which beat up a writer in the street. The Charter also demanded the right for writers to organize an association, something not permitted in Iran. He worried now about the fate of his colleagues in Iran because five years ago when writers published a Charter and sent the text abroad, the government had reacted and killed a famous translator and dumped his body in the street and murdered a famous poet in his home.
Sarkohi noted that German PEN and other PEN centers had prepared a resolution for the Congress making it clear to the Iranian government that International PEN was watching the fate of Iranian writers so they would know before they arrested or killed someone that Iranian writers were supported. He believed that support let all the world see that writers were not alone.

L to R: Mansur Rajih from Yemen, one of the first ICORN guests in subsequent years, and Iranian writer Faraj Sarkohi, former WiPC main case at PEN International’s 65th Congress in Helsinki, Finland, 1998
While the Helsinki Congress focused on the traditional work of PEN and its Committees, it was also a watershed Congress addressing the structure and governance of PEN. The Ad Hoc Committee, elected at the previous congress in Edinburgh (see PEN Journey 20), had examined the draft of revised Regulations and Rules and presented a final draft for the Assembly’s adoption. The revised Regulations and Rules were the product of two years’ work and consultations among centers. These were the first amendments to the Regulations of PEN since 1988 and the first major revision since 1979.
International PEN’s reform to provide more democratic decision-making, more communication between the International and the Centers and more transparency was not an entirely smooth transition and reflected a larger global trend at the time among the 100+ nationalities represented in PEN.
At the Congress a new International Secretary—Terry Carlbom from Swedish PEN—was elected as the only candidate, Peter Day, editor of PEN International magazine, having stepped down from consideration because of health reasons. The former International Secretary Alexandre Blokh, who had served for 16 years, didn’t attend the Congress, but was elected a Vice President and returned to subsequent Congresses.
Marian Botsford Fraser of PEN Canada, representing the Ad Hoc Committee, presented the new proposed Rules and Regulations, noting that they were “the nuts and bolts or the strings and hammers of a piano or the engine of a car or mother board of a computer. In any case their workings were unfamiliar to most writers,” she said. “It was as if we had been asked to rebuild the engine of a 1979 Audi, a vehicle renowned for the complexity of its construction. Frankly I can think of only one more difficult assignment for nine writers and that would have been to collaborate on the writing of a novel.”
She noted that the Committee of nine was a diverse collection of individuals with the wisdom that democracy sometimes magically bestowed upon its practitioners. The Edinburgh Assembly had chosen a group of people who represented the linguistic, cultural and geographic diversity of PEN and who brought to the table individually and collectively their commitment to the history and the future of PEN, their desire to remain true to the spirit of the Charter of PEN and to the identity of PEN as first and foremost an organization of writers working together to protect language, literature and the fundamental human right of freedom of expression. “We brought to the process different and strongly held views on how to make the regulations that we were charged with drafting embody those principles, how to create a structure that would become the foundation for the future of this organization,” she said.
She thanked certain Ad Hoc members, who in fact did seem to have some knowledge of the workings of a 1979 Audi and added special thanks to Administrative Director Jane Spender “who took the whole mess of scribbled bits of paper, half sentences, cryptic clauses, clearly articulated ideas and sometimes incoherent good intentions back to London, and through another process of consultation and discussion and writing and rewriting was able to turn all of this into two documents that were sent to all Centers as Draft Regulations and Rules.” Homero Aridjis, the new International PEN President, also participated in this task along with the Ad Hoc Committee.
As I read through the minutes of the Helsinki Assembly, I recalled the tensions that arose, particularly around single words such as “a-political”—after all we were an organization of writers where words and translation of words mattered—and around events that had happened off stage. Changing the way a 77-year old organization worked was perhaps more like shifting from an Audi into an SUV which could hold more people, handle more difficult terrain but also consumed more fuel and energy. But metaphors aside, after debate and discussion, agreement was ultimately achieved.
The most important change was the move to form an Executive Committee that would be the main implementing body for International PEN, a step agreed by most all Centers who chose to participate in the process. Instead of government by a small executive of the President, International Secretary and Treasurer between the Assembly of Delegates’ meetings, an Executive Committee of seven members drawn from the centers around the globe and elected for three-year terms (and up to six years) would operate along with the three executives of PEN. The election for the first Executive Committee was to take place at the 1999 Congress in Warsaw. Until then the Ad Hoc Committee would continue to function and also act as a Selection Committee to assure qualified candidates were put forward.
Details of this new structure were modified over the next twenty years. The Selection Committee evolved into an elected Search Committee to assure qualified candidates were proposed for the various offices and to gather their required papers. The Search Committee was not set up to be a guardian council or an arbiter of candidates, but a facilitator for the process. In 2005 an Executive Director was added to the equation. As with any organization, PEN keeps growing and changing, but the essential structure to broaden and democratize governance of this global organization was set in place in 1998 in Helsinki. I’m not sure what vehicle I would compare PEN to these days, probably not a finely tuned Audi, but it continues to drive.
As for Vice Presidents, that office was not changed during this watershed period of reform, but over time, PEN changed the role of Vice Presidents and designated the ex-Presidents as Presidents Emeritus instead and divided the Vice Presidents into two equal categories with twelve in each: those elected for “service to PEN” and those designated for “service to literature;” the later included internationally renowned writers and Nobel laureates such as Nadine Gordimer, Toni Morrison, Svetlana Alexievich, Orhan Pamuk, Margaret Atwood, Ngũgĩ wa Thiong’o, J.M. Coetzee.
When I became International Secretary (2004-2007), the Executive Committee (now called the Board) and I proposed, and the Assembly agreed, that Vice Presidents’ terms should be limited, at least in the category of service to PEN—ten years or sometimes twenty—then most would move to emeritus status. It took another ten years before this change was implemented.
These are arcane details but illustrate PEN as an organization striving to keep those experienced engaged at the same time keep the organization unencumbered so it can grow and bring in new ideas and talent. It is a vehicle constantly re-tooling with the Charter as its base and a body of creative members whose greatest talents are not necessarily in rules and regulations yet who respect their necessity. Vice Presidents Emeritus, as I now am, are invited to the Congresses and show up and are still sought out for the bit of history we know and for the bits of wisdom we might offer from our experience and for continuity. We knew PEN in the days of the Audi, though even then it was perhaps not so finely tuned, I think, but it got from here to there across the globe as it still does.
Next Installment: PEN Journey 22: Warsaw—Farewell to the 20th Century
PEN Journey 20: Edinburgh—PEN on the Move, Changes Ahead
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest
I begin with the memories…
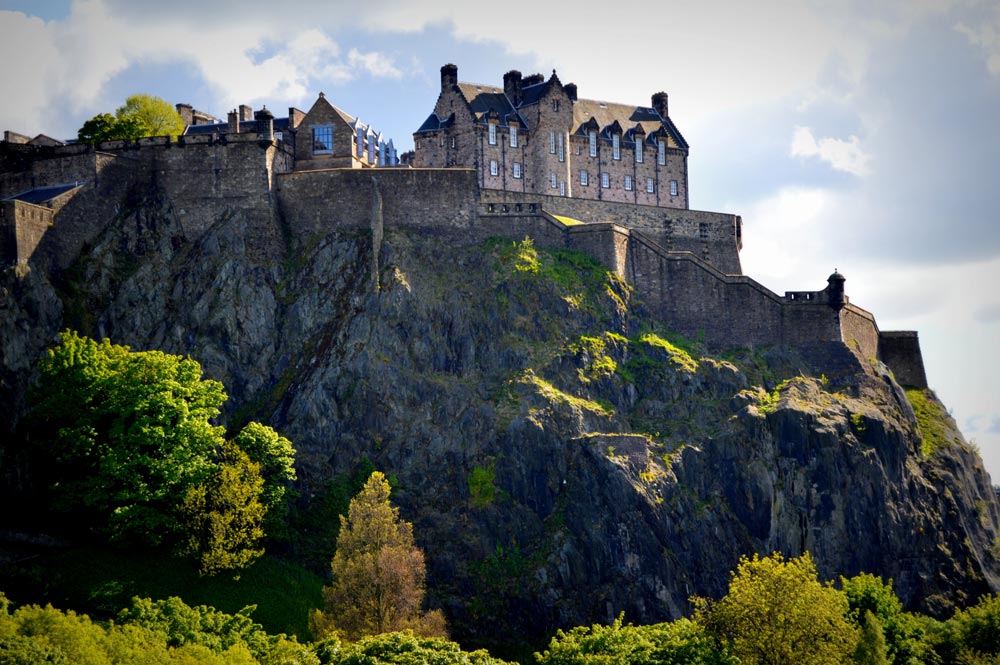

Castle Rock and Edinburgh Castle in Edinburgh, Scotland
—the imposing walls around Castle Rock which stands above the city of Edinburgh and dates back to the Iron Age,
—the 12th century castle/fortress inside,
—the Old Parliament building,
—the New Parliament building where we sat in high-backed theater-style seats in an arena,
—the dorm room residence inside Pollack Halls where we stayed at Edinburgh University near the city center, beside an extinct volcano,
—the receptions at Parliament House and Signet Library and the City Arts Center where there was never quite enough food for the overly hungry delegates who descended upon the platters,
—the UNESCO seminars on women and literature, including my paper The Power of Penelope,
—and elections, so many elections and speeches—three candidates for Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC) Chair, seven candidates for International PEN President, nine Ad Hoc Committee members as precursors to a new governing board for International PEN.
These were the first contested elections I remembered in International PEN. A wider democracy was spreading with ballots and speeches. I also remember the tension and the occasional flares of anger, and the effort to hold us all together and ultimately the confident results and the determination to move forward in unity. International PEN President Ronald Harwood warned that while PEN badly needed to democratize “power” so it wasn’t too centralized, residing in the hands of a few, the delegates should not make the struggle personal and should go forward with a sense of humor. We were an organization of writers, not the government of the world, he admonished, warning members not to confuse bureaucracy with democracy.
—I remember the trip to Glasgow where a few of us had a stimulating visit and tea at the home of James Kelman (Booker Prize winner How Late It Was, How Late) who had been with us in the protests in Turkey a few months before (see PEN Journey 19) and the old Mercedes tucked in the garage in the working class neighborhood.
—And the Edinburgh International Festival, including the Edinburgh Book Festival, happening simultaneously all around us.
—And finally the exquisite August light in Scotland.

Program for 1997 PEN International Congress
I begin with memory then plunge into the minutes and documents of the 64th PEN Congress August, 1997 when delegates from 77 PEN centers around the world gathered. The Congress theme Identity and Diversity posed the questions:
In the contemporary world there are intense pressures, political or commercial, deliberate or unconscious, towards an imposed uniformity. One example is the effect on language. Indigenous languages, which embody particular traditions and experience, are in many countries under threat of displacement and extinction. These tendencies are inimical to literature which depends on its local personality for its color and effectiveness even when it achieves universal significance.
On the other hand, we live in an inter-dependent world where peace, prosperity and ultimately even survival, require co-operation. This international co-operation may be assisted by the use of a few languages which are widely understood. International exchange of the appropriate kind can also bring cultural enrichment.
How can these apparently contradictory objectives of diversity and co-operation be reconciled? Does literature have a role in this respect?
As with most abstract themes and questions, there is no simple answer, but the theme was a pivot, in this case both in the literary sessions and inadvertently in the business of PEN as the organization sought to restructure itself. Because this was my last congress as Chair of the Writers in Prison Committee, the work of that Committee absorbed my focus. My two reports—one the official printed International PEN Writers in Prison Committee report and the other an address to the Congress—observed, and in a fashion related, to this theme:
[Written report:]

PEN Writers in Prison Committee Report, 1997
Tension between the individual and the state underlies the work of PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee. In some countries constitutions and governing principles are set out to protect the individual from the state, but in the majority of countries which PEN monitors where writers are imprisoned, threatened or killed, the state is organized to protect itself from the individual. Whether those countries be totalitarian regimes like China, Myanmar/Burma, Syria, Vietnam, Cuba or democracies like Turkey and South Korea, when the state holds itself superior to the rights of its individual citizens, freedom of expression is seen as a threat to stability rather than a sign of stability.
In 1997 the Writers in Prison Committee has defended individual writers in at least as many of the new and older democracies around the world as in totalitarian states. Since 1990 dozens of nations in Latin America, Africa, Europe, and Asia have restored or initiated multi-party democratic elections. The turn to the democratic process initially freed up restrictions on writers and journalists in many countries. However, after the first flush of these freedoms, after dozens of independent publications sprang up in Argentina, Belarus, Cambodia, Ethiopia, Russia, Sierra Leone, Zambia, etc., tensions mounted between the individual voice and the state. Restrictions and press laws followed, and writers once again found themselves facing prison terms on such charges as “insulting the President”, “writing derogatory statements against the government and government officials”, and “seditious libel.”
In some states like Sierra Leone harsh restrictions on the media preceded coups and the loss of democracy. Reporting restrictions and brief detentions of journalists enforced by the crumbling Mobutu government in Zaire (now Congo), did not serve to protect it from its eventual collapse. Earlier this year the political crackdown in Belarus was preceded by severe censorship and curtailment of publications. The collapse of the government in Albania was followed by severe restrictions on publications and attacks and death threats on journalists and writers.
When a coup occurs and democracy fails, the consequences for free expression are usually disastrous as has been seen in Nigeria where journalists continue to serve lengthy prison terms and are arbitrarily detained, sometimes for months without charge. Another instance of a threat to freedom of expression in Nigeria is that of PEN member and Nobel laureate Wole Soyinka who is among 12 dissidents charged in Nigeria this year with the capital offense of treason. Soyinka remains free outside the country but is certain to be imprisoned if he returns.
Pressure on writers and the media continued or increased in many new and old democracies, including Algeria, Argentina, Bosnia, Cameroon, Croatia, Ethiopia, Egypt, Indonesia, Kyrgystan, Mexico, the Palestinian authority, Turkey, Uganda and Zambia. Pressures took the form of legislation which required publications to obtain government licenses and approval and/or required journalists to have state-approved credentials. Pressure also took the form of arrest, arbitrary detention and death threats…
When democracy fails, there are hosts of reasons embedded in history and politics. Curtailment of free expression is not necessarily the precipitating cause, and curtailment of free expression does not always lead to failure of democracy. However, repression of the written word and of the writer remains at the very least a symptom and often a warning light that political failure lies ahead…
The report goes on to outline situations of individuals under threat. Reading these reports is reading a political history of the time, told through the circumstances of individual writers. One of the highlighted cases at the Congress in 1997 was that of Iranian writer Faraj Sarkohi who’d signed a petition calling for freedom of expression, along with 134 other Iranian writers. Sarkohi had been kidnapped by the Iranian secret service while on his way to visit family in Germany; he was tortured and threatened with execution. Because of the worldwide protests by PEN and others, he was eventually released the following year and sent into exile.
Visiting the WiPC meeting in Edinburgh, Egyptian professor Nasr Hamed Abu-Zeid, a leading liberal theologian on Islam, told his story of being declared an apostate for his research and forced to divorce his wife, also an academic. They had fled Egypt where apostates could be killed. Şanar Yurdatapan, the Turkish activist who’d organized the Gathering in Istanbul for Freedom of Expression which many of us attended earlier that spring, had just been released from prison and also spoke to the meeting. The cases of Sarkohi and Abu-Zeid and Şanar were among 700 on the WiPC records.
[Address to Assembly of Delegates:]
After four years chairing International PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee, I’ve come to appreciate the simplicity of the Committee’s mandate and the complexity of its execution. To defend the individual’s right to free expression is to defend not only the essence of literature but also a cornerstone of free society. Our defense begins with the individual writer, but inevitably we are caught in the movements of politics and history where individuals struggle to shape, divert or oppose the tides. One of the most significant developments in the past few years has been the expansion of multi-party democracies across the globe, a development that at first glance would signal progress for free expression. However, from our work we have seen that democracy takes more than a polling booth and a list of candidates on a ballot to come to fulfillment. Freedom of the written word is essential for a democracy to work over the long term, and attacks on this freedom usually foreshadow larger repression and even the failure of the democracy itself.
This year PEN has seen repressive laws enacted and/or writers arrested and killed in the new and old democracies of Albania, Algeria, Argentina, Belarus, Bosnia, Cambodia, Cameroon, Croatia, Ethiopia, Egypt, Indonesia, Kyrgyzstan, Mexico, Russia, Palestinian territory, Peru, Sierra Leone, South Korea, Turkey, Zambia. Many governments have passed or tried to pass laws to bring publications under their control through licensing and government-approved credentials. These laws have been followed by the arrest of writers.
Repression remains the most severe in totalitarian states such as China, Cuba, Iran, Myanmar (Burma), Nigeria, Syria, Vietnam. China continues to imprison more writers for longer periods of time—over 70 individuals, many serving 10-20 years—than any other country. Many of the writers who were imprisoned during Tiananmen Square have been released in the past two years, but others have taken their place. The Writers in Prison Committee is watching with great concern legislation which could lead to restrictions on writers in Hong Kong as China takes over. The Committee is also following closely the continued repression in Myanmar (Burma) where prison conditions remain harsh and at least 25 writers remain behind bars, many with sentences exceeding ten years…
Many of the cases in Africa this year came from new democracies struggling with issues of free expression, including Cameroon, Ethiopia, Uganda, and Zambia. The military dictatorship of Sani Abacha in Nigeria continued to occupy the focus of many PEN centres who worked on behalf of writers still in prison. Protests from a number of PEN centres assisted in the release of two Nigerian writers…Our Committee heard a statement from PEN main case Koigi wa Wamwere from Kenya, where riots have broken out after calls for democratic reform. Centres around the world have lobbied for his release, and he is now out on medical bail, and the Writers in Prison Committee has assisted his return to Norway where he is living. He sent a message thanking PEN for its work on his behalf. He writes, “When dictators arrest writers, they guard them with more guns and soldiers than they guard enemy armies in captivity. Dictators fear ideas and writers more than they fear guerrilla armies. Afterall they know that without ideas even guerrilla armies would wither away and die…”
In Latin America PEN continued to protest this year the imprisonment and detention of writers in Cuba. This spring the Writers in Prison Committee issued its report on its Cuba trip last fall, focusing on dissident writers who often had to choose between prison and exile…In Peru, though legislative and judicial reforms have occurred in the last years, at least 11 writers there have reported threats and/or attacks from both governmental and non-governmental sources, and sixty writers and journalists have reported death threats or attacks in Argentina…
The Writers in Prison Committee continues to work closely with freedom of expression organizations around the world, sharing our research and disseminating via the internet so that when a writer is arrested as far away as Tonga, the King of Tonga suddenly found himself receiving faxes from all over the world.
Over the years the political tides have shifted, but members’ work on behalf of individuals and the friendship of writer to writer remain even after the writers are released. This year we saw releases in Cameroon, China, Cote d’Ivoire, Cuba, Indonesia, Iran, Kenya, Kuwait, Maldives, Myanmar (Burma), Nigeria, Peru, and Russia. On occasions we have gotten to meet and know the individuals personally. This year when the Nigerian government picked up Ladi Olorunyomi, the Writers in Prison Committee was quickly alerted. A number of us had had the opportunity to meet with her husband Dapo, a prominent editor and dissident now living in exile in the United States. Isabelle Stockton, our Africa researcher and I spoke in the morning, and she called him to gather more details. When I phoned him later in the day, he said, “I was going to call you, but before I could, PEN was already calling me.” As soon as we determined that Ladi Olorunyomi had not been charged with a crime, had no access to lawyers and was not allowed to see her family, we put out a Rapid Action to our centres and shared the information with other freedom of expression organizations all around the globe. During her almost two months in captivity we were able to monitor the case, share information, and hear with great relief when this writer and mother was finally released.
Dapo, who had secretly fled Nigeria a year earlier lest he be imprisoned, wrote PEN, “Thank you for everything! I am very grateful, but I lack the words, appropriate enough to convey my gratitude…to our good friends at PEN International.”
The business of PEN throughout the year and at the annual Congress also included the work of the Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee, Women’s Committee, Peace Committee, the growing activity of the Exile Network and the literary sessions. The UNESCO seminars on Women’s Cultural Identity linked to the seminars on Literature and Democracy at the Guadalajara Congress the year before. In many parts of the world women still did not have full democratic rights. Significantly, in Latin America only 10% of books published were by women, and in Africa it was as few as 2%. But I must leave others to elaborate these activities.
At the 64th Congress results of the many elections yielded the next group of leaders who would take the organization into the last years of the 20th Century and into the transformation of governance. At the Congress Ronald Harwood was elected a Vice President as I had been at the previous Congress and as such we stayed connected and in the wings for the changes ahead.
Election results of the 64th PEN Congress:
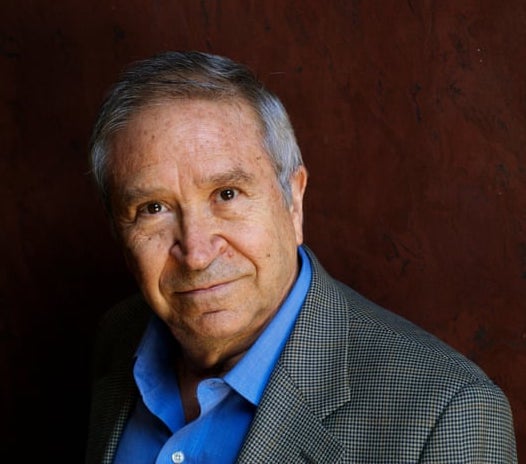

Homero Aridjis
Seven candidates stood for the presidency from Europe, Africa and the Americas though one dropped out. Homero Aridjis of Mexico, well-known poet, journalist and diplomat, was elected the next President of International PEN.

Moris Farhi
Novelist Moris Farhi, former chair of English PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee, was elected chair of the WiPC. The two runner-ups Louise Gareau-Des Bois (Quebec PEN) and Marian Botsford Fraser (PEN Canada) agreed to serve for a year as Vice Chairs. In 2009 Marian Botsford Fraser was elected chair of WiPC and served till 2015.
The new Ad Hoc Committee elected at the Congress included Marian Botsford Fraser (Canada), Takashi Moriyama (Japan), Boris Novak (Slovenia), Carles Torner (Catalonia), Jacob Gammelgaard (Denmark), Vincent Magombe (Africa Writers Abroad), Gloria Guardia (Colombia), Gordon McLauchlan (New Zealand) and Monika van Paemel (Belgium). This committee was charged with considering all the restructuring proposals and preparing a draft for discussion and adoption by the Assembly of /Delegates at the 1998 Helsinki Congress. The Ad Hoc Committee was also tasked as a Nominating Committee to search for a new International Secretary. Alexander Blokh, re-elected for another year as International Secretary, planned to step down at the 1998 Helsinki Congress. Little did I know nor aspire to take on that role six years later.
New PEN Centers voted in at the Edinburgh Congress included Cuban Writers in Exile, Somali-speaking Center, Sardinian PEN Center, and a reconstituted Mexican PEN Center.

PEN International’s Writer in Prison Centre to Centre newsletter, July, 1997
Next Installment: PEN Journey 21: Helsinki–PEN Reshapes Itself
PEN Journey 19: Prison, Police and Courts in Turkey: Initiative For Freedom of Expression
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.
We sat on the ferry drinking strong Turkish coffee then handing over the emptied cups to a woman who read fortunes from the pattern of the leftover coffee grounds. As we huddled in the wind off the Sea of Marmara en route to the prison in Bursa, we speculated who among the passengers was following us. We were assured we were being followed.

Program for Initiative for Freedom of Expression Gathering, March 1997
I came to Turkey in March 1997 as the returning Chair of PEN International’s Writers in Prison Committee (WIPC) (PEN Journey 18). I was heading a delegation of 20 PEN members from 12 countries. We’d arrived to support Turkish PEN, the Turkish Writers’ Syndicate, the Literary Writers Association and the Initiative for Freedom of Expression in the first Gathering in Istanbul for Freedom of Expression. We had signed on as “publishers” to an abridged version of the book Freedom of Expression. The original book included essays by those who were in prison or facing charges for their writing, particularly former president of Turkish PEN, the prominent novelist Yaşar Kemal. He was tried for an article he’d published in the German magazine Der Spiegel. (PEN Journey 17). Headlined “Campaign of lies,” the article called out the government for its human rights abuses, particularly its treatment of the Kurds.

Arthur Miller letter to Yaşar Kemal, March 1997
Bearing a letter from Arthur Miller, who knew Kemal and had himself come to Turkey with Harold Pinter in solidarity a dozen years before, I was among the 141 “foreign publishers” of the booklet Mini Freedom of Expression. This book contained a paragraph from each article published in the larger book. We joined the 1080 Turkish “editors” of the larger volume who included writers, theater actors, politicians, painters, cinema actors and directors, cartoonists, musicians, trade unionists, academics, lawyers, architects and others. The Turkish Penal Code made it a crime to re-publish an article that had been defined as a “crime” so that the publisher as well as the writer was charged.
The “publishers” had presented themselves before the State Security Court and faced charges of “seditious criminal activity.” After questioning the first 99 people, the prosecutor demanded the accused be tried under Article 8 of the Anti-Terror Law and Article 312 on “disseminating separatist propaganda.” After six months only 185 of these individuals had been questioned and brought to trial. If these individuals were given the usual 20-month jail sentence, that would mean ten popular television programs would have to be canceled because their stars or directors would be in prison; five series would have to find new stars and change their story lines. The media would lose over 30 well-known journalists; 15 popular columns would be left blank. Eight professorial chairs would be left vacant, and universities would require new teaching staff. Theater stages and film sets would require many other artists, directors, musicians, etc., and 20 new books about prison life would be added to literature if every author wrote.
Turkey already had over 200 writers either in prison or entangled in legal processes, more than any other country. This protest initiative was unique and creative. The challenge to the court was to bring charges against so many. The State Prosecutor had dropped charges against the foreign participants on the grounds that he wasn’t able to bring us to Istanbul for questioning though the Turkish citizens who had prepared and distributed the booklet could be tried. The organizer of the initiative Şanar Yurdatapan suggested we come to Istanbul and challenge the prosecutor. Though PEN members were willing to come to support their Turkish colleagues, no one wanted to end up in a Turkish prison.
“No one will go to prison,” Şanar assured. The prosecutor had to act within six months, and even in the unlikely event charges were brought, we’d go home before a trial, and there was no extradition from the US, UK and many other countries because no such “offense” existed under their laws. Unlike organizations such as Greenpeace, PEN was not a direct action organization. PEN dealt in words, protest letters, diplomacy, meetings, on occasion candlelight vigils outside embassies and stories in the media. But Şanar, who was a song writer, civic activist, not a PEN member, instinctively understood the dynamics of nonviolent direct action and understood how to get attention and make the point that the Turkish laws were unjust and unfairly administered.
On our first day, which was Women’s Day, we joined the Saturday Mothers’ rally of relatives of the disappeared who gathered every Saturday seeking information on their family members. The gathering had been held every Saturday for a year and a half at Galatasaray Square, ten minutes from our small hotel in Taksim. The crowd of mothers and children held pictures and signs of their loved ones, mostly Kurds, who had been taken away, assumedly by the government and likely killed. On the edges of the crowd police in riot gear gathered but didn’t interfere. Meeting at Galatasaray Square is now banned for Saturday Mothers by the Ministry of Interior since August 25, 2018. They still keep the rally at Human Rights Association branch in one of the back streets.
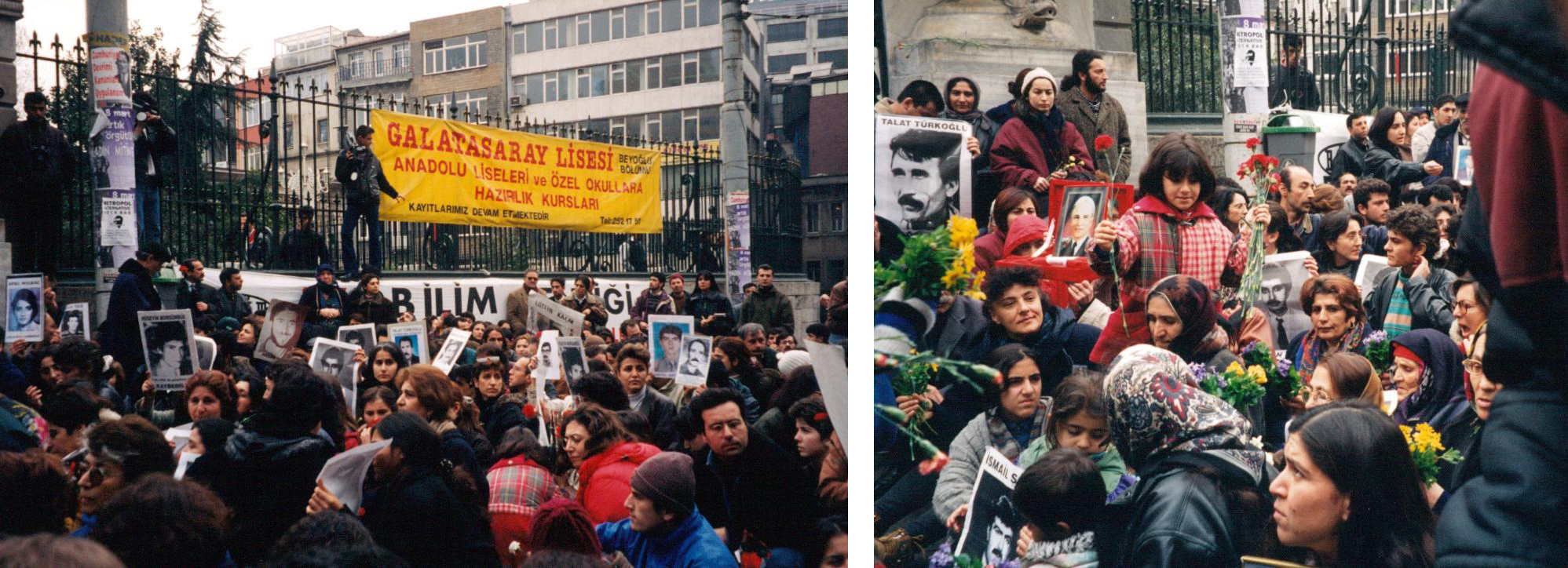

Saturday Mother’s Rally of relatives of the disappeared who gathered every Saturday seeking information on their family members.
From there a number of us went to a women’s rally where hundreds of Kurdish women in traditional dress marched with banners shouting, “We are mothers; we are for peace! Mafia is in Parliament; students are in prison.” Along the route men cheered and dozens of police lined the road frisking and checking bags. This was the last weekend of a 40-day protest all over Turkey. At 9pm every night people around the country turned out their lights or blinked their lights and shouted out their windows and in the street, “Go Away!” in protest over the government. The idea was that people would have one minute of darkness to get years of light. At dinner that Saturday evening we watched as the streets filled with shouting and the lights in restaurant blinked on and off.
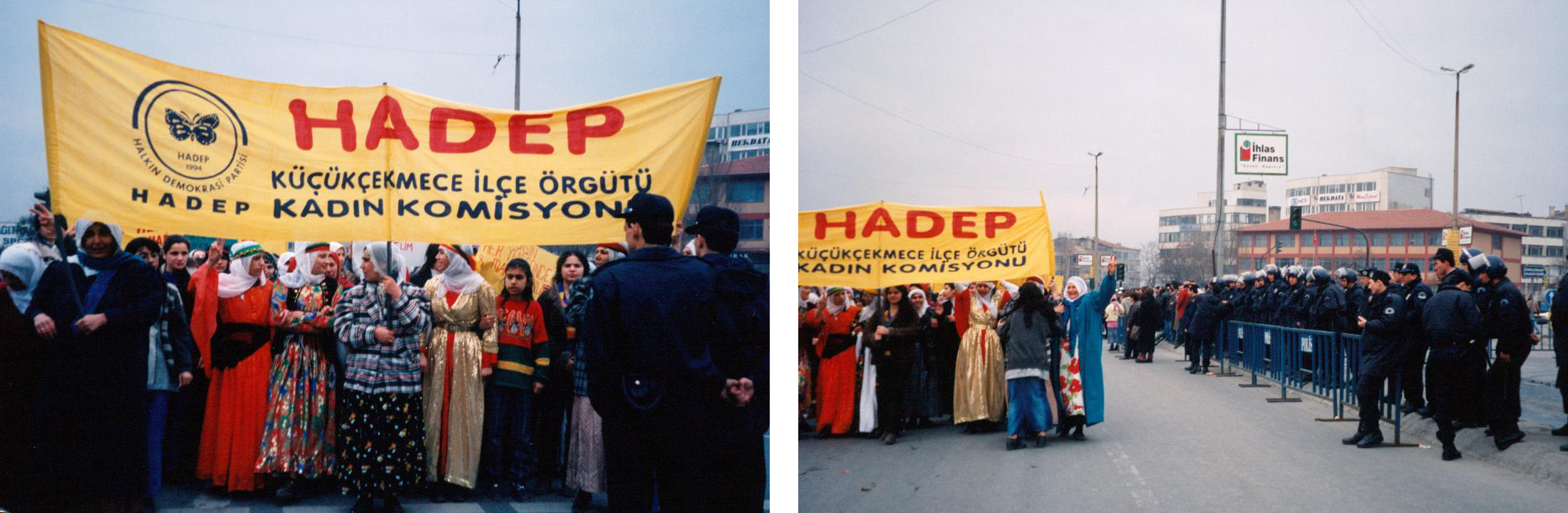

Women’s Day march of Kurdish women with police positioned along the route.
The trip to Istanbul was my first of what would turn out to be dozens of visits to Turkey over the years for PEN, for other organizations, and for family. In 1997 the times were tense; soldiers with their weapons and machine guns were stationed at the airport; armed police were on the streets; we were followed; the phones at the hotel were likely tapped. It was difficult to imagine then that it would get much better in the following decade as it did and then much worse in recent years. I’m not sure today we could hold such a gathering with confidence.
Throughout our visit we were covered by the press, including two visits to the State Security Court. In 1997 the legal way to meet publicly was to hold a press conference so we spent our days in press conferences, including one at the Journalists Association. Because I was Chair of the WiPC, I was often the one explaining why we were there. I emphasized that we had come out of respect for Turkish literature and writers. We had not come to break Turkish laws; we did not consider editing a book a crime. We were there to uphold the international covenants that Turkey had signed, approved and became a party to: the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (Article 19), Article 19 of the UN Convention on Civil and Political Rights and Article 90 in the European Convention on Human Rights. We noted that Article 90 in Turkey’s own Constitution declared that no law should supersede these international covenants.
Our PEN delegation included representatives from Canada (Quebec), Finland, Germany, Holland, Israel, Mexico, Palestine, Russia, Sweden, United Kingdom, United States and Turkey. The delegates included James Kelman, Booker Prize winner from Scotland and Turkish writers including Yaşar Kemal, Orhan Pamuk and others.
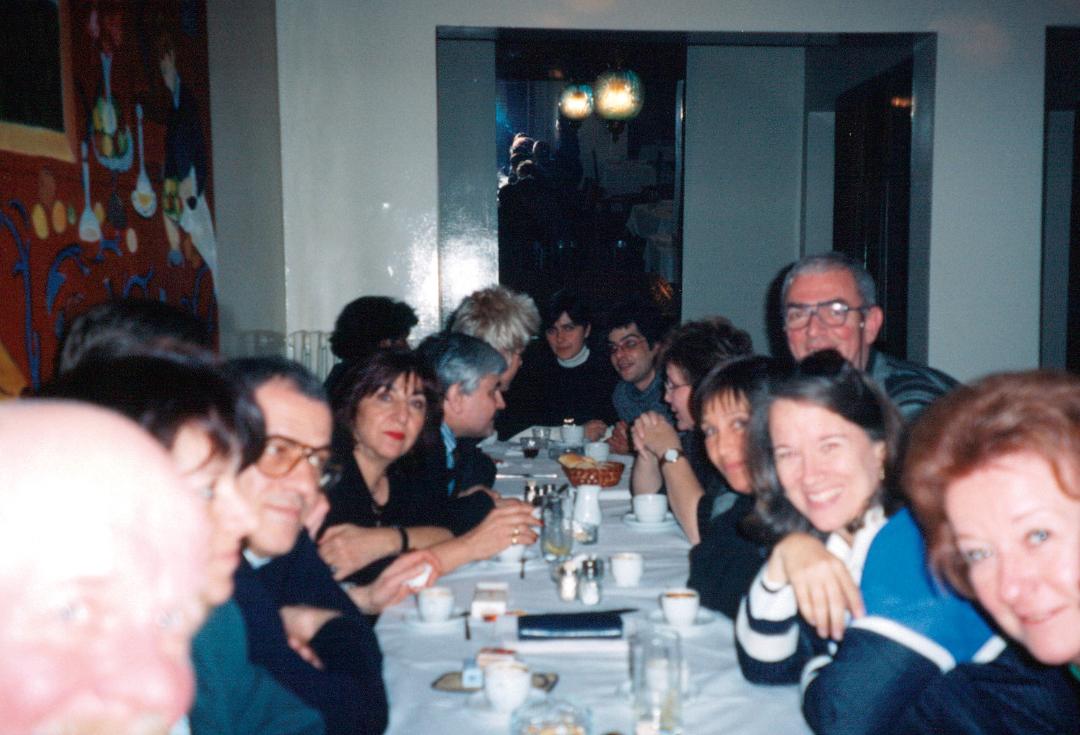

PEN members from 12 countries join Turkish colleagues for dinner at the first Gathering of the Initiative for Freedom of Expression in Istanbul, March 1997
On Monday we started the day at the State Security Court where Şanar petitioned the prosecutor for an appointment to question one delegate who had to leave early. Because the prosecutor didn’t want to bring charges against “international editors”, an act that would bring international attention, the “Turkish editors” could use this failure as further evidence of the unfair nature and application of the law when they took the case to the World Court. We approached the State Security Court again on Wednesday, when the prosecutor actually locked the gates and wouldn’t see any representative of our group. In the end nine of us—from USA, England, Scotland, Finland, Holland, Sweden, Canada (Quebec), Mexico and Russia—signed a form which said, “I accepted to be one of the collective publishers of this book willingly and I am aware of the legal responsibility. I have nothing else to say.” These forms were then sent registered mail to the prosecutor.
Two small groups visited prisons and the prisoners of conscience, including Dr. İsmail Beşikçi and his publisher Ünsal Öztürk in Bursa and journalist Işık Yurtçu in Adapazarı prison. Louise Gareau-Des Bois from Quebec PEN went to the Adapazari prison and was able to visit with Işık Yurtçu.
Kalevi Haikara from Finland and I went with Şanar on the ferry to the prison in Bursa where we met Ünsal Öztürk’s wife Süreyya. We waited and waited and talked together in the bleak courtyard with grey concrete walls rising around us topped with barbed wire, with guard towers looming over us. We went to the pink concrete building of Bursa Prison with a shield on the door “Ministry of Justice Bursa Special Prison” and waited there too. But we were not allowed to see İsmail Beşikçi, the noted Turkish sociologist and philosopher who wrote about the Kurds history and living conditions. He was one of the few non-Kurdish writers in Turkey speaking out about the treatment of the Kurds. At the time he was also one of the longest serving prisoners. He’d been sentenced to over 100 years though he was released from jail two years after our visit. Of his 36 books, 32 were banned in Turkey.
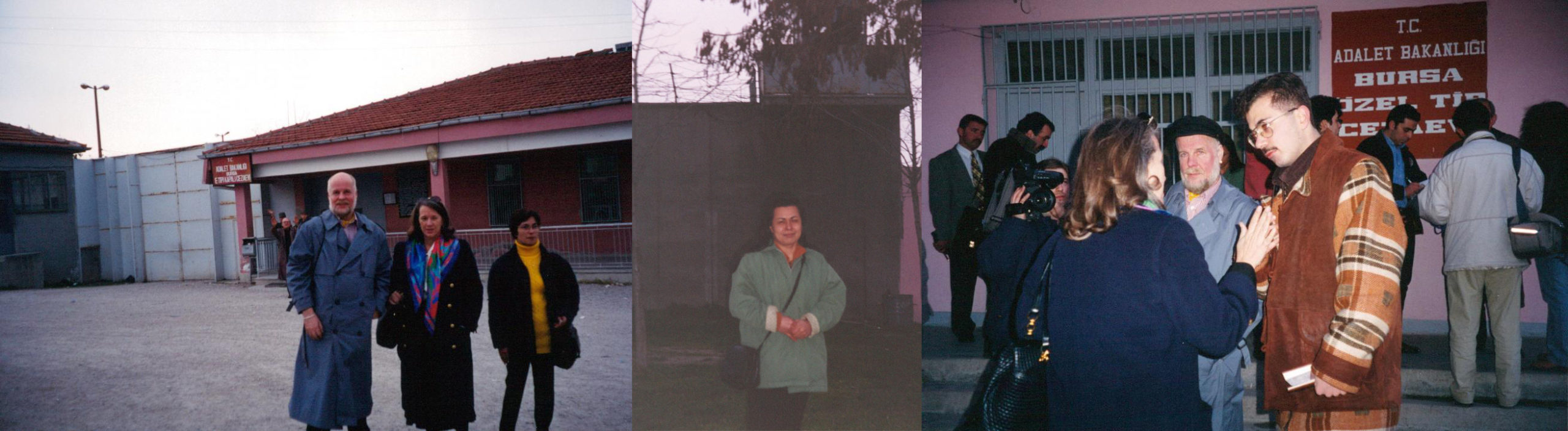

Kalevi Haikara from Finish PEN and Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, WiPC Chair and member American PEN outside prison in Bursa, along with Süreyya, wife of prisoner Ünsal Öztürk (middle picture) and in conversation at Bursa Prison (far right picture.)
We were also not allowed to see Ünsal Öztürk, Beşikçi’s publisher, who had completed more than a three-year sentence. We met with the press which had gathered. We paid the outstanding fine against Öztürk with funds raised from Turkish writers, artists and many of the visiting PEN members. Öztürk was released the following day though there remained 30 outstanding cases against him, 62 charges waiting to be brought to court, all relating to Beşikçi. Every time he published a book, a charge was brought, but he kept publishing. Öztürk and his wife joined the conference.
The following day we attended the Justice House hearing of the “Kafka Trial.” When one editor of the Freedom of Expression book—actor Mahir Günşiray—faced the judges, he’d read a paragraph from Kafka’s The Trial. The paragraph offended the judges, and they brought a civil suit against him. Sixty-five other writers and artists signed on and said they also endorsed the reading of Kafka and should thus be guilty too. We all piled into the small room where the defendant Mahir Günşiray and his lawyer and the judge met. The hearing was the second or third for him, but with the room full of observers, the judge again postponed the proceedings.
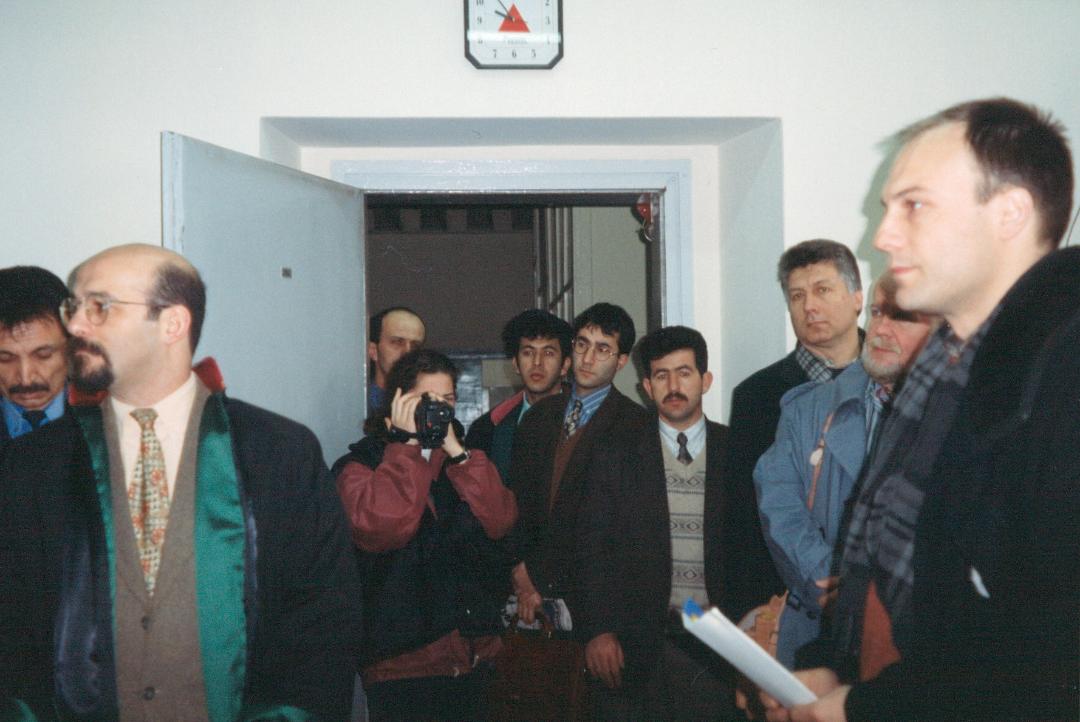

At hearing of “Kafka Trial” in the Justice House
Many of us went next to Istanbul University to participate in a Forum on Freedom of Expression. However when we arrived, hundreds of students were protesting in the plaza, surrounded by riot police with shields. The situation was tense. In Ankara students had recently been arrested after they’d unfurled a banner in Parliament challenging the 300% tuition increase at state universities. The student protesters there were tried with the demand of 18-year prison sentences. The students at Istanbul University asked if we would speak at the rally. None of us were prepared for this potentially explosive scene. The writers who’d come to speak on freedom of expression asked me to talk for the group, all except Sascha from Russian PEN who also wanted to speak. Sascha, Şanar and I addressed the crowd. I emphasized that we were there to uphold the right for free expression, not to take a side with any particular party of government or to take sides on how education was financed in Turkey, but to insist that individuals should have the right to discuss, debate and write about these issues without facing prison terms. We urged that the protest stay nonviolent. We were then ushered out through the police corridor.
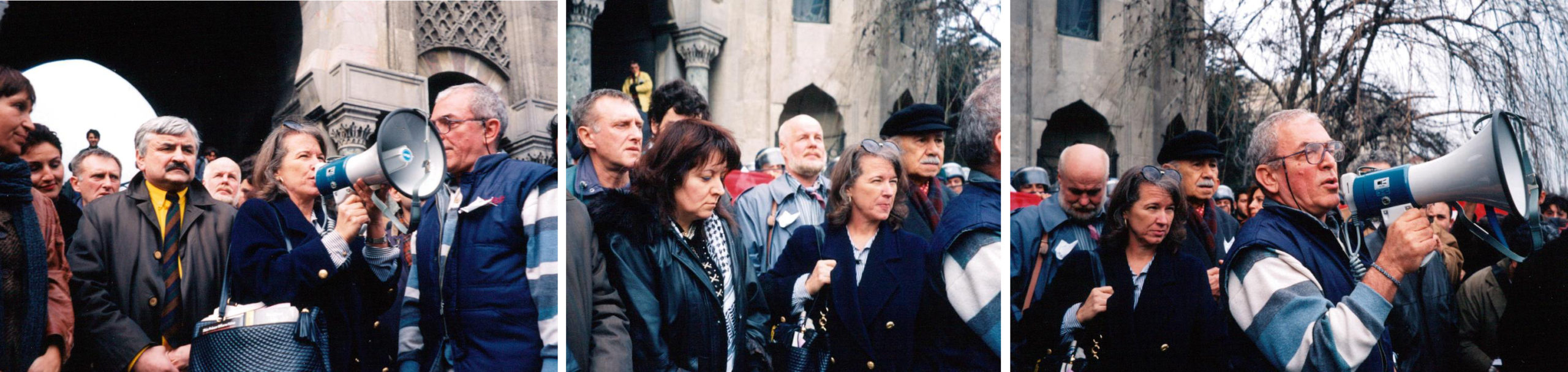

Rally at Istanbul University (Includes Soledad Santiago (San Miguel Allende PEN), James Kelman (Scottish PEN), Alexander (Sascha) Tkachenko (Russian PEN), Kalevi Haikara (Finish PEN), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, (WiPC Chair/American PEN), Hanan Awwad (Palestinian PEN), Turkish writer Vedat Türkali, and Şanar Yurdatapan (with bullhorn).
In the evening the Istanbul Bar Association hosted us. The head of the Bar noted that the Turkish Constitution protects the state against the individual rather than the other way around as in the US. Everyone agreed there was free expression in many quarters of Turkey, but that the danger arose when one addressed Kurdish issues and Kurdish separatism and referred to the PKK.
Attending the meeting was the former PEN main case Eşber Yağmurdereli, a blind poet/dramatist, who’d served 14 years in prison. Released August 1991, he’d spoken in September 1991 at a meeting on behalf of Kurdish prisoners and had new charges brought against him. After five years he was still awaiting the resolution of that case. His passport had been taken from him. He could be sent back to prison for more than 20 years. He said he was unable to write, and if he wrote, he had to hide the writing and not publish. He earned his living now as a lawyer.
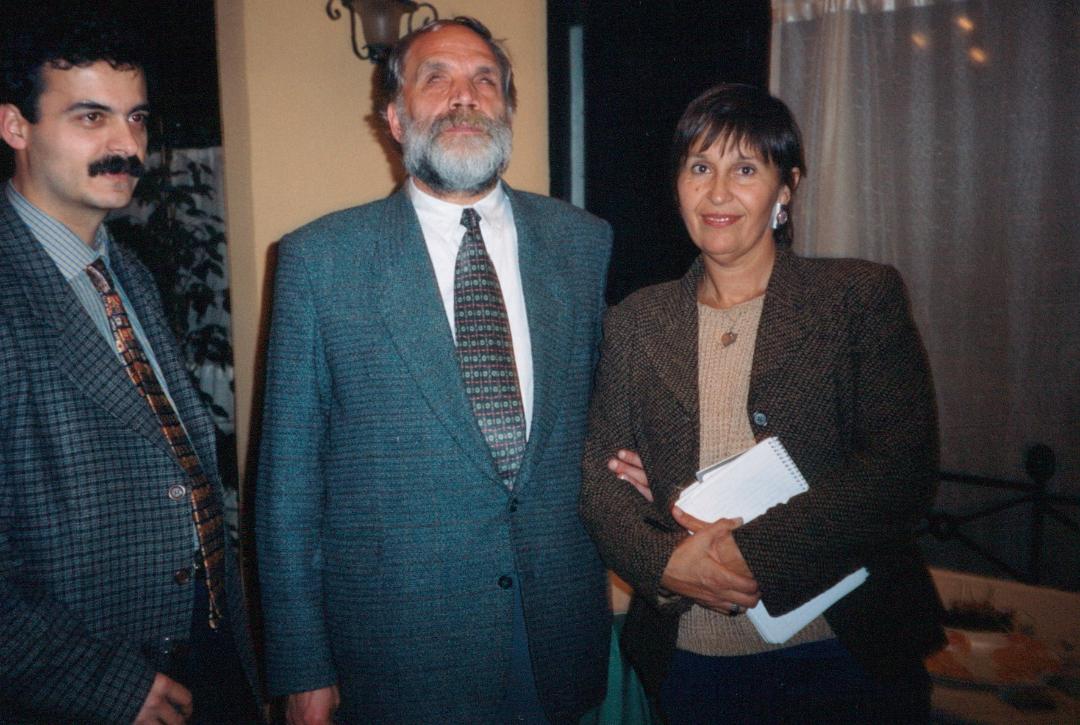

Meeting with Istanbul Bar Association. Eşber Yağmurdereli (middle) and Soledad Santiago (San Miguel Allende PEN) on right.
I also met the young brother of Bülent Balta, an investigation case. Balta, a chemistry honors graduate, a Turk, not a Kurd, had agreed to edit Özgür Gündem, the Kurdish newspaper, because of his sympathies for the difficulty of the Kurds. He had no particular experience as an editor, and after only 11 days was arrested and was serving a four-year prison sentence.
That evening the protest at Istanbul University was all over the news, including pictures of me with a bull horn speaking, but my words had been translated into Turkish so I had no clear idea what it was reported I was saying.
Early the next morning I slipped out of our hotel and walked to a large international hotel nearby where I called home. I asked my husband to confirm my return flight the following day. He asked what the flight was, but I told him to check with the travel agent and confirm. Over the phone I didn’t want to give flight details. I told him what was happening, including the widespread coverage of the protest with my participation, and he told me a colleague in Washington said that the American Embassy knew I was there and warned me not to leave the hotel. I had to leave the hotel, I explained. I was leading the delegation and events were planned, including a farewell dinner on the Bosphorus.
At the final panel/press conference, I noted that I had two sons, and as I observed the young people here, especially the young police officers and the young students, I felt sorrow that these youth were set across battle lines from each other. There was so much talent and promise we had seen. For the first time in the three days of speeches and press conferences, emotion stirred in my voice and I paused for a moment. One of the headlines the following day read something to the effect: “She Cries for Turkey!”
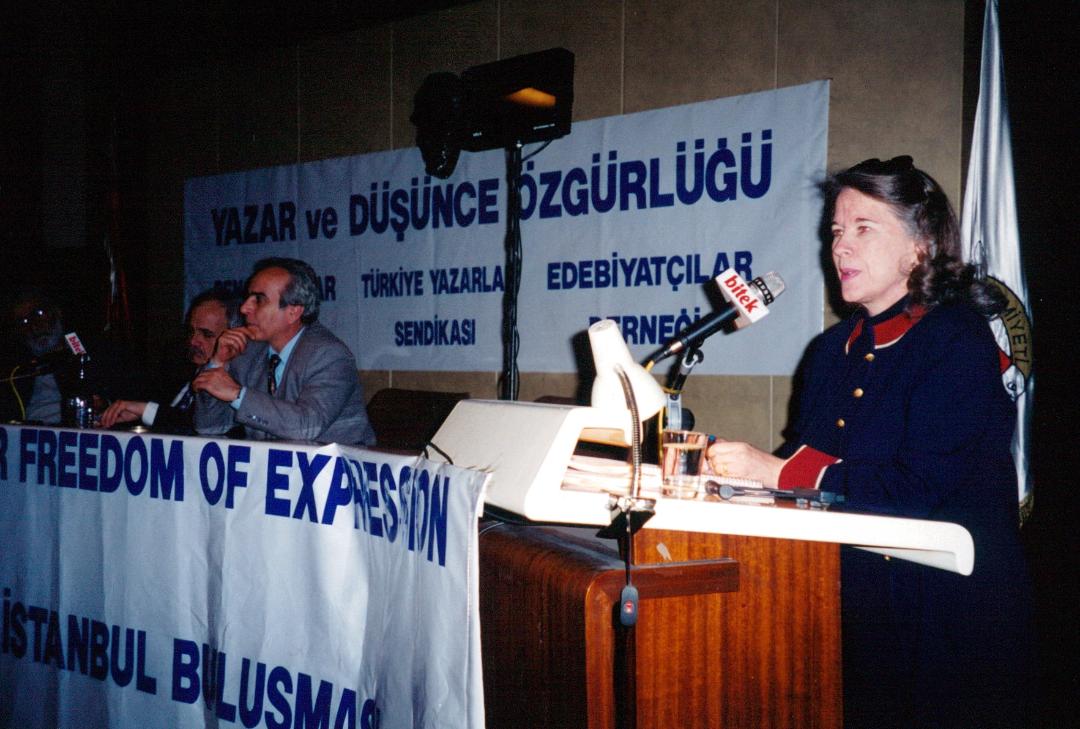

Panel at Initiative for Freedom of Expression Conference, Istanbul March, 1997
The following morning I was to be driven to the airport, but the driver didn’t show up, and I was left to find my own transportation in a taxi. The atmosphere around the conference had slowly made each of us cautious, even slightly paranoid. As I climbed into the taxi, driven by a stranger, I remembered the fortune teller on the ferry a few days before. Proceed with caution…was that her warning? You will make friends…was that the prediction? The road ahead is fortuitous but also fraught? In fact, I no longer remembered what her fortunes were, and I didn’t believe in fortunes or scattered coffee grounds, but I left Istanbul with a strong belief in the people and a commitment to the country and to the writers and publishers and lawyers and journalists and to the young people I had met and to the promise they represented.
In years following I returned to Turkey on numerous missions for PEN and for meetings with Human Rights Watch, with the International Crisis Group, on a trip with UNHCR looking at the Syrian refugee crisis, and several trips with my oldest son who wrestled in the World Championships and European Championships in Ankara and in the World Championships again in Istanbul and also lectured in mathematics at Koc University and other universities and with my youngest son who lived in Istanbul for two years with his two young children and wrote as a journalist on the Turkish/Syrian border and has set two of his four published novels in Turkey.


PEN International Writers in Prison Committee Centre to Centre newsletter special Turkey section April 1997
Next Installment: PEN Journey 20: Edinburgh—PEN on the Move, Changes Ahead
PEN Journey 12: Tolerance on the Horizon?
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey might be of interest.
It was a time of hope, the year when Nelson Mandela and Frederik de Klerk joined in free elections in South Africa, when Yasser Arafat, Yitzhak Rabin and Shimon Peres shook hands and began to live side by side, when the Irish Republican Army and the Ulster Defense Association laid down their arms after twenty-five years of terrorist conflict. The idea of tolerance quivered in the imagination in 1994 even if the realization of tolerant societies still seemed an imaginative leap.

As theme of the 61st PEN Congress, tolerance also challenged the ethnic, national and religious intolerance that gripped dozens of countries in the last decade of the twentieth century. In retrospect the time was perhaps not so different from times since, but we felt we were standing on an historic threshold. The PEN Congress theme of tolerance expressed this hope and optimism.

Liechtenstein Palace, garden view
Writers from over 75 PEN centers* around the world came together in Prague that fall for literary and working sessions. The Congress was a grand affair with public gatherings in stately ballrooms, including the Liechtenstein Palace, home of the Prague Academy of Music. Writers who had been imprisoned under the old Soviet regime, including Václav Havel, now ran the country.
Guests of honor included novelist and poet Taslima Nasrin, whom PEN had recently helped extract from the threat of death in Bangladesh (see PEN Journey 11). For protection she was driven around in a state car, and because Sara Whyatt, coordinator of the PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC), and I agreed to look after her, we at times found ourselves whisked from meeting to meeting with a police escort, not the usual transport at a PEN Congress.
Though PEN had no mechanisms to change societies, to the extent society changed individual by individual, PEN worked for the writer, turning a spotlight on cases of abuse and challenging the laws which legitimized intolerance.
The voice of the individual writer has always been the most compelling testimony. My report to the Assembly of Delegates that year as Chair of the Writers in Prison Committee focused on those voices:
“Yes, I can hear birds singing. But they are not my friends. They are too far from me. My best friends are spiders and mantis. They are only living things to watch amusedly in my solitary cell. I live and play with them all day long. This excerpt is from a prisoner ten years into a twenty-year sentence written to his PEN minder.
“The image of the spider recurs in the writings of prisoners. One former prisoner I met shortly after taking over as Chair of this committee had come to London to receive treatment for the torture he’d endured. He told of being handcuffed to a generator outside during monsoon season, of not being allowed to wash, using a bucket as a toilet, his arms and hands wrapped around the generator for weeks. Then he talked about being inside in solitary confinement. ‘I had a chance to observe nature: rats, cockroaches, spiders,’ he recalled. ‘Ah, spiders, they are brilliant!’
“Cuban writer Yndamiro Restano, who was arrested in 1991 and sentenced to ten years in prison for preparing and distributing counter-revolutionary propaganda, has written a poem entitled Prison:
Mother,
Do you know where your poet is?
Well, they have dragged me into a dark,
Narrow, lonely cell,
And do you know why,
Mother?
For not allowing fear to carry me away.
But I am not completely alone,
Mother.
I have got to know a good friend here.
A small spider visits me every day
And spins in the door of my cell.
When the guard comes,
I let it know so it hides away.
And doesn’t get killed.
I want it to live,
Mother,
Because I know that it has inside it
Something that I also possess.
However,
It seems that the guard does not know this.
Mother,
Do you know where your poet is?
Well, they have dragged me to a cold,
Narrow, lonely cell.
And do you know why,
Mother?
Because the poet is the only person
Who never forgets
The meaning of freedom.
“The quality the spider has inside so like the writer is the ability to survive, to weave and to work wherever it is. The more difficult the circumstances, the more ingenious the web it weaves. Scientists are in fact currently studying the unique structure of the spider’s silk which gives it the tensile strength of a steel fiber, yet allows it to stretch and rebound from at least ten times its original length, something no metal or synthetic fiber can do.
“The writer’s silk, his tensile yet flexible fiber, is his imagination. It is the imagination and the life of the mind that allows the writers for whom the Writers in Prison Committee works to survive what are sometimes quite desperate physical conditions. One quality that gives the imagination its greatest flexibility and strength is tolerance, the theme of this Congress. It also is that quality and the ability to imagine and empathize with another’s life that prompts those not in prison or under attack to work on behalf of their fellow writers.
“The work of PEN members and Centers in 1994 has been inspiring even if the situation for the writers has been very difficult in many areas of the world. This past year has witnessed some remarkable moves towards tolerance: in South Africa with the first free elections, in Israel and the West Bank with the Israeli-Palestinian peace accord. The WiPC case load has declined with release of political prisoners in these areas, but writers remain in the line of fire and are still targets of those who are trying to disrupt the peace process.
“The past year over 120 writers have been released from prison. Unfortunately many times that number have been arrested, threatened and killed.
“Religion, ethnic and nationalistic tolerance has led to attacks and detention of writers in every area of the world. Religious intolerance of one kind or another continues to undermine intellectual freedom in Iran, Iraq, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Mauritius, Sudan, Egypt, Vietnam and Algeria.
“Often religion is used to justify political interests. No place has the confrontation between “religious” and state power been more devastating than in Algeria, where over 25 writers and journalists have been killed and dozens detained in the past two years.
“Ethnic, national and religious intolerance often merge as in the former Yugoslavia and other areas of the Balkans.
“The most brutal outbreak of ethnic intolerance globally this year has been in Rwanda, where over 37 writers and journalists have been killed, most targeted for their ethnic, and thus political background.
“Ethnic conflict, which is also political conflict, currently stirs in Nigeria where Ken Saro Wiwa, advocate for the Ogoni people, is in jail and reportedly tortured and in Kenya where Koigi wa Wamwere exposed “ethnic cleansing” in the Rift Valley and has been detained on charges which carry the death penalty.
“The most difficult country with the largest number of Writers in Prison Committee cases continues to be Turkey where those discussing and debating the Kurdish situation in the Southeast are charged with “disseminating separatist propaganda” under Article 8 of the Anti-Terror Law and are imprisoned. Killings and torture are reported by both sides of this conflict. PEN records over 250 cases in Turkey.
“The other country which continues to lead our list with the most main cases is China where over 45 writers, a third of these in Tibet, are imprisoned. Though China has released some prominent dissidents this year, the Chinese authorities have also arrested at least twice as many writers as they have released…”

From PEN’s Centre to Centre newsletter October/November, 1994.
The Chair’s report for 1994 notes progress but also shows how little has changed for writers in the past 25 years in many areas of the world such as Turkey and China though there has been progress in Algeria, Rwanda, the Balkans, Nigeria and Kenya. The Day of the Imprisoned Writer campaign in November, 1994, noted in the newsletter above, focused on five writers. Of these Ma Thida was released and eventually started a Myanmar/Burma PEN Center and now serves on the PEN International Board; Koigi wa Wamwere was released and is a celebrated Kenyan writer. Gunay Aslan and Gustavo Garzon, also released, continue to create. Ali-Akbar Sa’idi Sirjani died in Iranian prison under mysterious circumstances in November 25, 1994.
With attention and advocacy, circumstances improve for individual writers, but many writers who are released have to go into exile. At the Prague Congress PEN began to expand its thinking and resources to develop services for exiled writers. (Future blog post.)
A highlight of the 61st Congress was the address by Czech President Václav Havel, fellow writer and playwright whose first play “Garden Party” lampooned the communist system in 1963. In 1969 he was barred from his job as a writer/editor after the suppression of the Prague Spring reforms in 1968, and he was forced to work as a manual laborer. In 1977 he became the spokesman for the Charter 77 dissident group that criticized the communist officials and was given a suspended sentence of 14 months. After publishing in 1978 “Power of the Powerless” which was an analysis of how a totalitarian regime kept power by corrupting and manipulating citizens, he was sentenced to four and a half years in prison for “subversion” against the state. During this time PEN worked actively on his case, pressuring diplomats around the world. Havel was released after three and a half years but then imprisoned again after meeting dissidents and the French President in Prague in 1989. Havel was sentenced to nine months, but widespread protests from home and abroad, many generated by PEN, brought his release in May. In November, 1989 the communist regime fell. In December 1989 Václav Havel was elected President of Czechoslovakia, which eventually split. At the time of the PEN Congress he was in his first year as President of the newly independent Czech Republic.

Left to right: Jiří Stránský, President Czech PEN, and Czech President Václav Havel
Abridged speech of Václav Havel to the Opening of the 61st PEN Congress in Prague November 7, 1994:
“Several times in my life I have had the honour of being invited to a world congress of the International PEN Club. But the regime always made it impossible for me to attend. I had to live to the age of fifty-eight, go through a revolution in my country, become the nation’s president, and see the World Congress held in Prague, to be able to participate in this important event for the first time in my life. I am sure you will understand therefore, that this is a very moving moment for me.
“Yes, we live in a remarkable time. It is not just that we now learn, almost instantaneously, about all the deeply shocking atrocities that take place in the world; it is also a time when every local conflict has the potential to divide the international community and become the catalyst for a far wider conflict, one that in many cases is even global. Who among us, for instance, can tell where the present war in Bosnia and Herzegovina may lead, to what tragic confrontation of three spheres of civilization, if the democratic world remains as indifferent to that conflict as it has so far?
“I think that in these matters, writers and intellectuals can and must play a role that only they can fill. They are people whose profession, indeed, whose very vocation is to perceive far more profoundly than others the general context of things, to feel a general sense of responsibility for the world, and to articulate publicly this inner experience.
“To achieve this, they have essentially two instruments available to them.
“The first is the very substance of their work—that is, literature, or simply writing. Deep analysis of the tangled roots of intolerance in our individual and collective unconsciousness and consciousness, a merciless examination of all the frustrations of loneliness, personal inadequacies and the loss of metaphysical certainties that is one of the sources of human aggression—quite simply, a sharp light thrown on the misery of the contemporary human soul—this is, I think, the most important thing writers can do. In any case, there is nothing new in this: they have always done that, and there is no reason why they should not go on doing so…
“But there is another instrument, an instrument that intellectuals sometimes avail themselves of here and there, though not nearly often enough in my opinion. This other instrument is the public activity of intellectuals as citizens, when they engage in politics in the broadest sense of the word. Let us admit that most of us writers feel an essential aversion to politics. We see entering politics as a betrayal of our independence, and we reject it on the grounds that the job of the writer is simply to write. By taking such a position, however, we accept the perverted principle of specialization, according to which some are paid to write about the horrors of the world and human responsibility, and others to deal with those horrors and bear the human responsibility for them. It is the principle of a rather doubtful division of labour: some are here to understand the world and morality, without having to intervene in that world and turn morality into action; others are here to intervene in the world and behave morally without being bound in any way to understand any of it…
“In short, I am convinced that the world of today with so many threats to its civilization and so little capacity to deal with them, is crying out for people who have understood something of that world and know what to do about it to play far more vigorous role in politics. I felt this when I was an independent writer, and my time in politics has only confirmed the rightness of that feeling, because it has showed me how little there is in world politics of the mind-set that makes it possible to look further than the borders of one’s own electoral district and its monetary moods, or beyond the next election.
“I am not suggesting, dear colleagues, that you all become presidents in your own countries, or that each of you go out and start a political party. It would, however, be wonderful if you were to do something else, something less conspicuous, but perhaps more important: that is, if you would gradually begin to create something like a world-wide lobby, a special brotherhood or, if I may use the word, a somewhat conspiratorial mafia whose aim is not just to write marvelous books or occasional manifests, but to have an impact on politics and its human perceptions in a spirit of solidarity, and in a coordinated, deliberate way…”
“Let me conclude with one final plea: do not fail to raise your common voice in defence of our colleague and friend Salman Rushdie, who is still the target of a lethal arrow, and in defence of Nobel Laureate Wole Soyinka, who is unable to join us here because his government prevented him from coming. I also beg you to express our common solidarity with all Bosnian intellectuals who have been waging a courageous and unequal struggle on the cultural front with the criminal fanaticism of the ethnic cleansers, those living examples of the lengths to which human intolerance can eventually go.”
Next Installment: PEN Journey 13: PEN and the U.N in a Changing World
*Delegates representing 73 PEN Centers attended the 61st Congress, along with observers from three proposed new centers—Malawi, Guadalajara and Iranian Exiles Abroad. All three were elected as new PEN centers at the Congress, along with new centers in Ghana and Kyrgyzstan and a revived Egyptian PEN center.
PEN Journey 10: WiPC: Beware of Principles
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey might be of interest.
In the summer of 1993 before taking over the Chair of PEN International’s Writers in Prison Committee I studied hundreds of individual cases on PEN’s list of over 900 cases which was published twice a year. I studied the regions of the world where conflict was rife, where governments were most oppressive and where writers were most threatened. I also used the time to conceive three long term projects because I knew when the job began, there would be less time for long term thinking.
First, I hoped we could gather the many poems and stories from imprisoned writers over the years and get these published into a book. In studying the cases, I came to understand that those who survived harrowing experiences were often those able to keep their imaginations alive and if possible were able to write. “We lived in Paris in our minds,” one prisoner in dire conditions inside the Western Sahara recounted. A book of these writings would celebrate and inspire and could also be used by PEN centers in their work.
Second, I wanted to convene the Writers in Prison Committees from around the world in a conference to strategize our work. PEN’s other standing committees had such meetings outside of the congresses, but WiPC never had. The PEN congresses were often filled with competing programs and those working on WiPC issues were not always the delegates. We needed to gather and plan together for several days.
Finally, I hoped to expand the roster of Writers in Prison Committees in the PEN Centers so that we could increase the number of members working and the number of writers on whose behalf we worked.
WiPC Coordinator Sara Whyatt and researcher Mandy Garner and I agreed on each of these goals. Every two weeks we met in the large airy WiPC office at the top of the Charterhouse Buildings in London or often at the tea shop across the alley. At the end of our strategy sessions we would discuss how to move forward the longer range goals. I learned an important lesson—first, a goal begins with an idea then is realized by having talented, committed people around. For me that began with Sara and Mandy, who set steps in motion. And then each project found a path forward as people arrived into our circle to help accomplish the tasks.
One day a publisher showed up in our office and asked if we had ever considered doing a book of prisoners’ writings. As a matter of fact…We quickly outlined our idea, put together a team with former WiPC coordinator Siobhan Dowd as editor, and a year and a half later in 1996 This Prison Where I Live was on book stands with selections from more than 65 writers who had been imprisoned, many of whose cases PEN had worked on, from Arthur Koestler to Cesar Vallejo, Alexander Solzhenitsyn, Jacobo Timerman, Breyten Breytenbach, Pramoedya Ananta Toer, Primo Levi, Wole Soyinka, Vaclav Havel, Ngugi wa Thiong’o, Nazim Hikmet, Ken Saro-Wiwa, and many others, current and former writers in prison.

From This Prison Where I Live:
You took away all the oceans and all the room.
You gave me my shoe-size with bars around it.
Where did it get you? Nowhere.
You left me my lips, and they shape words, even in silence.
—Osip Mandelstam, former USSR, 1935
When we shared our second hope for a global gathering, Danish PEN offered to host the conference in Helsingor, the home of Hamlet. With representatives of PEN centers on every continent, this first WiPC conference convened in the spring of 1996. The WiPC gathering has been held biennially ever since at locations around the world. (More on this conference in a later post.)
Regarding the third goal, the number of PEN centers with Writers in Prison Committees has grown each year because of PEN members around the globe. Unfortunately, the number of cases of writers threatened, imprisoned or killed has also continued to grow, but individual cases are released.

In that summer preparing to take over the Chair, my predecessor and mentor Thomas von Vegesack gave me advice I found puzzling at first. He invoked: “Beware of principles!” Thomas was an empathetic and principled man so I was perplexed by his counsel, but over the years I’ve come to understand what he meant. He meant that declarations and statements can often keep you from seeing a way forward and from understanding how to work on a case if you get tangled in abstractions.
There are of course principles that govern our work enshrined in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. These are fundamental, but Thomas was warning that it is important to understand each situation and not let rigidity, a kind of authoritarianism of principles or political correctness limit.
PEN’s Charter itself contains contradictory concepts. The Charter asserts that PEN members should “use what influence they have in favour of good understanding and mutual respect between nations and people; they pledge themselves to do their utmost to dispel all hatreds and to champion the ideal of one humanity living in peace and equality in one world.”
At the same time the Charter notes that “PEN stands for the principle of unhampered transmission of thought within each nation and between all nations, and members pledge themselves to oppose any form of suppression of freedom of expression in the country and community to which they belong…”
These two ideas of respect and freedom of expression have been challenged more than once, a decade ago in the case of the Danish cartoons. (More on this in a future post.)
Ultimately each PEN member has to resolve the inherent tension. Those from societies with longer democratic traditions are more accustomed to balancing competing ideas; but there are no certain answers. PEN has had lengthy discussions and debates on such questions as “hate speech”—what constitutes it, are there limits to freedom of expression—on slander and libel, holocaust denial, blasphemy.
These challenges for PEN are manifested in individual cases. Early in my tenure as Writers in Prison Chair, one such case blew up quickly, gathering headlines across the globe—the case of Bangladeshi writer Taslima Nasrin. Dr. Nasrin (she was a medical doctor turned writer) had written a novel Lajja (Shame) which described the Muslim backlash against Bangladesh’s Hindu minority after the destruction of a mosque. She was also quoted (misquoted, she said) suggesting that the Koran should be revised in favor of women. An arrest warrant was issued for her; demonstrators called for her death, and at one point snake charmers in Dhaka threatened to release their cobras into the streets if she wasn’t executed. PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee and PEN’s Women’s Committee took up the case, which had bizarre twists along the way.
Next Installment: PEN Journey 11: Death and Its Threat: The Ultimate Censor
PEN Journey 8: Thresholds of Change…Passing the Torch
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey might be of interest.
In fall, 1991 I went to Moscow just months after the August coup attempt in which hardline Communists sought to take control from President Mikhail Gorbachev. I hopped onto the visa of my husband who was traveling to Russia as a Visiting Scholar at the International Institute of Strategic Studies in London. I went as a writer, interested in meeting other writers. I contacted fellow PEN member and Russian translator Michael Scammell, who had previously chaired International PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC). Michael gave me a list of writers to contact in Moscow.

Statues toppled of Lenin and Stalin and others in park after failed coup attempt in Moscow, 1991.
My husband and I stayed in what I was told was one of the government hotels where guests were hosted but also watched. We were watched too, I’m fairly certain, though there was little for anyone to see with me. I was cautious as I made contact with the writers lest my reaching out compromise them. Only a few years before, PEN’s case list had included many dissident Soviet writers in prison. Michael and later WiPC Chair Thomas von Vegesack and PEN’s WiPC committees around the world had advocated for the release of dissident Soviet writers, many of whom were imprisoned in the gulags. PEN had also covertly sent aid to them and their families through the channels of the PEN Emergency Fund.
I no longer remember if I called or faxed the writers in advance. (Fall, 1991 was before an active internet.) I likely made contact when I arrived. The writers welcomed me. We met in simple apartments with old holiday cards on the mantles as decorations, a paper mobile hanging from the light fixture over one dining room table I recall, strips of newspaper stacked by the toilets in lieu of tissue. The economy was spare for these writers. They hoped for change and for freedoms to come, but they were cautious. In these meetings and in other random encounters, people were curious about the United States. On the street, vendors not only sold Russian nesting dolls with the rushed visages of Boris Yeltsin, who had defied the tanks of the coup, and of Gorbachev but also stacking dolls of U.S. presidents, including one set that had George Washington and Abraham Lincoln. I was asked by numbers of people, including the writers, if I could get them copies of the U.S. Constitution and the Federalist papers. The Berlin Wall had fallen and times were changing, but no one knew how that change would settle out in the Soviet Union.

Stall of street vendor selling Russian Matryoshika dolls, including stacking dolls of Boris Yeltsin and Mikhail Gorbachev and also U.S. Presidents.
I remember one meeting in Moscow with members of a women’s theater cooperative—actresses, director, costume designer, and playwright. Before the member who spoke English arrived, we were left to communicate with each other by hand gestures and a few common words. Finally, the sturdy, broad-chested Russian writer who spoke English entered. I asked her what she did during the coup attempt. She stood, spread out her arms and declared triumphantly, “I stopped the tanks with my breasts!” This image has stayed with me, along with her words and the determined words of her fellow thespians and writers in that apartment, women demanding as their due freedoms they hadn’t yet experienced.
Joanne and members of Russian women’s theater cooperative in Moscow apartment, 1991.
Not only in the USSR but elsewhere, old dictatorships were crumbling, in Africa and Latin America. PEN was a refuge writers often looked to before democracy and political liberalization took hold in their countries. In September 1991 at the Vienna Congress, a month after the coup attempt, the Soviet Russian Center applied and received approval to change its name to Russian PEN. The debate within PEN was when to recognize a center. It was necessary to have enough qualified writers committed to the freedoms embedded in the PEN Charter and to have an environment in which the writers could feasibly operate, at least to some extent.
As the USSR broke apart, writers gathered and petitioned for PEN centers, sometimes before the regions claimed full independence. A PEN Center of the Soviet Asian Republics, including the literatures of the five separate regions of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tadzhikistan had been recognized at the Paris gathering in April 1991, but by PEN’s September 1993 Congress in Santiago de Compostela, Spain, writers from Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Turkmenistan all proposed separate centers of PEN. Russian PEN supported the disbanding of the Soviet Central Asian Center because it had not functioned, because the Soviet Union no longer existed, and because the President of the center had made public statements racially slandering others, and he refused to withdraw these. It is rare for PEN to challenge a member and withdraw membership, but the use of PEN to advocate racially intolerant and provocative positions is a rationale; PEN did so as well with certain members in the Balkans during the war there.
The Kazakhstan Center was accepted as a PEN Center at the Congress in 1993; the vote on Kyrgyzstan’s proposal was delayed until more information about the writers could be gathered, and it was agreed the situation in Turkmenistan, still governed by a dictatorship, remained too problematic for a PEN center to exist.
PEN often mirrored the global landscape. In the early 1990’s PEN added centers in Albania, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Moldova, Mongolia, Montenegro, Bosnia, and an ex-Yugoslav Center for writers in exile from the former Yugoslavia. Also new centers formed in the Congo, Mozambique, Malawi, Kenya, Guadalajara, Palestine as well as a Chinese Writers Abroad Center, an Iranian Writers in Exile Center, and an African Writers Abroad Center. The abroad and exile centers included members living outside the regions. At the Barcelona Congress in 1992 the acceptance of a Palestinian PEN Center was unanimous, including by the Israeli PEN and represented a hope that writers in the region would engage with each other. Also a Welsh Center and an Esperanto Center were added in the early 1990s.
PEN was growing quickly. It doubled in size in ten years, from 50 centers to more than 100 centers in 1992. Its finances, however, did not grow at the same rate, and the governing structure was essentially the same—an elected President, International Secretary and Treasurer who comprised the executive of International PEN. Staff also had hardly grown. Elizabeth Paterson, the Administrative Secretary had to manage the increasing workload with the addition of Jane Spender as her assistant. The Writers in Prison Committee, which operated with a separate budget, in a separate room, consisted of only two researchers—Sara Whyatt ,coordinator, and Mandy Garner and later a few interns.
During Michael Scammell’s years as Chair of WiPC and later during Thomas von Vegesack’s term, the Writers in Prison Committee focused its work on behalf of imprisoned and threatened writers, and on occasion tension arose between the Secretariat’s goal of promoting literature and comity among writers and the WiPC’s goal of protecting writers in oppressive regimes. The ultimate organizational decisions fell to the Secretariat between Congresses and in consultation with the Assembly of Delegates which met twice a year at Congress. Because of budgetary restraints and the growing size and expense of the Congresses, PEN reduced its Congresses to only once a year, beginning in 1994.

PEN International’s Writers in Prison Committee Report, September 1991 presented to the November 1991 PEN Congress in Vienna. PEN’s complete Case List for this period included 143 pages of cases of writers and journalists around the world reported kidnapped, “disappeared,” executed, having died in custody, imprisoned, banned, under house or town arrest, deported or awaiting trial.
Controversy around the narrow base of decision-making came to a confrontation over the April 1993 Congress in Dubrovnik, Croatia. The Balkan War was raging. At the Rio Congress in December 1992 the American delegate questioned the wisdom of holding the Congress in a war zone not only for reasons of safety but also for the appearance and possible “political misuse” of PEN in one corridor of the riven community and the restrictions on talking freely with the press. Others felt holding the Congress, most of which would be on a ship that would sail from Venice to Dubrovnik, would have a symbolic message of peace and also commemorate PEN’s Dubrovnik Congress 60 years earlier in 1933 when PEN exlcuded official writers of Nazi Germany from the organization. The host center assured that all centers from the region would attend. When delegates asked that the Dubrovnik Congress either be cancelled or postponed, they were told the decision had been made two years before, and there was no need for the Assembly to take a vote. Later as the war escalated, a mail vote was taken and the majority who responded voted for postponement, but the Croatian center, which had put in considerable work, wanted to hold the Congress, and so the plans went ahead.
On April 12, a week before the PEN gathering, the Army of the Republic of Srpska launched an attack on the town of Srebrenica in Bosnia, 200 miles from Dubrovnik. Many PEN Centers chose not to send delegates, including American and German PEN. The Writers in Prison Committee in the person of Thomas also chose not to attend nor did many of the WiPC members. Because there was not a quorum, the gathering was declared not an official congress, but a meeting.
I did not attend either the Dubrovnik meeting nor the earlier Rio Congress. Before the November 1992 Congress in Rio, Thomas and International Secretary Alexander Blokh without consulting with each other asked if I would take over the Chair of the Writers in Prison Committee when Thomas finished his term in September 1993. The fact that these two individuals both came to me made me consider carefully, but I was among the younger generation of PEN members who was urging more democratic procedures for PEN. I didn’t think the Chair should be an appointive office but should have the input of the PEN members, but in 1992, PEN had no such systems in place. Alex told me that he would canvas people at the Rio Congress to see if they agreed and get back to me. I don’t know what process was used nor how widely he asked, but he and Thomas returned in agreement and urged me to accept. I agreed, though I said that when my term was up, I wanted to assure we had set in place a more democratic system for nominations and election of the WIPC Chair. And so we did and have ever since.
Next Installment: PEN Journey 9: The Fraught Roads of Literature
PEN Journey 3: Walls About to Fall
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I have been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions, including as Vice President, International Secretary and Chair of International PEN’S Writers in Prison Committee. With memories stirring and file drawers bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. In digestible portions I will recount moments and hope this personal PEN journey may be of interest.
Our delegation of two from PEN USA West—myself and Digby Diehl, the former president of the Center and former book editor of the Los Angeles Times—arrived in Maastricht, The Netherlands in May 1989 for the 53rd PEN International Congress. We joined delegates from 52 other centers of PEN around the world, including PEN America with its new President, fellow Texan Larry McMurtry and Meredith Tax, founder of what would soon be PEN America’s Women’s Committee and later PEN International’s Women’s Committee. Meredith and I had met at the New York Congress in 1986 where the only picture of the Congress on the front page of The New York Times showed Meredith and me in the background at a table taking down the women’s statement in answer to Norman Mailer’s assertion that there were not more women on the panels because they wanted “writers and intellectuals.” Betty Friedan argued in the foreground.

Front page of the New York Times, 1986. Foreground: left – Karen Kennerly, Executive Director of American PEN Center, right – Betty Friedan, Background: (L to R) Starry Krueger, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, Meredith Tax.
Over the previous months the two American centers of PEN had operated in concert, mounting protests against the fatwa on Salman Rushdie and bringing to this Congress joint resolutions supporting writers in Czechoslovakia and Vietnam.
The theme of the Maastricht Congress—The End of Ideologies—in large part focused on the stirrings in Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union as the region poised for change no one yet entirely understood. A few weeks earlier, the Hungarian government had ordered the electricity in the barbed-wire fence along the Hungary-Austrian border be turned off. A week before the Congress, border guards began removing sections of the barrier, allowing Hungarian citizens to travel more easily into Austria. In the next months Hungarian citizens would rush through this opening to the West.
At PEN’s Congress delegates from Austria and Hungary sat a few rows apart, separated only by the alphabet among delegates from nine other Eastern bloc countries which had PEN Centers, including East Germany. This was my third Congress, and I was quickly understanding that PEN mirrored global politics where writers were on the front lines of ideas and frequently the first attacked or restricted. Writers also articulated ideas that could bring societies together.
In those days PEN had close ties with UNESCO, and attending a PEN Congress was like visiting a mini U.N. Assembly. Delegates sat at tables with name tags of their countries in front of them. Action was taken by resolutions which were debated and discussed and then sent to the International Secretariat and back to the Centers for implementation. At the time PEN operated with three standing Committees, the largest of which was the Writers in Prison Committee focused on human rights and freedom of expression. The other two were the Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee and the Peace Committee. Soon, in 1991, a fourth—the Women’s Committee—would be added. At parallel and separate sessions to the business of the Assembly of Delegates, literary sessions explored the theme of the Congress.
PEN USA West was particularly active in the Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC) where we advocated for our “adopted/honorary” members, most prominent for us at that moment was Wei Jingsheng in China. We had drafted and brought to the Congress a resolution, noting that China had recently released numbers of individuals imprisoned during the Democracy Movement, but Wei Jingsheng had not been among them and had not been heard from. We addressed an appeal to the People’s Republic of China to give information on the condition and whereabouts of Wei Jingsheng and to release him.

Before we spoke to this resolution on the floor of the Assembly, we met with the delegate of the China Center. The origins of this center was a bit of a mystery since it was one of the few centers that defended its government’s actions rather than PEN’s principles. I still recall the delegate with thick black hair, square face, stern visage and black horn-rimmed glasses, though this last detail may be an embellishment. He argued with me that Wei Jingsheng was an electrician, not a writer, that he had simply written graffiti on a wall, but that he had committed a crime by sharing “secrets” with western press.
The Chair of the Writers in Prison Committee Thomas von Vegesack, a Swedish publisher, arranged for the celebrated Chinese poet Bei Dao, a guest of the Congress, to speak in support of the PEN USA West resolution. The delegate from Taipei PEN stood next to Bei Dao and translated his words which contradicted the China delegate. Bei Dao noted that Wei Jingsheng had been in prison ten years already, having been arrested when he was 28-years-old. He had already published his autobiography and 20 articles and for years had been editor of the magazine SEARCH. In his posting on the Democracy Wall and in his essay “The Fifth Modernization,” Wei had suggested that democracy should be added as a fifth modernization to Deng Xiaoping’s four modernizations. “This shows that Wei Jingsheng’s status as a writer can’t be questioned,” Bei Dao said. I still remember that moment of Bei Dao addressing the Assembly and his country man with a Taiwanese writer translating. For me it demonstrated PEN in action.
In Beijing at that time thousands of students and citizens were protesting in Tiananmen Square.
PEN Center USA West’s resolution passed. The China Center and Shanghai Chinese Center refused to accept the resolution. The Maastricht Congress was the last PEN Congress they attended for over twenty years.
In the months preceding the gathering in Maastricht International PEN Secretary Alexander Blokh, International President Francis King and WiPC Chair Thomas von Vegesack had visited Moscow where the groundwork was laid to bring Russian writers into PEN with a Center independent of the Soviet Writers Union.
Twenty-two years before, Arthur Miller, International PEN President, had also traveled to Moscow at the invitation of Soviet writers who wanted to start a PEN center.
In 1967 Miller met with the head of the Writers’ Union and recounted in his autobiography:
At last Surkov said flatly, “Soviet writers want to join PEN….”
“I couldn’t be happier,” I said. “We would welcome you in PEN.”
“We have one problem,” Surkov said, “but it can be resolved easily.”
“What is the problem?”
“The PEN Constitution…”
The PEN Constitution and the PEN Charter obliged members to commit to the principles of freedom of expression and to oppose censorship at home and abroad. Miller concluded that the principles of PEN and those of the Soviet writers were too far apart. For the next twenty years PEN instead defended and assisted dissident Soviet writers.
At the Maastricht Congress Russian writers, including Andrei Bitov and Anatoly Rybakov attended as observers in order to propose a Russian PEN Center. Rybakov (author of Children of the Arbat) told the Assembly that writers had “endured half a century of non-democratic government and had lived in a dehumanized and single-minded state.” He said, “Literature could be influential in the fight against bureaucracy and the promotion of the understanding between nations and cultures. Now Russian writers want to join PEN, the principles and ideals of which they fully shared, and the responsibilities of belonging to which they recognized…and hoped for the sympathy of the members of PEN.”
The delegates unanimously elected Russian PEN to join the Assembly. In the 1990’s and until he passed away in 2007, one of the most outspoken advocates for free expression in Russia was poet and General Secretary of Russian PEN, Alexander Tkachenko. (Working with Sascha, as he was called, will be included in future blog posts.)
Polish PEN was also reinstated at the Maastricht Congress. After seven years of “severe restrictions and false accusations by the Government which had resulted in their becoming dormant,” the Polish delegate said they were finally able to resume normal activity in full harmony with PEN’s Charter. “I must stress here that our victory we owe in great part to the firm and unbending attitude of International P.E.N. and to almost unanimous solidarity of the delegates from countries all over the world.”

At the Congress PEN USA West, American PEN, Canadian PEN and Polish PEN presented a resolution on Czechoslovakia, calling for the government to cease the recent campaign against writers and to release Vaclav Havel and all writers imprisoned. The Assembly recommended that the International PEN President and International Secretary get permission from Czech authorities to visit Vaclav Havel in prison. Two weeks after the Congress Vaclav Havel was released. In December of 1989 Havel was elected President of Czechoslovakia after the collapse of the communist regime. In 1994, President Havel, along with other freed dissident writers, greeted PEN members at the 61st PEN Congress in Prague.
Also at the Maastricht Congress was an election for the new President of International PEN. Noted Nigerian writer Chinua Achebe stood as a candidate, supported by our two American Centers, Scandinavian centers, PEN Canada, English PEN and others, but Achebe was relatively new to PEN, and at the time there were only a limited number of African centers. Achebe lost by a few votes to the French writer Rene Tavernier, who passed away six months later.
Achebe admitted that he was not as familiar with PEN but said that if the organization had wanted him as President he had been persuaded that “it would be exciting.” He noted the world was very large and very complex. He hoped that in the years to come the voices of those other people would be heard more and more in PEN.
Our delegation had the pleasure of having dinner with Achebe in a castle in Maastricht which had a gourmet restaurant that served multiple courses with tiny portions. The small dinner, which also included the East German delegate and I think fellow Nigerian writer Buchi Emecheta and an American PEN member, lasted over three hours. I’m told when Achebe left, he asked his cab driver if he had any bread in his house because he was still hungry. When I saw Achebe a few times in the years following, he always remembered that dinner.
At the Maastricht Congress two new Africa Centers were elected: Nigeria, represented by Achebe, and Guinea. The election of these centers signaled a growing presence of PEN in Africa. Today PEN has 27 African centers.
A few weeks after we returned from the Congress to Los Angeles, tanks entered Tiananmen Square. Hundreds of citizens, including writers, were arrested and killed. One of my first thoughts was, what will happen to Bei Dao, but fortunately he hadn’t yet returned to China. Our small PEN office started receiving faxes from London with dozens of names in Chinese, and we and PEN Centers around the globe began writing and translating those names and mounting a global protest. Among those on the lists I am sure, though I didn’t know him at the time, was Liu Xiaobo, who was instrumental in helping protect the students and in clearing the square.

Tiananmen Square. June 4th, 1989. © 1989 Stuart Franklin/MAGNUM

Liu Xiaobo (with megaphone) at the 1989 protests on Tiananmen Square.
Twenty years later Liu Xiaobo would be a founding member and President of the Independent Chinese PEN Center. He would also later help draft and circulate the document Charter 08, patterned after the Czechoslovak writers’ document Charter 77, calling for democratic change in China. In 2009 Liu Xiaobo was again arrested and imprisoned. He won the Nobel Prize for Peace in 2010 and died in prison in 2017.
The opening of the world to democracy and freedom which we glimpsed and hoped for and which seemed imminent in 1989 appears less certain now.
Today, June 3-4, 2019 memorializes the thirtieth anniversary of the tanks rolling into Tiananmen Square. During the years after Tiananmen when Liu Xiaobo and others were in prison I chaired PEN International’s Writers in Prison Committee. But that is a story to come…
Next Installment: PEN Journey 4: Freedom on the Move West to East
PEN Journey 2: The Fatwa
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I have been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions, including as Vice President, International Secretary and Chair of International PEN’S Writers in Prison Committee. With memories stirring and file drawers bulging with documents, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. In digestible portions I will recount moments, though I’m not certain I can contain all these, but I hope this personal PEN journey may be of some interest.
It was President’s weekend in the US—between Lincoln and Washington’s birthday, coinciding with Valentine’s Day, 1989. I was President of PEN Center USA West and had just hired the Center’s first executive director ten days before. I’d been working hard with PEN and was also finishing a new novel, teaching and shepherding my 8 and 10-year old sons. For the first time in a year and a half my husband and I were going away for a long weekend without our children. He had also been working nonstop and had managed to clear his schedule.
On the plane to Colorado where we planned to ski, I read that Salman Rushdie’s The Satanic Verses had been burned in Birmingham, England. The next day Ayatollah Khomeini issued a fatwa against Rushdie. What was a fatwa? The Supreme Leader of Iran was calling for the murder of Rushdie wherever he was in the world, and he was offering a $6 million reward. As information about the fatwa developed, it also included a call for the death of whoever published The Satanic Verses.

I began making phone calls. This was a time before omnipresent cell phones so I had to find phones and numbers where people could reach me. (Usually our vacation dynamic was that my husband was on the phone.)
That first day I skied and wrote press releases on the ski lift and stopped at lodges on the mountain to use the pay phones to communicate with our new executive director. I’d ski another run then call the office again to answer questions from the press. What exactly was a fatwa, we were still asking? What did this mean for a writer? By the end of the day, I told my husband I had to return to LA.
“Can’t this wait?” he asked.
“No, it can’t,” I said.
Though a fatwa was a new concept, I understood, as did PEN members around the world, that a threshold had been crossed when a head of state issued a death warrant on a writer wherever he was in the world. Our two sons came out to be with my husband, and I returned to LA. Our board went into action as did PEN Centers around the globe to protest the fatwa. We organized a public event at the Los Angeles Times with writers and experts, an event which included readings from Rushdie’s book. Some were frightened by the threat, but most in PEN gathered. We contacted US government officials and began coordinating with global PEN centers, including American PEN in New York to confirm the support of writers for Rushdie and to protest Khomeini’s action.

Davis Dutton, center, of Dutton’s Books with some of his employees who voted to ignore the threats from Iran and stock “The Satanic Verses.”
Whatever the controversy over The Satanic Verses and its “insult” to Muslims, PEN was clear that the right of the writer to write without fear of death was primary.
The mobilization included discussions with bookstores to encourage them to keep the book on the shelves for many were quietly removing it. The fuller scope of our PEN’s actions at the time is described in the column below in the PEN Center USA West’s newsletter and in a story in the Los Angeles Times.


Los Angeles Times, February 23, 1989
Next Installment: PEN Journey 3: Walls About to Fall
Arc of History Bending Toward Justice?
PEN International was started modestly almost 100 years ago in 1921 by English writer Catherine Amy Dawson Scott, who, along with fellow writer John Galsworthy and others conceived that if writers from different countries could meet and be welcomed by each other when traveling, a community of fellowship could develop. The time was after World War I. The ability of writers from different countries, languages and cultures to get to know each other had value and might even help reduce tensions and misperceptions, at least among writers of Europe. Not everyone had grand ambitions for the PEN Club, but writers recognized that ideas fueled wars but also were tools for peace.

Catherine Amy Dawson Scott and John Galsworthy
The idea of PEN spread quickly, and clubs developed in France and throughout Europe, the following year in America, and then in Asia, Africa and South America. John Galsworthy, the popular British novelist, became the first President. Members of PEN began gathering at least once a year in a general meeting. A Charter developed to focus the ideas that bound everyone. In the 1930s with the rise of Hitler, PEN defended the freedom of expression for writers, particularly Jewish writers. In 1961 PEN formed its Writers in Prison Committee to work systematically on individual cases of writers threatened around the world. PEN’s work preceded Amnesty, and the founders of Amnesty came to PEN to learn how it did its work. PEN’s Charter, which developed over a decade, was one of the documents referred to when the Universal Declaration of Human Rights was drafted at the United Nations after World War II.
Today there are over 150 PEN Centers around the world in over 100 countries. At PEN writers gather, share literature, discuss and debate ideas within countries and among countries and defend writers around the globe imprisoned, threatened or killed for their writing. The development of a PEN center has often been a precursor to the opening up of a country to more democratic practices and freedoms as was the case in Russia, other countries in the former Soviet Union and in Myanmar. A PEN center is also a refuge for writers in certain countries.
Unfortunately, the movement towards more democratic forms of government and freedom of expression has been in retreat in the last few years in a number of these same regions, including in Russia and Turkey.
As part of PEN’s Centennial celebrations, Centers and leadership at PEN International have been asked to share archives for a website that will launch in 2021. As I dug through my sizeable files of PEN papers, I came across this speech below which represents for me the aspirations of PEN, the programming it can do and the disappointments it sometimes faces.
At a 2005 conference in Diyarbakir, Turkey, the ancient city in the contentious southeast region, PEN International, Kurdish and Turkish PEN hosted members from around the world. The gathering was the first time Kurdish and Turkish PEN members shared a stage and translated for each other. I had just taken on the position of International Secretary of PEN and joined others at a time of hope that the reduction of violence and tension in Turkey would open a pathway to a more unified society, a direction that unfortunately has reversed.

PEN Diyarbakir Conference, March 2005
This talk also references the historic struggle in my own country, the United States, a struggle which is stirring anew. “The arc of the moral universe is long, but it bends toward justice,” Martin Luther King and others have been quoted as saying. This is the arc PEN has leaned towards in its first century and is counting on in its second.
When I was younger, I held slabs of ice together with my bare feet as Eliza leapt to freedom in Harriet Beecher Stowe’s UNCLE TOM’S CABIN.
I went underground for a time and lived in a room with a thousand light bulbs, along with Ralph Ellison’s INVISIBLE MAN.
These novels and others sparked my imagination and created for me a bridge to another world and culture. Growing up in the American South in the 1950’s, I lived in my earliest years in a society where races were separated by law. Even after those laws were overturned, custom held, at least for a time, though change eventually did come.
Literature leapt the barriers, however. While society had set up walls, literature built bridges and opened gates. The books beckoned: “Come, sit a while, listen to this story…can you believe…?” And off the imagination went, identifying with the characters, whatever their race, religion, family, or language.
When I was older, I read Yasar Kemal for the first time. I had visited Turkey once, had read history and newspapers and political commentary, but nothing prepared me for the Turkey I got to know by taking the journey into the cotton fields of the Chukurova plain, along with Long Ali, Old Halil, Memidik and the others, worrying about Long Ali’s indefatigable mother, about Memidik’s struggle against the brutal Muhtar Sefer, and longing with the villagers for the return of Tashbash, the saint.
It has been said that the novel is the most democratic of literary forms because everyone has a voice. I’m not sure where poetry stands in this analysis, but the poet, the dramatist, the artistic writer of every sort must yield in the creative process to the imagination, which, at its best, transcends and at the same time reflects individual experience.
In Diyarbakir/Amed this week we have come together to celebrate cultural diversity and to explore the translation of literature from one language to another, especially to and from smaller languages. The seminars will focus on cultural diversity and dialogue, cultural diversity and peace, and language, and translation and the future. This progression implies that as one communicates and shares and translates, understanding may result, peace may become more likely and the future more secure.
Writing itself is often an act of faith and of hope in the future, certainly for writers who have chosen to be members of PEN. PEN members are as diverse as the globe, connected to each other through 141 centers in 99 countries. They share a goal reflected in PEN’s charter which affirms that its members use their influence in favor of understanding and mutual respect between nations, that they work to dispel race, class and national hatreds and champion one world living in peace.
We are here today as a result of the work of PEN’s Kurdish and Turkish centers, along with the municipality of Diyarbakir/Amed. This meeting is itself a testament to progress in the region and to the realization of a dream set out three years ago.
I’d like to end with the story of a child born last week. Just before his birth his mother was researching this area. She is first generation Korean who came to the United States when she was four; his father’s family arrived from Germany generations ago. I received the following message from his father: “The Kurd project was a good one! Baby seemed very interested and has decided to make his entrance. Needless to say, Baby’s interest in the Kurds has stopped [my wife’s] progress on research.”
This child will grow up speaking English and probably Korean and will also have a connection to Diyarbakir/Amed because of the stories that will be told about his birth. We all live with the stories told to us by our parents of our beginnings, of what our parents were doing when we decided to enter the world. For this young man, his mother was reading about Diyarbakir/Amed. Who knows, someday this child who already embodies several cultures and histories, may come and see this ancient city for himself, where his mother’s imagination had taken her the day he was born.
It is said Diyarbakir/Amed is a melting pot because of all the peoples who have come through in its long history. I come from a country also known as a melting pot. Being a melting pot has its challenges, but I would argue that the diversity is its major strength. In the days ahead I hope we scale walls, open gates and build bridges of imagination together. –Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, International Secretary, PEN International

