Posts Tagged ‘freedom of expression’
The Power of One: Dissent in Russia
With the war in the Ukraine front and center in the news, I can’t help thinking back to my Russian colleague from PEN, the General Secretary of Russian PEN Alexander Tkachenko, or Sascha as we called him. I wonder how he would have responded to what is unfolding. During his tenure at Russian PEN, he stood up and argued with Vladimir Putin face to face on behalf of Russian writers and resisted when the government tried to close down PEN in Russia.
Sascha was complex—a former professional soccer player, a Tartar, son of the Crimea, a poet. Those who knew him may still hear his voice on the floor of PEN Congresses challenging his government’s imprisonment of writers, apologizing to new Afghan PEN delegates for his country’s incursion into their country, or remember Sascha swimming off the coast of Perth, Australia in spite of the signs warning of sharks or singing and reciting his poetry at the Writers in Prison Conference in Denmark, or strategizing with the Writers in Prison Committee in the hills of Nepal.
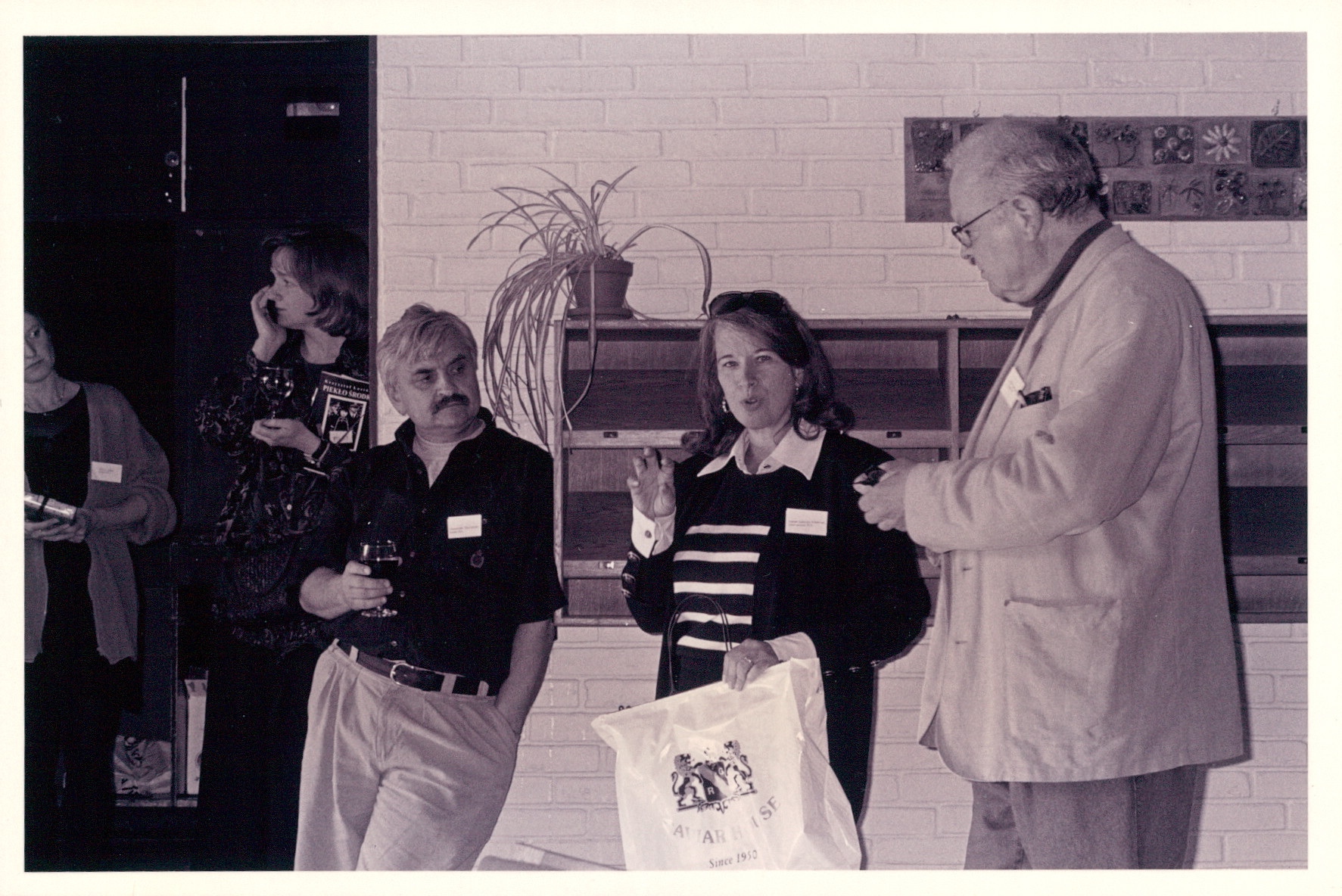

Alexander (Sascha) Tkachenko (Russian PEN), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (Chair of PEN International Writers in Prison Committee), and Niels Barfoed (Danish PEN) at the first Writers in Prison Committee Conference held in Helsingør, Denmark in 1996
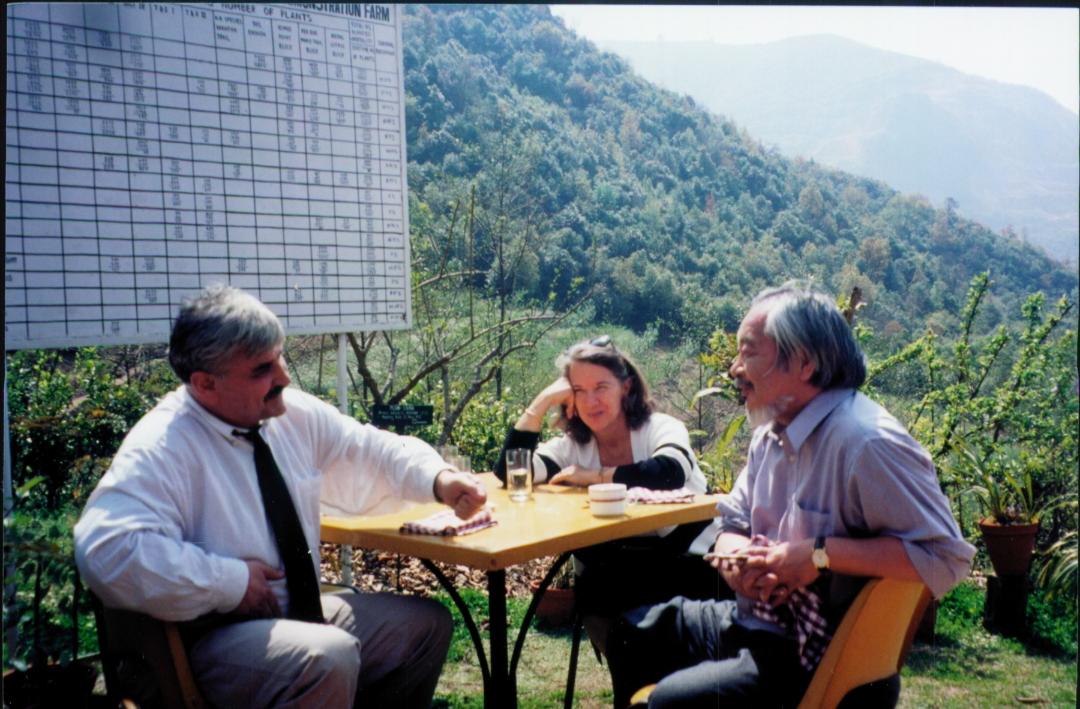

Alexander (Sascha) Tkachenko (Russian PEN), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (American PEN/PEN Int’l), Mitsakazu Shiboah (Japan PEN) at the 2000 Writers in Prison Committee meeting in Kathmandu, Nepal
When Sascha suddenly turned up dead in 2007 at age 63, we were all shocked. Some speculated perhaps he drank too much vodka; he had a heart condition. We accepted that it was “heart failure” though even at the time, the skeptical voice questioned whether there could have been foul play. As I witness now the carnage in the Ukraine and have since seen the incidents of murder and recently read accounts of those who have been eliminated in Russia in books such as Bill Browder’s Red Notice and the new Freezing Order, doubts again stir about Sascha’s sudden end. I wonder how he would have reacted to the drama playing out today and the closing down of any freedom of dissent in Russia. Today there are additional PEN Centers in Russia—PEN Moscow, PEN St. Petersburg, Tartar PEN, and writers I’m told have differing views among them. But Sascha I feel certain would have defended the right to dissent, to stand up for the freedom to live.
Below is the tribute I wrote at the time. I feel I am mourning Sascha all over again as we mourn the loss of the freedoms he and others struggled for, and we mourn the loss of this vision of a nation.
December 7, 2007
General Secretary of Russian PEN Alexander Tkachenko –Sascha as he is known to his friends—died this week, peacefully in his sleep, we are told. It is hard to imagine Sascha passing anywhere peacefully, certainly not from this world.
As Russian PEN’s General Secretary, this hearty man with salt and pepper hair and moustache, this former professional soccer player and respected poet campaigned fearlessly for writers threatened in Russia. He often stood his ground with officials, bureaucrats, the military and with Vladimir Putin himself. When Putin once visited the Russian PEN offices, Sascha challenged him directly on the rights of writers and freedom of expression in Russia.
Sascha traveled the huge expanse of Russia from one end to the other to lobby, to argue, to advocate on behalf of writers who faced imprisonment by the Russian state, writers such as Grigory Pasko, the journalist and poet who was arrested after reporting on Russia’s dumping of nuclear waste. He championed as well those in former regions of the Soviet Union, in Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan. He also spoke out and represented the voice of Russian writers on behalf of imprisoned writers around the world.
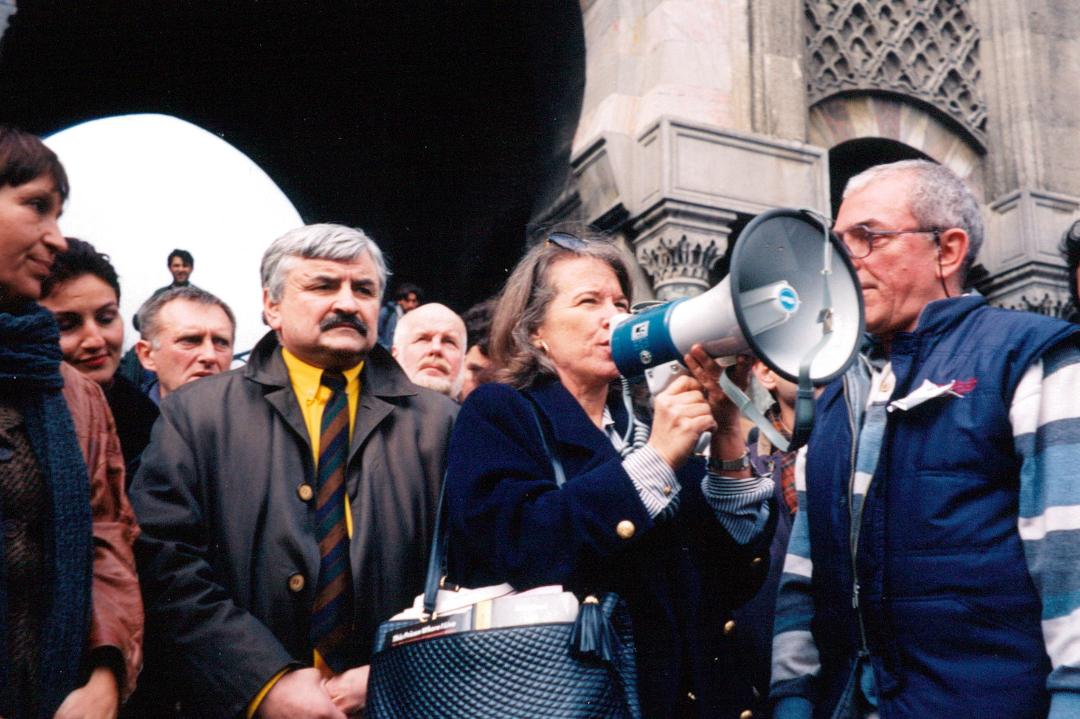
Sascha served on the Board of International PEN and attended PEN conferences and Congresses for the past decade. My personal memories are many. I particularly remember standing side by side with Sascha at Istanbul University in 1997 surrounded by riot police as we addressed a crowd of thousands with a bull horn. We were the two representatives of PEN advocating for freedom for Turkish writers in prison.
When the Russian government threatened to close Russian PEN in 2006 because of alleged tax payments suddenly demanded, PEN centers around the world rallied to help. I was International Secretary of PEN at the time and able to meet with Sascha and members of Russian PEN in Moscow as these payments were secured. That meeting was also attended by Rakhim Esenov from Turkmenistan, an elderly former general whose novel had been banned and who had been imprisoned for his book allegedly being “historically inaccurate.” Only a week before American PEN had given Esenov its Freedom to Write Award in New York. He was on his way home through Moscow, where Sascha and Russian PEN offered additional moral support as he returned to face the threats of his government.Rally at Istanbul University [Includes Soledad Santiago (San Miguel Allende PEN), James Kelman (Scottish PEN), Alexander (Sascha) Tkachenko (Russian PEN), Kalevi Haikara (Finish PEN), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, (PEN International Writers in Prison Committee Chair/American PEN), and Turkish Conference organizer Şanar Yurdatapan]
Russian PEN members meeting in Russian PEN office, including General Secretary Alexander (Sascha) Tkachenko (center), 2006
When I think of Sascha, I first hear his laughter and then his arguments, then his particular English; I see his hands waving as he talks, see him reluctant to yield a microphone until his point is made; I see him as he must have been as a young man blocking and running down the field as a soccer player, bobbing and weaving, pushing past those who would try to stop him as he drove to the goal. In his last decades that goal was getting writers out of prison. Sascha was an advocate we all would want on our side should we find ourselves threatened or in prison. He will be mourned and sorely missed.
His funeral is in his home village of Peredelkino December 10, Human Rights Day. He would have liked that framing of time on his passing, though he will not really pass; he will simply rest in our thoughts and rise in our thoughts when courage is called for and an advocate is needed. When a government acts as though it is more powerful than the individual, Sascha’s memory will remind us of the power of one. His voice continues through his writing, and the impact he has had on the lives of writers imprisoned continues.
—Joanne Leedom-Ackerman
Hope: A Threshold of History
My wedding anniversary is June 3, but ever since the events at Tiananmen Square June 4, 1989, I merge the dates in my mind. I’m not sure why, but this year included, I made quiet dinner plans for our anniversary on June 4 by mistake. The Tiananmen memory for those who work on human rights does not recede. It isn’t visceral because I wasn’t there, but many of us watched first with hopeful attention the gathering of students and others in Beijing that spring and then in horror as the tanks rolled in.

Liu Xiaobo (with megaphone) at the 1989 protests on Tiananmen Square.
Though the Tiananmen Square protests and the names of participants like Liu Xiaobo have been struck from the internet in China and not recorded in history books for mainland Chinese students, the courage of the demonstrators and the repression of the government remain as historical facts and as memory.
Unfortunately, the memory is amplified today like a solemn tolling bell, repeating a mournful sound in places like Belarus, Venezuela, Iran, and Myanmar, where citizens push against authoritarian forces with nonviolent resistance. That bell, however, also echoes a higher enduring strain of freedom sought and won over the decades by citizens in Eastern Europe, South Africa, Chile and other countries, citizens who ultimately prevailed.
Those outside the direct struggles can remember and can support those in the resistance. For many of my colleagues, the support is through the work of PEN which campaigns for writers on the front lines. Often it is writers who are early victims since they are articulating an alternate vision to the authoritarian regime and are reporting the facts. Others open space for those who must leave their countries or lose their freedom or their lives and must work from the outside, organizations like the International Cities of Refuge Network (ICORN) which finds alternate locations for writers and artists.
In the last few months, I’ve taken this space of a monthly blog to return to posts from years past. I’ve taken a core sample as a slice of my history during that month. I do so again here and note several posts: June 2008: Back on the River, June 2009: A Time of Hopening and June 2017: Storm Cloud on a Summer’s Day. Hope is a fragile but essential tool, one that holds history together so that it doesn’t shatter on the shoals, on the disappointments and misbehaviors of humankind.
Liu Xiaobo was China’s first citizen to win the Nobel Prize for Peace in 2010, but he was in prison in China as “an enemy of the state.” Liu Xiaobo died in custody July 2017.
As I celebrate my wedding anniversary with my husband of many decades this June 3/4, I do so with the hope offered by Liu Xiaobo to his friends and fellow citizens whom he believed in when he noted in his “Final Statement:”
“I have no enemies and no hatred…Hatred can rot away at a person’s intelligence and conscience. Enemy mentality will poison the spirit of a nation, incite cruel mortal struggles, destroy a society’s tolerance and humanity, and hinder a nation’s progress toward freedom and democracy…
“For there is no force that can put an end to the human quest for freedom, and China will in the end become a nation ruled by law, where human rights reign supreme…
“Freedom of expression is the foundation of human rights, the source of humanity, and the mother of truth. To strangle freedom of speech is to trample on human rights, stifle humanity, and suppress truth.”
Since April I’ve been back on the Potomac River, sculling in the rushing waters after the spring rains, dodging logs and flotsam flowing downstream from Great Falls and beyond. I’ve been pressing into the middle of the river on hot, sultry days in June when barely a breeze stirs the air, though the current still hurries beneath the boat. I’ve been rowing beside much larger sculls from the universities, dodging the wake of the speed boats which cruise along beside the Viking-size crafts as coaches shout instructions. In my small white scull I’ve tried to hear what they call and emulate the grace and power of the collegiate oarsmen and women.
Facing forward, watching the landscape recede as I move backwards, I’ve been thinking about the past even as I plunge into the future. This perspective of the rower, driving headlong towards what he can’t see except for quick glimpses over his shoulder, is a useful one to master.I’m back in Los Angeles this week for readings and interviews and will be talking about my own earlier fiction—No Marble Angels and The Dark Path to the River. Many of the short stories in No Marble Angels are set during the Civil Rights era—the Nashville sit-ins, the Little Rock school integration, the aftermath of the ’68 riots in the cities. It was a time when ordinary citizens took extraordinary actions. It’s easy to romanticize the times, but the consequence of many of those actions changed our laws and our lives and opened up our society. The future grew out of the clarity of purpose of those who could glance over their shoulders and press towards the future even as they had to face the restrictions of their present day.
As the U.S. moves into its next era—whatever that may eventually be called—one hopes it will be a period of national and international Rights Realized.
As a young mother, I used to tell stories to my two sons constantly—on the way to school, standing in long lines anywhere, on car, plane or bike rides, on hikes. I would ask each to give me two things (people, ideas, places, plots) they would like in the story, and then I would weave the disparate ingredients into a tale. Their elements might include something like a dog, a butterfly, a battle of some sort, and a waterfall…the possibilities were open and endless, though usually there was some battle involved and some animal in most of the stories.
Over the last year and a half, partly urged by my now adult sons, I’ve committed to writing a blog post once a month. For me the process is a bit similar to the earlier exercise as I look over the month and try to wrap ideas, thoughts, events into 600 words. This month’s elements are particularly rich, probably too rich for a 600-word essay, though the literary form of the blog hasn’t been established or defined so it can, I suppose, be whatever one wants.
I began June at an International PEN Writers in Prison conference joined to the Global Forum on Freedom of Expression conference in Oslo, Norway, where the sun doesn’t set in the summer. In Oslo, activists from organizations around the globe discussed, debated, and strategized into the summer nights about the state of freedom of expression around the world and the mechanisms to protect it. Everyone understood that societies without this freedom are most often without political and civil freedoms as well so the defense of freedom of expression is the front line.
The timing of the conference coincided with the 20th anniversary of the crackdown in Tiananmen Square in China. This year of 2009 is also the 20th anniversary of the popular uprising against the military government in Burma/Myanmar after the election of Aung San Sui Kyi, who was re-arrested this May; it is the 20th anniversary of the fatwa in Iran against Salman Rushdie after the publication of The Satanic Verses, and it is the 20th anniversary of the fall of the Berlin Wall.
The year 1989 was a threshold year. So where have we come twenty years later?
After Oslo, I went briefly to Paris en route to Normandy, where the 65th anniversary of the World War II invasion was being celebrated. I was headed to Normandy for a bike trip through the countryside and the historical sites, not for the official celebrations, but I was in Paris the day President Obama and his family arrived. It was also the day of the men’s semi-finals of the French Open in tennis. (You see the elements of this blog complicating…)
Driving back to the hotel after Federer beat Del Potro and Soderling beat Gonzalez, I was talking in my broken French with the taxi driver talking in his broken English about the matches and about the arrival of Obama and about world politics in general. The driver was ebullient—an oxymoron perhaps for a French taxi driver—but he was ebullient nonetheless.
“The world…the U.S…France…Europe…it is hopening,” he said, gesturing with his arms, trying to explain what he meant about the opening he saw in the world and the hope he felt. “We have hopening between us!”…[cont]
June 2010: Summer Reading: Under a Tree With a Book
Summer has come with hot, steamy breath in Washington this year—already days nearing 100°. Even with the sudden flash of thunderstorms, the air clears only to steam up again. So much for my assurance to a newcomer that summer wasn’t so bad here, though maybe we will pay our dues in June and be rewarded with the summer breezes and cool evenings in July. August, we know, will be hot.
In the dog days it is a time to be indoors, or at least in the shade—biking along the Potomac or sculling on the river only early in the morning or as the sun is setting. Indoors or under the shade of a tree, it is a time to read.
Summer reading—the term brings back delicious childhood memories even of hot Texas summers where I would find a patch of shade in the back yard and lose myself in a book, or bike to a nearby pool and sit reading between laps, or curl up in a chair under the fan on the screened porch. I can still smell the mowed grass and the sweet fragrance of white gardenias on the bushes just outside.…[cont]
June 2011: Mockingbirds at Fort McHenry: A Tribute to Elliot Coleman
(The excerpt below is from a larger article about the poet and teacher Elliott Coleman in the recent Fortnightly Review:)
I was 20 years old, applying to Johns Hopkins graduate Writing Seminars from a small Midwestern college. I had come to campus to meet Elliott Coleman, the director and founder of the program. He had read my application and invited me to lunch at the Faculty Club. Looking back now and understanding the processes of application and the competition for a position in the Writing Seminars, I realize how remarkable his attention was, but he showed that kind of attention to students, making each feel important and valued.
I had sought out his work before I came to Baltimore. I no longer remember how I found the slim volumes of poetry in my remote college town before online ordering, but I did, and I had read his book of poems Mockingbirds at Fort McHenry. When I spoke about those poems, he was genuinely humbled and surprised that I had made the effort to read his books.
He asked, “Would you like to go see Fort McHenry?” That afternoon, the student showing me around drove us all out to Fort McHenry, and I walked around the area with Elliott Coleman as he talked about poetry and the genesis of his poems. I’m sorry I didn’t write down what he said, or if I did, I can no longer find the notes of that afternoon. But I knew then that Hopkins was where I wanted to be if I had the chance, and even though I was a fiction writer, I wanted to study with Elliott Coleman. Fortunately, I got that opportunity.
Elliott Coleman radiated a gentleness, a caring and a humility that shed light, illumining those around him. He didn’t seek the center of attention; he didn’t draw the spotlight to himself, rather he shined so that light fell on others.
From Mockingbirds at Fort McHenry:
Through a window in Tunis the green searolls its light. A few square white houses dazzle the Atlas mountains, the color of lions and honey. This foothill is hardly Africa; this bay is hardly Mediterranean. They partake of each other by reflection, absorbed as they are in the depths of space.
I recently engaged with facebook (no, I didn’t buy stock), but I gave in. I concluded that I needed at least to understand (is that possible?) and experience the social media phenomena and at most learn from and enjoy the connection to friends and colleagues, most of whom I know, but some of whom I just read and some of whom read me.
For the last three months I’ve checked my “wall” every few days and scroll through hundreds of shared observations, photos, and comments. The process is surprisingly quick. I engage more like a magazine editor with an unexamined metric for judgment, pausing to “like” certain contributions, commenting on a few and sharing even fewer on my own personal and authors’ facebook pages.
For the present at least I’ve limited my fb world and page largely to literature and human rights in order to put some boundary on the possibilities and on that evaporating commodity of privacy–not a 21st century value and an oxymoron in a discussion of facebook. That is not to say I don’t enjoy the news and photos and commentary on a range of issues from all the friends, but in my fb space, this is my focus for now.…[cont]
June 2013: No blog posted
June 2014: No blog posted
June, 2015: What Are You Not Reading This Summer?
I was recently sent a questionnaire as part of a profile asking me what I was reading:
I find myself reading several books at the same time. I just finished Phil Klay’s Redeployment today, am reading Jennifer Clement’s Prayers for the Stolen, am re-reading Graham Greene’s The Comedians, re-reading Kate Blackwell’s you won’t remember this and can’t leave this question without noting Elliot Ackerman’s Green On Blue. Because I read both e-books and paper books, I move around among narratives easily.
The answer was a snapshot in reading time, indicative of the pleasure of dancing among narratives. I find myself enjoying on several platforms the movement  between hard-edged, nuanced stories of war and its aftereffects in Klay’s Redeployment and Ackerman’s Green on Blue, the harsh and surprising world of Clement’s indigenous Mexican women in Prayers for the Stolen and the gentle, but no less desperate stories of Southern women trying to find their lives in Kate Blackwell’s you won’t remember this, a collection recently re-published by a new small press—Bacon Press—in paperback. Graham Greene is a master who I am always re-reading, appreciating how he integrates the international world of politics and deceit with compelling narratives set around the world.
between hard-edged, nuanced stories of war and its aftereffects in Klay’s Redeployment and Ackerman’s Green on Blue, the harsh and surprising world of Clement’s indigenous Mexican women in Prayers for the Stolen and the gentle, but no less desperate stories of Southern women trying to find their lives in Kate Blackwell’s you won’t remember this, a collection recently re-published by a new small press—Bacon Press—in paperback. Graham Greene is a master who I am always re-reading, appreciating how he integrates the international world of politics and deceit with compelling narratives set around the world.
Recently I returned from PEN International’s biennial Writers in Prison conference and the International Cities of Refuge Network (ICORN) meeting, a gathering this year in Amsterdam focused on Creative Resistance, a gathering of over 250 individuals from 60 countries around the world who work on behalf of writers threatened, imprisoned and killed for their writing. I remain conscious of these voices too. They occupy a kind of negative space—those we are NOT reading, not able to read because they are not able to write.
The list unfortunately is long, and many individuals stand out for me, but I will highlight two here. Though I couldn’t read either because of language differences, I read with attention their cases and link here to actions that can be taken on their behalf:…[cont]
June 2016: No blog posted.
June 2017: Storm Cloud on a Summer’s Day
It is an almost perfect summer day—the sun is shining in a white cloud sky; the air is warm, not yet sweltering. Light filters through white umbrellas shading diners at the outside restaurant by the park. On this almost perfect New York day I am thinking about the rulers in China who have imprisoned for the last nine years one of the country’s courageous thinkers for ideas that will outlast him and his jailers.
Today it was announced Nobel laureate Liu Xiaobo is in critical condition, on medical parole having been given a terminal diagnosis. As a principal author of Charter’08 which advocates for nonviolent democratic reform in China, Liu Xiaobo, writer, critic and activist has lived his life as a man of ideas.

As the sun shifts above me, skirting over skyscrapers, finding a gap between the umbrellas and spreading over my table, I consider the trajectory and the life of an idea as it dawns, unfolds, iterates, then flies off where it is embraced, where it empowers and takes on a life of its own. Ideas are connected to, but not owned or encumbered by, those who articulate them.
The fallacy—the fundamental fallacy—of the rulers in China and elsewhere lies here. No one can imprison ideas. No one can manage or own the imagination of another. Government leaders can physically restrain with the hope that the idea will die, but in the case of Liu Xiaobo, the ideas behind Charter ’08, which was signed by more than 2000 Chinese citizens from all walks of life, endure. These ideas calling for a freer society continue to grow wings, often quietly, but sometimes even more quickly as the physical confines grow harsh.
“Any man or institution that tries to rob me of my dignity will lose,” declared Nelson Mandela. It is an injunction worth noting.
June 2018: No blog posted.
June 2019: [Beginning in May, 2019 I started writing a retrospective of work with PEN International for its Centenary so posts were more frequent in 2019-2020. In June 2019 there are two posts in the PEN Journeys and in June 2020 there are four.]
June 2019: PEN Journey 3: Walls About to Fall
Our delegation of two from PEN USA West—myself and Digby Diehl, the former president of the Center and former book editor of the Los Angeles Times—arrived in Maastricht, The Netherlands in May 1989 for the 53rd PEN International Congress. We joined delegates from 52 other centers of PEN around the world, including PEN America with its new President, fellow Texan Larry McMurtry and Meredith Tax, founder of what would soon be PEN America’s Women’s Committee and later PEN International’s Women’s Committee. Meredith and I had met at the New York Congress in 1986 where the only picture of the Congress on the front page of The New York Times showed Meredith and me in the background at a table taking down the women’s statement in answer to Norman Mailer’s assertion that there were not more women on the panels because they wanted “writers and intellectuals.” Betty Friedan argued in the foreground.

Front page of the New York Times, 1986. Foreground: left – Karen Kennerly, Executive Director of American PEN Center, right – Betty Friedan, Background: (L to R) Starry Krueger, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, Meredith Tax.
Over the previous months the two American centers of PEN had operated in concert, mounting protests against the fatwa on Salman Rushdie and bringing to this Congress joint resolutions supporting writers in Czechoslovakia and Vietnam.
The theme of the Maastricht Congress—The End of Ideologies—in large part focused on the stirrings in Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union as the region poised for change no one yet entirely understood. A few weeks earlier, the Hungarian government had ordered the electricity in the barbed-wire fence along the Hungary-Austrian border be turned off. A week before the Congress, border guards began removing sections of the barrier, allowing Hungarian citizens to travel more easily into Austria. In the next months Hungarian citizens would rush through this opening to the West.
At PEN’s Congress delegates from Austria and Hungary sat a few rows apart, separated only by the alphabet among delegates from nine other Eastern bloc countries which had PEN Centers, including East Germany. This was my third Congress, and I was quickly understanding that PEN mirrored global politics where writers were on the front lines of ideas and frequently the first attacked or restricted. Writers also articulated ideas that could bring societies together.…[cont]
June 2019: PEN Journey 4: Freedom on the Move: East to West
I have attended 32 International PEN Congresses as president of a PEN Center, often as a delegate, as Chair of the International Writers in Prison Committee, as International Secretary and now as Vice President. The number surprises me when I count. The Congresses have been held on every continent except Antarctica. Many were grand affairs where heads of State such as Vaclav Havel in Czechoslovakia, Angela Merkel in Germany, Abdoulaye Wade in Senegal greeted PEN members. Some were modest as the improvised Congress in London in 2001 when PEN had to postpone the Congress planned in Macedonia because of war in the Balkans. PEN held its Congress in Ohrid, Macedonia the following year. At these Congresses writers from PEN centers all over the globe attended. Today PEN International has centers in over 100 countries.
Among the more memorable and grand was the 54th PEN Congress in Canada, held in September 1989 when PEN still held two Congresses a year. The Canadian Congress, staged in both Toronto and Montreal by the two Canadian PEN centers, moved delegates and participants between cities on a train. The theme—The Writer: Freedom and Power—signaled hope at a time when freedom was expanding in the world with writers wielding the megaphone.…[cont]
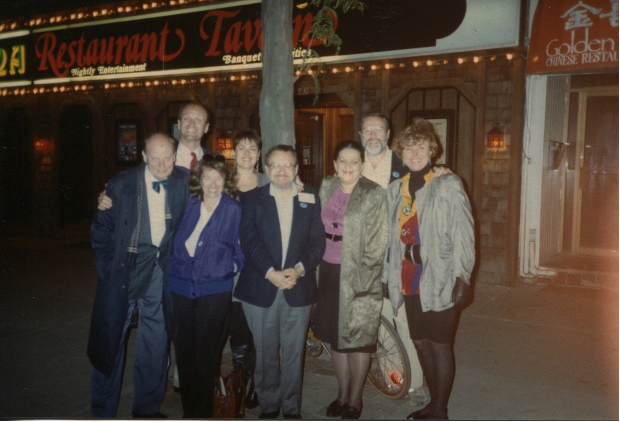

54th PEN Congress in Canada, 1989. Front row: WiPC chair Thomas von Vegesack, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman and PEN USA West Executive Director Richard Bray. Back row: Digby Diehl (right) and other delegates.
June 2020: PEN Journey 30: Barcelona: A Surprise
I was having lunch with my husband at a Georgetown restaurant in Washington, DC on a Saturday in May, 2004. I was due to fly out the next day for Barcelona to attend International PEN Writers in Prison Committee’s 5th biennial conference, part of a larger Cultural Forum Barcelona 2004. My husband and I were talking about our sons—the oldest was getting a PhD in mathematics and was also training for the 2004 Olympics as a wrestler, hoping to make the British team. (He had dual citizenship.) The younger, recently graduated with an advanced degree in International Relations, had just deployed to Iraq as a Marine 2nd Lieutenant and was heading into a region where the war was over but the insurgency had begun. It was an intense time for our family, yet as parents there was not much we could do except to be there, cheering for our oldest at his competitions and writing letters and sending packages and prayers for our youngest. It was a time when as parents we realized our children had grown beyond us and were taking the world on their own terms.
I was planning to be away for the week in Barcelona where PEN members from around the world were gathering for the Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC) and Exile Network meetings. Carles Torner, PEN International board member, chair of PEN’s Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee and former President of Catalan PEN, had helped arrange International PEN’s participation and funding as part of the Universal Forum of Cultures—Barcelona 2004. This would be the largest WiPC conference to date with delegates from every continent and multiple speakers and side events.
Carles, a poet, fluent in PEN’s three official languages English, French and Spanish, was one of the highly respected, organized and talented PEN members. He’d also been involved in the years’ long reformation of PEN International. As members looked to who could be a strong replacement for the current International Secretary when Terry Carlbom’s term ended in a few months, there was widespread enthusiasm for Carles to stand for the office. I was among the enthusiasts.
My phone rang at that Saturday lunch. International PEN Board member Eric Lax, already in Barcelona for meetings, said he had news and a question; he told me he was calling on behalf of others as well. The news: the Catalan government had also recognized Carles’ talents and had offered him a position as Director of Literature and Humanities Division at Institut Ramon Llull to promote Catalan literature abroad. A father of three, Carles had accepted this paid position which meant he couldn’t stand for PEN International Secretary, an unpaid position. He wouldn’t have the time for both, and there would be conflicts of interest.
Eric asked if I would allow myself to be nominated. A number of members and centers, including the two American centers, were asking, he said. PEN’s Congress where the election would take place was only a few months away in September and nominations were due soon. I was flattered but said no for a number of reasons. Eric asked that I not answer yet, just come to Barcelona, talk with people and let them talk with me.…[cont]
June 2020: PEN Journey 31: Tromsø, Norway: Northern Lights
The week before PEN’s 70th World Congress in Tromsø, Norway in the Arctic Circle, my oldest son competed in the Athens 2004 Olympic Games, the only wrestler to qualify for TeamGB (Great Britain). He had dual citizenship and was the first British champion to qualify for the Olympics in wrestling in eight years. In his sport, there was no seeding of competitors; instead, after making weight, each wrestler reached into the equivalence of a hat and drew their first round competitions. True to his history, my son drew the best opponents. As one news commentator noted: “Coming to the mat is Nate Ackerman, born in the US, wrestling for Great Britain, getting his PhD in mathematics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology…but that won’t help him now as he faces the three-time World Champion from Armenia.” My son lost to the Armenian wrestler. His other opponent was the world bronze medalist from Kazakhstan who went on to win the silver medal at the Olympics. Though my son didn’t win either match, he also didn’t get pinned, and he wrestled nobly. The Olympic Games in Athens was a magical time.
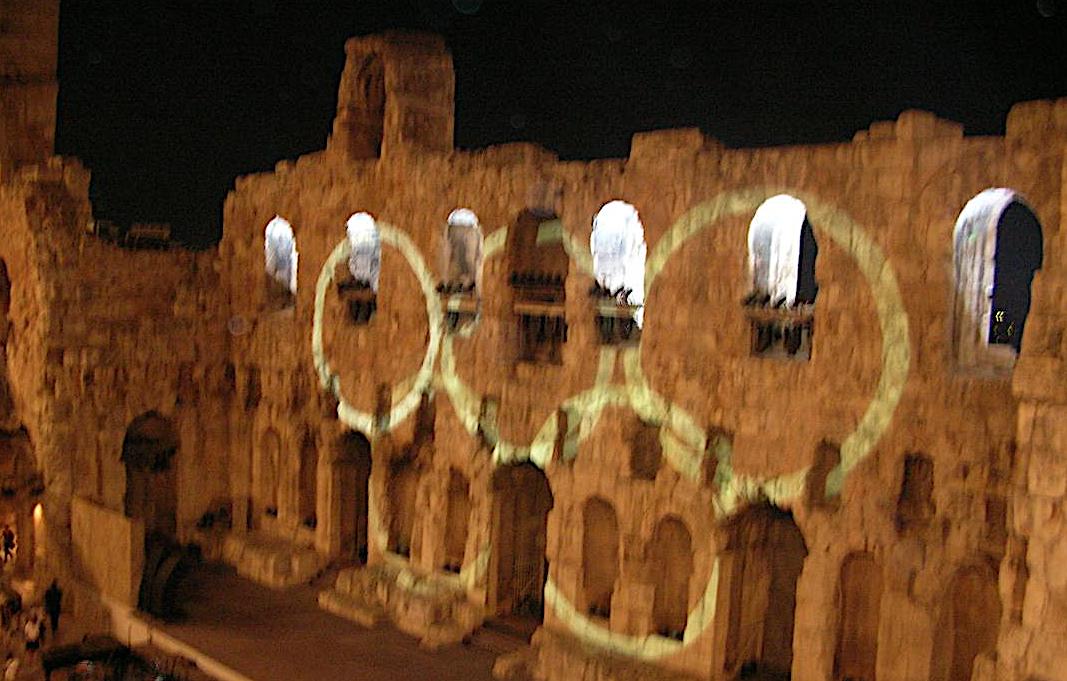

Olympic circles projected in light on the Acropolis at the 2004 Olympic Games in Athens
I was heading to Tromsø with a smile inside, though behind my smile was also a quiet attention that never left me for my youngest son, a Marine, was in Anbar Province, Iraq that summer, patrolling in 120° and alert for IED’s and snipers along the roadside. He had missed his brother in the Olympics and his brother missed being able to talk with him.
As I changed planes in northern Europe, I realized I was going to need a coat in the Arctic Circle and bought a light foldable one at an airport shop which I took to a decade worth of PEN Congresses after. On the plane I reviewed the stack of PEN papers and resolutions.
I was arriving at the Congress having agreed to stand for International Secretary. (See PEN Journey 30). The other PEN member standing was Giorgio Silfer, a poet and playwright and president of Esperanto PEN.
Norwegian PEN hosted over 300 writers, editors, and translators from at least 60 countries for the 70thWorld Congress whose theme was Writers in Exile—Writers in Minority Languages. The Rica Arctic Hotel where we stayed and met was an easy walk to the small downtown of Tromsø, capital of northern Norway, well above the Arctic Circle and called “the Paris of the North.”…[cont]
June 2020: PEN Journey 32: London Headquarters: Coming to Grips
PEN is a work in progress. It has always been a work in progress during its 100 years. Governing an organization with centers and members spread across the globe in over 100 countries can be like changing clothes, writing a novel and balancing a complex checkbook all while hang gliding. Perhaps an exaggeration, but not by much.
In 2004 the leadership of President and International Secretary were at the center of the governing structure along with the Treasurer and a relatively new Board. The President represented PEN in international forums. The International Secretary was tasked with overseeing the office and the centers of PEN and with any tasks the President handed over like running board meetings and setting up the agenda for work. The concept was that PEN should be able to elect as President a writer of international stature to represent PEN in global forums but not have the obligation to run the organization. That could be the role of the International Secretary, along with the Board and staff.
When I assumed the role of International Secretary, PEN did not yet have an executive director, though the consensus had built from the strategic planning process that we needed one. Both the President and International Secretary were volunteer, unpaid positions, which meant they were not full time. At the post-Congress board meeting after Tromsø, we agreed to begin a search for an executive director.

International PEN President Jiří Gruša
I suggested monthly board meetings, which had not been the practice. We could do these by phone, which meant there were only a few hours a day when everyone would be awake. If Judith Rodriguez in Melbourne, Australia could stay up past 11pm and Eric Lax in Los Angeles didn’t mind waking up at 7am, the rest of us—Takeaki Hori in Japan, Sibila Petlevski in Croatia, Eugene Schoulgin in Norway, Elisabeth Nordgren in Finland, Cecilia Balcazar in Colombia as well as President Jiří Gruša when he joined from Vienna or Prague and me in Washington, DC or London—could find our time zone and call in. The technology was not as sophisticated as today, and we didn’t yet use skype so the calls were not cheap, but we began to manage each month.…[cont]
June 2020: PEN Journey 33: Senegal and Jamaica: PEN’s Reach to Old and New Centers
A few days before I flew out to Dakar, Senegal for a PEN conference in November 2004, my youngest son, a Marine in Iraq, called and told my husband and me that we would not hear from him for a while. We knew, without being told, that the U.S. and British troops were likely about to return to Fallujah, the center of the insurgency. Civilians there had been advised to get out of the city, and they were leaving.
On the opening day of the PEN conference in Dakar, November 7, 2004, the battle for Fallujah began. The headlines in the newspapers in Dakar were about the civil war raging in neighboring Ivory Coast so I was not reading about Iraq during the five-day PEN Africa meeting. In 2004 there were no iPhones or phone news feeds and rare coverage of the Middle East was on the evening news. I was quietly attentive each day and prayerful and focused on PEN’s work.
I have modest notes from the first PAN Africa conference, but I have some of my most vivid memories, most particularly of the people I met and of my first trip to Gorée Island just off the Senegalese coast opposite Dakar, a place of its own historic upheaval. Gorée Island was the site of the largest slave-trading center on the African coast from the 15th to the 19th century, ruled successively by the Portuguese, Dutch, English and French. The dungeons and portals to the sea where men and women and children were sent out in chains still stood along with the stucco houses of former slave traders.
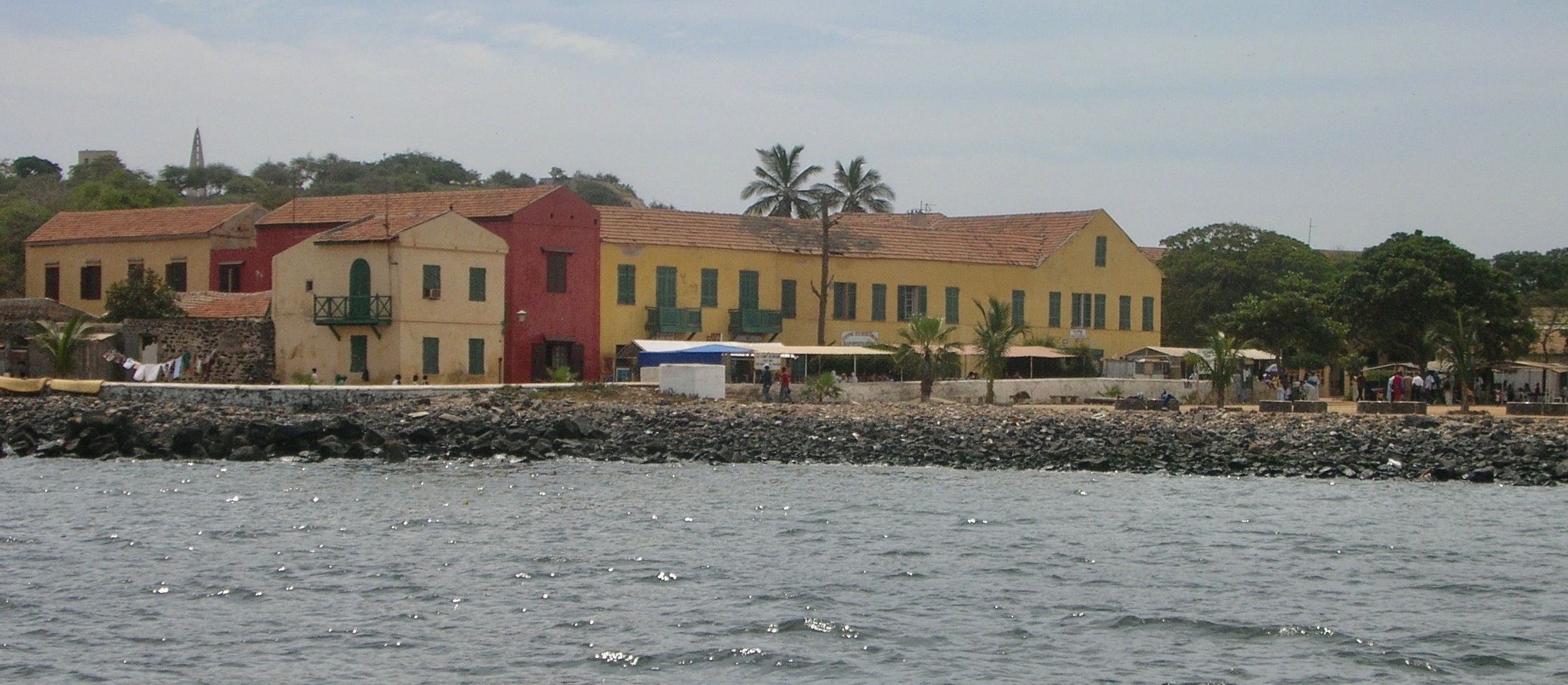

Gorée Island, site of slave trading in 15-19th centuries, off coast of Dakar, Senegal
A tall Gambian doctoral student assisting Senegalese PEN guided a few of us around Gorée. Fluent in French, English and Spanish, he was writing a doctoral thesis on the secrets of history and myth in the epic of Kaabu according to Mandingo oral traditions—clearly a future PEN member. Thoughtful, knowledgeable, he spent the day sharing history. During and after the Dakar meetings, our paths crossed in subsequent PEN conferences and congresses, and we know each other still. Dr. Mamadou Tangara earned his doctorate at the University of Limoges in France shortly after and eventually became the Gambian Permanent Representative to the United Nations. During Gambia’s constitutional crisis in 2016-17, he and other diplomats called for the president to step down peacefully; he was dismissed, but when power changed hands a few months later, he was reappointed as Minister of Foreign Affairs for the Gambia. The friendship with Mamadou Tangara remains and is one of my many valued friendships from PEN.

Mamadou Tangara (Gambia) and Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (PEN International Secretary) on Gorée Island at PEN’s 2004 Dakar conference
Mamadou’s mentor at the time was an older Gambian journalist and editor Deyda Hydara, who joined PEN members from more than a dozen African centers in this conference to prepare for PEN’s first PAN African World Congress in Senegal in 2007. The Congress would be PEN’s first in Africa since the 1967 Congress in the Ivory Coast when American playwright Arthur Miller was International PEN President. Though the Gambia didn’t yet have a PEN Center, Deyda was planning on starting one. At the time Deyda Hydara was co-founder and primary editor of The Point, a major independent Gambian newspaper. He was also correspondent for AFP News Agency and Reporters Without Borders and was an advocate for press freedom and a critic of his government’s hostility to the media.
A month after PEN’s Dakar conference, the Gambian government passed a bill allowing prison terms for defamation and another bill requiring newspaper owners to purchase expensive operating licenses and register their homes as security. Deyda Hydara announced his intent to challenge these laws. Two days later on December 16, 2004 Deyda Hydara was assassinated on his way home from work. To this day his murder remains unsolved. The following year Deyda Hydara won PEN America’s Freedom to Write Award posthumously and later the Hero of African Journalism Award of the African Editors Forum.…[cont]
Nobel Peace Prize for Liu Xiaobo Ten Years After
PEN International marks the ten-year anniversary of the awarding of the Nobel Peace Prize to writer, literary critic and human rights activist Liu Xiaobo on 10 December 2010. PEN’s Liu Xiaobo Anniversary Campaign acts as a commemoration of Liu Xiaobo’s life, his contribution to Chinese literature, and his selfless work promoting basic freedoms in the People’s Republic of China (PRC).
The campaign also highlights the cases of writers Gui Minhai, Kunchok Tsephel, Yang Hengjun and Qin Yongmin who are currently detained by the PRC government. The campaign seeks to raises awareness of their situation, to boost advocacy work on their behalf and to ensure that they and their families feel supported and not forgotten.
The following links to PEN’s campaign. Below is text and Chinese translation of my video tribute to Liu:
Hello, I’m Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, Vice President Emeritus of PEN International.
您好!我是乔安尼•利多姆-阿克曼,国际笔会荣休副会长。
Ten years ago, essayist, poet, activist and PEN member Liu Xiaobo was the first Chinese citizen to win the Nobel Prize for Peace. Liu envisioned and worked towards a peaceful and democratic pathway for China. Beginning with the protests in Tiananmen Square in 1989 and through the subsequent decades, he spoke out and wrote and gathered people and ideas in support of a China where individual freedom was valued and protected.
十年前,散文家、诗人、活动家、笔会成员刘晓波成为首位荣获诺贝尔和平奖的中国公民。刘先生设想并致力于中国走向和平民主的道路。他从1989年天安门广场抗议运动开始,在随后数十年言说和书写,并聚集民众及理念,以支持一个重视和保护个人自由的中国。
In 2008, he and others drafted Charter 08, which set out this democratic vision. He and others gathered hundreds and then thousands of signatures from Chinese citizens who endorsed the vision. Charter 08 did not call for an overthrow of the government so much as a transformation of the way government related to its citizens in a transition to a democratic society that would include freedom of expression and assembly.
2008年,他和其他人起草了《 零八宪章》,阐明这一民主愿景。他们从支持这一愿景的中国公民那里汇集了成百上千人签名。 《零八宪章》并未呼吁推翻政府,而是要转变政府相对于公民的方式,转型为包括言论自由和集会自由的民主社会。
Liu Xiaobo has been called the Nelson Mandela or Václav Havel of China because of his ideas, his activism and his leadership. Like Havel, Liu was committed to nonviolent action as a means of achieving change, and he was an inspired writer.
刘晓波因其理念、言行和领导能力而被称为中国的曼德拉或哈维尔。像哈维尔一样,刘晓波也致力于以非暴力行动来实现变革,他是一位受鼓舞的作家。

Liu Xiaobo (with megaphone) at the 1989 protests on Tiananmen Square.
I first encountered Liu Xiaobo through PEN. After the Tiananmen Square crackdown in 1989, PEN worked on behalf of the writers who had been arrested in the protest, including Liu Xiaobo. Liu had also been instrumental in persuading students to leave the Square before the soldiers and tanks rolled in to attack and possibly kill them. At the time of Tiananmen Square, I was President of PEN Center USA West. A few years later when Liu was again imprisoned for his writing, I was Chair of PEN International’s Writers in Prison Committee.
我首先通过笔会遭遇刘晓波。在1989年天安门广场镇压后,笔会致力于代表在抗议活动中被捕的作家,包括刘晓波。刘晓波还曾劝说学生离开广场,以免士兵和坦克席卷攻入广场可能杀死他们。在天安门广场抗议时,我担任美国西部笔会会会长。几年后,当刘晓波再次因写作而被监禁时,我是国际笔会狱中作家委员会主席。
Liu Xiaobo then went on to become one of the founders and the second President of the Independent Chinese PEN Center (ICPC), whose members lived inside and outside of China. He was instrumental in establishing the platforms by which these writers could communicate and share ideas about a society where freedom of expression and democratic processes could exist.
刘晓波随后成为独立中文笔会(ICPC)的创始人之一和第二任会长,该笔会成员居住在中国境内和海外。他发挥作用建立起这个平台,这些作家们可以借此平台,交流和分享有关这样一个社会的理念,在那里言论自由和民主进程得以存在。
During the time Liu was President of ICPC, I was the International Secretary of PEN. However, Liu was not allowed out of mainland China into Hong Kong where ICPC had its meetings, and I didn’t get to the mainland until in 2010 after he was arrested for the fourth and final time, so we never met in person, though over decades I have worked with many of his colleagues.
在刘晓波担任独立中文笔会会长期间,我曾担任国际笔会秘书长。然而,他没获准离开中国大陆前往独立中文笔会举行会议的香港,而直到他 第四次也是最后一次被捕后的2010年,我才去中国大陆,因此我们从未亲身见面,尽管数十年来我一直与他的许多同事共同工作。
Liu Xiaobo was the writer the Chinese government feared the most and therefore arrested. Liu was charged as “an enemy of the state” for “incitement of subverting state power” because of his ideas, his writing and his participation in the drafting and circulating of Charter 08. He was sentenced to 11 years in prison. He was the only recipient of the Nobel Prize who was in prison at the time and not allowed to attend the ceremony. Only an empty chair represented him. His wife Liu Xia was also not allowed to attend. Liu Xiaobo died in custody July 13, 2017.
刘晓波是中国政府最害怕的作家,因此而被捕。由于其理念、写作并参与起草和传播《 零八宪章》,刘晓波被指控为“煽动颠覆国家政权”的“国家敌人”。他被判处了十一年徒刑。他是当时在监狱中而未被允许参加颁奖典礼的唯一诺贝尔奖得主,只有一把空椅子代表他。他的妻子刘霞也被禁止出席。刘晓波于2017年7月13日去世。
 After his death, writers around the world who knew him began to write about him, his work, about China and the path of liberalism and democratic aspirations. This year THE JOURNEY OF LIU XIAOBO: FROM DARK HORSE TO NOBEL LAUREATE was published containing more than 75 of these essays—probably the largest gathering of writing from China’s democracy activists—and is both a memoir and tribute to Liu Xiaobo and a study of China’s Democracy Movement.
After his death, writers around the world who knew him began to write about him, his work, about China and the path of liberalism and democratic aspirations. This year THE JOURNEY OF LIU XIAOBO: FROM DARK HORSE TO NOBEL LAUREATE was published containing more than 75 of these essays—probably the largest gathering of writing from China’s democracy activists—and is both a memoir and tribute to Liu Xiaobo and a study of China’s Democracy Movement.
他去世后,全世界了解他的作家开始书写他及其作品,书写中国以及自由主义和民主理想之路。今年出版了《刘晓波之旅程:从黑马到诺奖得主》(文文版),包含75篇以上的文章,可能是来自中国民主活动人士的最大笔墨聚会,既是对刘晓波的回忆致敬,也是对中国民主运动的研究。
China’s Democracy Movement and Liu Xiaobo’s legacy still inspire those inside and outside of China, from the mainland to Xinjiang to Tibet to Hong Kong and to neighboring countries engaged in the struggle for political reform and an end to authoritarian rule.
中国民主运动和刘晓波的遗产,仍然激励着中国内外的人们,从大陆到新疆,到西藏,再到香港,再到争取政治改革和结束专制统治的邻国。
Some have said that because of China’s ascendency in the last decade, the legacy of Liu Xiaobo has been reduced to nothing. But a longer view of history shows that the same was said of those visionaries and martyrs for free societies in Eastern Europe and South Africa.
有人说,由于近十年来的中国崛起,刘晓波的遗产被削减为零。然而,更长的历史证明,同样的说法也曾针对过那些在东欧和南非争取自由社会的远见者和烈士们。
Societies move forward and are changed by ideas, by leaders, and ultimately by their citizens. Liu Xiaobo did not aspire to personal power, but those in power came to fear him because he understood how to move ideas into action.
社会向前发展,并通过理念、领导者及最终通过其公民而改变。刘晓波并不渴望个人权力,但是当权者却开始害怕他,正因为他知道如何将理念付诸行动。
As individuals one by one—be they writers, lawyers, academics or others—are put into prison and taken out of the discourse, those in power attempt to maintain their control. That is why it is important to keep an eye not only on the monolith of regimes and government, but to protect the individuals who hold the powerful to account.
当作家、律师、学者或其他人一个接一个地被关进监狱并从话语中带走时,当权者试图维持其控制。这就是为什么重要的不仅是着眼于政权的垄断和政府问题,而且要保护那些向当权者追责的个人。
Liu Xiaobo declared, “Freedom of expression is the foundation of human rights, the source of humanity, and the mother of truth.”
刘晓波声言:“表达自由,人权之基,人性之本,真理之母。”
Liu Xiaobo insisted that to transition to a state that one wanted to live in, one needed to have citizens who represented those values even in the struggle.
刘晓波坚持认为,要过渡到一个人们想要生活的国度,就需要有即使在斗争中也代表那些价值观的公民。
I’d like to read from his Final Statement to the judge who sentenced him: “…now I have been once again shoved into the dock by the enemy mentality of the regime. But I still want to say to this regime, which is depriving me of my freedom, that I stand by the convictions…I have no enemies and no hatred…Hatred can rot away at a person’s intelligence and conscience. Enemy mentality will poison the spirit of a nation, incite cruel mortal struggles, destroy a society’s tolerance and humanity, and hinder a nation’s progress toward freedom and democracy. That is why I hope to be able to transcend my personal experiences as I look upon our nation’s development and social change, to counter the regime’s hostility with utmost goodwill and to dispel hatred with love.”
我要朗读他的《我的最后陈述》,是他写给判决他的法官的:“……现在又再次被政权的敌人意识推上了被告席,但我仍然要对这个剥夺我自由的政权说,我坚守着……信念——我没有敌人,也没有仇恨。……仇恨会腐蚀一个人的智慧和良知,敌人意识将毒化一个民族的精神,煽动起你死我活的残酷斗争,毁掉一个社会的宽容和人性,阻碍一个国家走向自由民主的进程。所以,我希望自己能够超越个人的遭遇来看待国家的发展和社会的变化,以最大的善意对待政权的敌意,以爱化解恨。”
After Liu Xiaobo’s death, a colleague who had known and worked with him for decades was asked if he thought Xiaobo would have changed his statement had he known his end. His friend said No, that his final statement and sentiment that “I have no enemies, no hatred” was at the heart of who Liu Xiaobo was.
刘晓波去世后,一位与他认识并合作了数十年的同道被问到,如果刘晓波知道自己的结局,他是否认为晓波会改变自己的陈述。他的朋友说“不会”,因为“我没有敌人,也没有仇恨”的最后陈述和观点,正是刘晓波其人的核心。
Now Liu Xiaobo’s beloved wife Liu Xia, who is herself a poet, will read one of his poems written to her: “Van Gogh and You” addressed to “Little Xia”:
现在,刘晓波的挚爱妻子,自己也是诗人的刘霞,将朗诵他写给她的一首诗:《梵高与你——给小霞》:
PEN JOURNEY: Introduction—Raising the Curtain: The Arc of History Bending Toward Justice?
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and was asked by PEN International to write down memories. I have done so in 46 PEN Journeys and have been asked to write an introduction to these. Below is the introduction coming last, drawn in part from an earlier blog post of the same title, but not in this PEN Journey sequence.
“In a world where independent voices are increasingly stifled, PEN is not a luxury. It is a necessity.”—Novelist & poet Margaret Atwood, former President of PEN Canada
“…freedom of speech is no mere abstraction. Writers and journalists, who insist upon this freedom, and see in it the world’s best weapon against tyranny and corruption, know also that it is a freedom which must constantly be defended, or it will be lost.”—Novelist Salman Rushdie, PEN member
PEN International was started modestly 100 years ago in 1921 by English writer Catharine Amy Dawson Scott, who, along with fellow writer John Galsworthy and others, conceived if writers from different countries could meet and be welcomed by each other when traveling, a community of fellowship could develop. The time was after World War I. The ability of writers from different countries, languages and cultures to get to know each other had value and might even help reduce tensions and misperceptions, they reasoned, at least among writers of Europe.

PEN Founder Catherine Amy Dawson Scott and first PEN President John Galsworthy
The idea of PEN [Poets, Essayists & Novelists—later expanding to Poets, Playwrights, Essayists, Editors and Novelists and now including a wide array of Nonfiction writers and Journalists] spread quickly. Clubs developed in France and throughout Europe, and the following year in America, and then in Asia, Africa and South America. John Galsworthy, the popular British novelist, became the first President. A decade later when he won the Nobel Prize for Literature, he donated the prize money to International PEN. Not everyone had grand ambitions for the PEN Club, but writers recognized that ideas fueled wars but also were tools for peace. Galsworthy spoke about the possibilities of a “League of Nations for Men and Women of Letters.”
Members of PEN began to gather at least once a year in 1923 with 11 Centers attending the first meeting. During the 1920’s writers regardless of nationality, culture, language or political opinion came together. As the political temperature rose in Europe, PEN insisted it was an apolitical organization though its role in the politics of nations was soon to be tested and ultimately landed not on a partisan or ideological platform but on a platform of ideals and principles.
At a tumultuous gathering at PEN’s 4th Congress in Berlin in 1926, tensions rose among the assembled writers, and the debate flared over the political versus non-political nature of PEN. Young German writers, including Bertolt Brecht, told Galsworthy that the German PEN Club didn’t represent the true face of German literature and argued that PEN could not ignore politics. Ernst Toller, a Jewish-German playwright, insisted PEN must take a stand.
After the Congress Galsworthy returned to London and holed up in the drawing room of PEN’s founder Catharine Scott where he worked on a formal statement to “serve as a touchstone of PEN action.” This statement included what became the first three articles of the PEN Charter. At the 1927 PEN Congress in Brussels, the document was approved and remains part of PEN’s Charter today, including the idea that “Literature knows no frontiers and must remain common currency among people in spite of political or international upheavals.” The third article of the Charter notes that PEN members “should at all times use what influence they have in favor of good understanding and mutual respect between nations and people and dispel all hatreds and champion the ideal of one humanity living in peace and equality in one world.”
As the voices of National Socialism rose in Germany, PEN’s determination to remain apolitical was challenged though the determination to defend freedom of expression united most members. At the 1932 Congress in Budapest the Assembly of Delegates sent an appeal to all governments concerning religious and political prisoners, and Galsworthy issued a five-point statement, a document that would evolve into the fourth article of PEN’s Charter.
When Galsworthy died in January 1933, H.G. Wells took over as International PEN President. It was a time in which the Nazi Party in Germany was burning in bonfires thousands of books they deemed “impure” and hostile to their ideology. At PEN’s 1933 Congress in Dubrovnik, H.G. Wells and the PEN Assembly launched a campaign against the burning of books by the Nazis and voted to reaffirm the Galsworthy resolution. German PEN, which had failed to protest the book burnings, attended the Congress and tried to keep Ernst Toller, a Jew, from speaking. Some members supported German PEN, but the overwhelming majority reaffirmed the principles they had just voted on the previous day. The German delegation walked out of the Congress and out of PEN and didn’t return until after World War II. Their membership was rescinded. “If German PEN has been reconstructed in accordance with nationalistic ideas, it must be expelled,” the PEN statement read. During World War II PEN continued to defend the freedom of expression for writers, particularly Jewish writers. (Today German PEN is one of PEN’s active centers, especially on issues of freedom of expression and assistance to exiled writers.)
PEN was one of the first nongovernmental organizations and the first human rights organization in the 20th century. PEN’s Charter, which developed over two decades, was one of the documents referred to when the Universal Declaration of Human Rights was drafted at the United Nations after World War II. In 1949 PEN was granted consultative status at the United Nations as “representative of the writers of the world,” and is today the only literary organization with formal consultative status with UNESCO.
In 1961 PEN formed its Writers in Prison Committee to work systematically on individual cases of writers threatened around the world. PEN’s work preceded Amnesty, and the founders of Amnesty came to PEN to learn how it did its work.
Today there are over 150 PEN Centers around the world in more than 100 countries. At PEN writers gather, share literature, discuss and debate ideas within countries and among countries, defend linguistic rights and defend writers around the globe imprisoned, threatened or killed for their writing. The development of a PEN center has often been a precursor to the opening up of a country to more democratic practices and freedoms as was the case in Russia in the late 1980’s and in other countries of the former Soviet Union and in Myanmar where a former prisoner of conscience was instrumental in forming a center there and was its first President. A PEN center is a refuge for writers in many countries.
Unfortunately, the movement towards more democratic forms of government and freedom of expression has been in retreat in the last few years in a number of these same regions, including in Russia and Turkey.
For more than 35 years I have been engaged with PEN, as a member, as the President of one of PEN’s largest centers, PEN Center USA West during the year of the fatwa against Salman Rushdie and Tiananmen Square, as Chair of PEN International’s Writers in Prison Committee (1993-1997), as International Secretary (2004-2007), and continuing as an International Vice President since 1996. I’ve also served on the Board and as Vice President of PEN America (2008-2015). I lived for six years in London, where PEN International is headquartered.
In the run-up to PEN’s Centenary, I was asked if I would write an account of PEN’s history as I’d seen it. I began by posting a blog twice a month, taking on small slices of the history in each narrative. This serial blog of PEN Journeys recounts PEN’s history as I’ve witnessed it as well as history of the period and personal history during those years. The narratives are framed by the times, featuring writers, including the fatwa against Salman Rushdie, the protests in Tiananmen Square, the fall of the Berlin Wall—PEN members or future PEN members were central in all these events—the collapse of the Soviet Union and the formation of PEN Centers there; the opening up of Eastern Europe with its PEN centers; the release of PEN “main case” Václav Havel and his ascendency to the Presidency of Czechoslovakia; the mobilization of Turkish PEN members in opposition to recurring authoritarian governments; PEN’s mission to Cuba; PEN’s protests over killings and impunity in Mexico; protests and gatherings in Hong Kong on behalf of imprisoned Chinese writers; the awarding of the Nobel Prize for Peace to PEN member and Independent Chinese PEN Center founder and President Liu Xiaobo.
PEN and its members have played a pivotal role in defending freedom of expression around the world, in challenging systems that trap citizens, and in at least two instances, in taking on the presidencies of the new democracies that emerged. The PEN Charter, which sets out the principles and ideals, has united the global organization and guided its members who have often been at the forefront or in the wings of important historical moments—celebrated and outspoken writers like Václav Havel, Nadine Gordimer, Margaret Atwood, Orhan Pamuk, Yaşar Kemal, Chinua Achebe, Wole Soyinka, Koigi wa Wamwere, Ngũgĩ wa Thiong’o, Arthur Miller, Anna Politkovskaya, Salman Rushdie, Ken Saro-Wiwa, Carlos Fuentes, Liu Xiaobo. The list is long, and I have had the privilege of interacting with many of them in PEN and also with hundreds of perhaps lesser known, but courageous writers who have stood watch and engaged.
The view of PEN Journey is global though the work is often local. As well as chronicling global events and personal history, PEN Journey recounts the shaping and re-imagining of this sprawling nongovernmental organization, one of the largest in terms of geographic reach. PEN has had to evolve and re-shape itself to serve its 155 autonomous centers. With at least 40,000 members around the globe in more than 100 countries, there are many stories others might tell, but this narrative is a close-up view of a period of time and of the writers who continue to work together in the belief that the world for all its differences and complexities can aspire to and perhaps even achieve “the ideal of one humanity living in peace and equality in one world.”* [*PEN Charter]
Because I tended not to throw away documents over the decades, I have an extensive paper as well as digital archive which I used to refresh memories and document facts. As I dug through files, I came across a speech I’d given which represents for me the aspirations of PEN, the programming it can do and the disappointments it sometimes faces.
At a 2005 conference in Diyarbakir, Turkey, the ancient city in the contentious southeast region, PEN International, Kurdish and Turkish PEN hosted members from around the world. The gathering was the first time Kurdish and Turkish PEN members shared a stage and translated for each other. I had just taken on the position of International Secretary of PEN and joined others at a time of hope that the reduction of violence and tension in Turkey would open a pathway to a more unified society, a direction that unfortunately has reversed.

PEN International Secretary Joanne Leedom-Ackerman speaking at PEN International Conference on Cultural Diversity in Diyarbakir, Turkey, March 2005
The talk also references the historic struggle in my own country, the United States, a struggle which is ongoing. “The arc of the moral universe is long, but it bends toward justice,” Martin Luther King is quoted as saying. This is the arc PEN has leaned towards in its first century and is counting on in its second.
From Diyarbakir Conference:
When I was younger, I held slabs of ice together with my bare feet as Eliza leapt to freedom in Harriet Beecher Stowe’s UNCLE TOM’S CABIN.
I went underground for a time and lived in a room with a thousand light bulbs, along with Ralph Ellison’s INVISIBLE MAN.
These novels and others sparked my imagination and created for me a bridge to another world and culture. Growing up in the American South in the 1950’s, I lived in my earliest years in a society where races were separated by law. Even after those laws were overturned, custom held, at least for a time, though change eventually did come.
Literature leapt the barriers, however. While society had set up walls, literature built bridges and opened gates. The books beckoned: “Come, sit a while, listen to this story…can you believe…?” And off the imagination went, identifying with the characters, whatever their race, religion, family, or language.
When I was older, I read Yasar Kemal for the first time. I had visited Turkey once, had read history and newspapers and political commentary, but nothing prepared me for the Turkey I got to know by taking the journey into the cotton fields of the Chukurova plain, along with Long Ali, Old Halil, Memidik and the others, worrying about Long Ali’s indefatigable mother, about Memidik’s struggle against the brutal Muhtar Sefer, and longing with the villagers for the return of Tashbash, the saint.
It has been said that the novel is the most democratic of literary forms because everyone has a voice. I’m not sure where poetry stands in this analysis, but the poet, the dramatist, the artistic writer of every sort must yield in the creative process to the imagination, which, at its best, transcends and at the same time reflects individual experience.
In Diyarbakir/Amed this week we have come together to celebrate cultural diversity and to explore the translation of literature from one language to another, especially to and from smaller languages. The seminars will focus on cultural diversity and dialogue, cultural diversity and peace, and language, and translation and the future. This progression implies that as one communicates and shares and translates, understanding may result, peace may become more likely and the future more secure.
Writing itself is often an act of faith and of hope in the future, certainly for writers who have chosen to be members of PEN. PEN members are as diverse as the globe, connected to each other through PEN’s 141 centers in 99 countries. [Now 155 centers in over 100 countries.] They share a goal reflected in PEN’s charter which affirms that its members use their influence in favor of understanding and mutual respect between nations, that they work to dispel race, class and national hatreds and champion one world living in peace.
We are here today as a result of the work of PEN’s Kurdish and Turkish centers, along with the municipality of Diyarbakir/Amed. This meeting is itself a testament to progress in the region and to the realization of a dream set out three years ago.
I’d like to end with the story of a child born last week. Just before his birth his mother was researching this area. She is first generation Korean who came to the United States when she was four; his father’s family arrived from Germany generations ago. I received the following message from his father: “The Kurd project was a good one! Baby seemed very interested and has decided to make his entrance. Needless to say, Baby’s interest in the Kurds has stopped [my wife’s] progress on research.”
This child will grow up speaking English and probably Korean and will also have a connection to Diyarbakir/Amed because of the stories that will be told about his birth. We all live with the stories told to us by our parents of our beginnings, of what our parents were doing when we decided to enter the world. For this young man, his mother was reading about Diyarbakir/Amed. Who knows, someday this child who already embodies several cultures and histories, may come and see for himself this ancient city, where his mother’s imagination had taken her the day he was born.
It is said Diyarbakir/Amed is a melting pot because of all the peoples who have come through in its long history. I come from a country also known as a melting pot. Being a melting pot has its challenges, but I would argue that the diversity is its major strength. In the days ahead I hope we scale walls, open gates and build bridges of imagination together.
–Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, International Secretary, PEN International, March 2005
PEN Journey 45: Dakar, Senegal: The Word, the World and Human Values
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.

Program for PEN International’s 73rd World Congress in Dakar, Senegal, July 2007
PEN International’s 73rd World Congress in Dakar, Senegal July 2007 celebrated the first Pan African PEN Congress with over 200 writers gathered from over 70 countries around the theme “The Word, the World, and Human Values.” The theme had been developed by PEN’s African centers who assisted in the planning of the Congress which brought together writers from every continent as well as from across Africa.
The setting was grand on the rugged Atlantic coast at Le Meridien Hotel. Government luminaries, including the President of Senegal Abdoulaye Wade and Prime Minister Cheikh Hadjibou Soumaré greeted delegates at the opening and closing ceremonies in the tiered auditorium where the Assembly of Delegates conducted PEN’s business. Ministers of Culture, Information and Foreign Affairs hosted dinners in the evening as did the President and Prime Minister.
Because PEN monitored the human rights situation in countries, particularly regarding freedom of expression, PEN vetted carefully countries where it held its Congresses. Senegal had prosecuted four journalists the past year, but none were in detention, and PEN Senegal and the International Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC) were advocating to abolish defamation laws used to repress writers across the continent. Senegal in general was an open society for writers. On the few occasions when PEN hosted Congresses in countries with more repressive regimes, it took no assistance from the government and used the occasion to advocate on behalf of the writers.
The 73rd Congress marked the end of my term as PEN International Secretary. At my first Congress as International Secretary, I’d opened with the image of a bridge soaring into the sky, a bridge that had taken decades to construct. I had suggested that for the last decade International PEN had been building an organizational bridge into the 21st century. Having occupied the position of International Secretary for three years on a daily basis, I could attest that PEN was a robust, though occasionally fragile, organization whose bridges across cultures were real, whose joints were welded by the principles of the PEN Charter and by the fellowship among writers.
For me, memories abounded—memories of the ancient city of Diyarbakir, Turkey where Kurdish and Turkish writers translated each other side by side for the first time; the gathering in Hong Kong where writers from mainland China, Taiwan, Hong Kong and the diaspora, along with other writers from around the world, met and shared ideas and literature; and the memory of the dungeons of Gorée Island with its dark doorway to the Atlantic, similar to “the door of no return” on Ghana’s Cape (Gold) Coast where the most basic human rights had been violated centuries before when men and women were shipped as slaves to other countries, including to my own.
At the Congress PEN members traveled to Gorée Island off the coast of Dakar to see and to pay homage to this history and through PEN’s work to act on behalf of freedom and human dignity today.

Visit to Gorée Island, Senegal. L to R: Carles Torner (Catalan PEN), Eugene Schoulgin (Norwegian PEN), Lucian Kathmann (San Miguel PEN), Eric Lax (PEN USA West), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (PEN International Secretary), Mamadou Tangara (Gambia.)
A Nobel Laureate in science once said, “Discovery consists in seeing what everyone else has seen and thinking what no one else has thought.” That could be said of the writer whose imagination saw bridges between people and cultures where others saw clashes and conflict.
Before each Congress I made a point of reading histories of PEN, particularly the history of the place where PEN was holding its Congress. The 73rd Congress was only the second time PEN’s whole international body had met in Africa. Forty years before a PEN delegate at the 35th Congress in Abidjan, Ivory Coast recalled ascending the stairs of the Congressional Hall between a double row of guards dressed in scarlet and gold with raised sabers. At that Congress PEN members took special notice of writers in prison in Communist and noncommunist countries. There were not many PEN centers in Africa then, but PEN Senegal existed. At the Congress the prior year in New York City in 1966, delegates from the Ivory Coast and Senegal had attended as had observers from Ghana, Kenya and Nigeria. By 2007 PEN had 15 centers in Africa, including in those countries whose writers had visited the New York Congress. Today PEN has 28 African centers.
At the Dakar Congress, writers from regions who hoped to develop PEN centers observed, including Uighur writers, Afar-speaking writers and writers from Tunisia, Bahrain, Iraq and Jordan, all of whom eventually formed PEN centers. Forty years ago International PEN also had observers from the Soviet-bloc. In all these instances, PEN had acted as a bridge to writers who aspired to share their literature and to work for freedom of expression in their societies.

PEN International President Jiří Gruša addressing PEN Assembly of Delegates at 73rd Congress, 2007.
In Dakar, International PEN President Jiří Gruša noted, “International PEN and its Centers are glad to be gathering in Senegal, a country which holds literature in high regard, in part because its first President Leopold Senghor was the internationally renowned poet and also a Vice President of International PEN.”
Mbaye Gana Kébé, Senegal PEN President, affirmed, “Senegal has remained a welcome land at the crossroads of all civilizations. In addition to that we have its democratic ideal and respect of human rights. This Congress taking place here consecrates a lasting and beautiful tradition of African hospitality.”

International PEN Board Member Mohamed Magani (Algerian PEN) talking with Alioune Badara Bèye (General Secretary Senegal PEN).
The Congress theme “The Word, the World, and Human Values” was explored thorough round table sessions including “Literature and the Oral Tradition” and “The Role of Contemporary African Literature in Intercultural Dialogue” and at International PEN’s first literary event “Freedoms” held outside under the stars. Hosted with TrustAfrica, a new African foundation that promoted peace, economic development and social justice, the evening and the panels featured writers from across Africa, noted Senegalese PEN Vice President Amadou Lamine Sall and General Secretary Alioune Badara Bèye who were instrumental in arranging the Congress. Writers included Bernard Dadié (Ivory Coast), Jean-Baptiste Tati Loutard (Congo), Fernando d’Almeida (Cameroon), Dieudonné Miuka Kadima Nzuji (Congo), Tanure Ojaide (South Africa), Frédéric Pacéré Titinga (Burkina Faso), Aminata Sow Fall and Pr. Abdoulaye Elimane Kane (Senegal), and Jack Mapanje (Malawi).
In the hotel’s meeting rooms, PEN’s standing committees adjourned. The Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC), chaired by Karin Clark (German PEN), focused on criminal insult and defamation laws, particularly in Africa. These laws endangered writers and resulted in imprisonments. During the previous year WiPC had followed 1100 cases worldwide of attacks on writers, ranging from killings, long term detentions, threats, and harassments. Around 320 of those had been in Africa.
PEN also brought attention to the refugee crisis in Iraq with an appeal for translators, writers and journalists who were being targeted for death because of their work. In a resolution supported by American PEN and passed unanimously, International PEN urged the US to protect these refugee writers and translators and to increase funding for UNHCR and other refugee services and remove barriers to resettling Iraqi refugee writers and intellectuals.
The Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee (TLRC), chaired by Kata Kulavkova (Macedonia PEN), considered the mounting threats to linguistic diversity in an English-dominated world. Delegate Esther Allen (PEN America) presented “To Be Translated or Not to Be: Globalization, Translation, and English,” a major survey of barriers to the exchange of literature and entrance into the international literary marketplace. The Assembly of Delegates passed a resolution calling on UN member states to comply with international conventions on linguistic rights.

International PEN Women Writers Committee Conference, Dakar, Senegal, July 2007.
The Women Writers Committee (IPWWC), chaired by Judith Buckrich (Melbourne PEN), met during the Congress and also at its own conference right after the Congress to examine the challenges faced by women writers, especially as related to freedom of expression and censorship, particularly in Africa. The writers also discussed women’s literacy and educational opportunities and explored the publishing potential for voices which struggled to be heard.
PEN’s Peace Committee, chaired by Edvard Kovač (Slovene PEN), met with an appeal to bring writers in countries at war together in an exchange of literature and ideas such as at a recent meeting between Turkish and Kurdish members
The Writers in Exile Network, chaired by Haroon Siddiqui (PEN Canada), reported that PEN continued to assist resettling writers under threat, often at universities, and also through partnership with the International Cities of Refuge Network (ICORN).
International PEN’s Executive Director Caroline McCormick and her team worked before, during and after the Congress on regional development. “International PEN is working in partnership with its African Centers to address challenges which they have identified in the region. Essential to this work is the role of continued engagement with reading, writing and ideas in bringing about change and empowering civil society.”
Each African center had its own history and focus though many overlapped. PEN Senegal, the first and oldest center in Africa, was dedicated to raising the profile of young and new unpublished writers and published an anthology of young writers and actively promoted work through its publications and competitions. The center had the advantage of a permanent writers house which was a drop-in center and focal point for the writing community and also accommodated visiting writers.
Guinean PEN had been established by the Women Writers Association of Guinea, which made it one of few African centers that had majority of women writers as members. Headed by Zeinab Koumanthio Diallo, President of Guinea PEN, the center ran its own museum and cultural center and raised the majority of funds through income-generating activities, including performances and cultural activities with a focus on literature and on raising awareness of social issues to include communities who didn’t normally have access to the world of literature. Projects included promoting reading in rural agricultural communities and using literature to support the rights of women and girls.
PEN International’s next regional focus would be Latin America in anticipation of the 2008 Congress. After a vigorous debate at the Congress, the Assembly of Delegates voted to move the 2008 Congress from Oaxaca, Mexico because of challenges to freedom of expression there to Bogotá, Colombia, hosted by Colombian PEN which was monitoring closely, along with International PEN, the situation for writers there.

Members of PEN International Foundation Board, final meeting. L to R: Fawzia Assaad (Suisse Romand PEN), Caroline McCormick (PEN International Executive Director), Karin Clark (German PEN), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (PEN International Secretary), Jiří Gruša (PEN International President), Britta Junge Pedersen (PEN International Treasurer), Eric Lax (PEN USA West).
The work of the 73rd Congress included the final disbanding of the International PEN Foundation which had served its purpose for over a decade as a charitable entity that existed with its own board alongside PEN International and enabled PEN International to receive charitable donations. Now that British charitable tax law had changed, PEN International, which was headquartered in London, could finally be incorporated as a charity.
The work of the Assembly of Delegates included elections of:
—International Secretary Eugene Schoulgin (PEN Norway), former WiPC Chair and International PEN Board member,
—Treasurer Eric Lax (PEN USA West), former International PEN Board member and former President of PEN USA West,
—International PEN Board members: Mike Butscher (Sierra Leone PEN), Haroon Siddiqui (PEN Canada), Takeaki Hori (Japan PEN) and Kristin T. Schnider (Swiss German PEN),
—Vice Presidents: Margaret Atwood (PEN Canada) for service to literature and Niels Barfoed (Danish PEN) for service to PEN.

PEN International Board Meeting and Staff in Dakar, Senegal, July 2007.
Three new PEN centers were welcomed: Iraq, Jordan and Afar-speaking.
The Assembly adopted twelve resolutions from the Writers in Prison Committee focusing on the imprisonment of writers in China, Tibet, Iran, Uzbekistan, Eritrea, Cuba, Turkey, Tunisia and Vietnam, the killing of journalists in Mexico & Afghanistan and the forced closure of television stations in Venezuela.
One unexpected controversy arose just a few weeks before the Congress when the British government conferred a knighthood on Salman Rushdie. The act stirred disputes in literary and political circles which threatened to follow us to the Congress. We came prepared should questions arise. I don’t recall now if the question was asked at the closing press conference where Jiří and I sat in our new African dress which had been given to us by the Congress hosts. Along with the President of Senegal PEN we recalled the successes of the Congress and the African programs which PEN International committed to continuing.
Rather than revisit the Rushdie controversy, I quote here PEN International’s response from Vice President and Nobel Laureate Nadine Gordimer: “International PEN deplores the reaction of extremists to the honor conferred upon one of the world’s great writers, Salman Rushdie, by the Queen of the United Kingdom for his services to literature. The appalling reaction from extremists threatens not alone the principle of freedom of expression as a basic tenant of justice, but seeks to decree the violent end to the life of a writer, solely on the grounds of written words that did not call for any aggression against any group or individual.”
My personal memories of the impressive Dakar Congress include being driven around in a limousine as International Secretary. Because PEN Board Member Eric Lax was hobbling on crutches with his foot in a cast, he also hitched a ride. I would have been happy to go on the bus, but we both appreciated the gesture.
Before each PEN Congress while I was International Secretary, I studied French. I hired a tutor and talked with her for hours, practicing conversation and comprehension and jotting down what I might want to say. I understood that it was important to know the language of so many of PEN’s members, especially when the Congress was in a French-speaking country. I didn’t do the same with Spanish because my Spanish was more remedial, but I had studied French at university and so had some base. French colleagues used to say, “Your accent is cute and you are fearless,” which I think was a nice way of saying you’re not very good, but at least you’re trying.
Before I came to the Dakar Congress, I had taken out my notebook from French lessons and copied on a single page the phrases I thought I might want to say at some point. When I arrived at the opening ceremony, I was seated on the dais along with Jiří, PEN’s Vice Presidents, the President of Senegalese PEN and the President of Senegal. I had not been informed that I was expected to give a speech, but my name, along with Jiří’s, was on the program. I knew Jiří didn’t speak French, and I felt it would be insulting for neither of us to speak in one of the languages of the country. That morning I’d tucked my sheet of phrases into my bag, and as I sat there, I glanced at the accumulation of sentences; they were a kind of speech so for the first few minutes I spoke in French then said, “Now I’d like to shift to English so I can speak better from my heart.” Everyone had translation equipment.
When the closing ceremonies arrived, the same situation arose. With the Prime Minister of Senegal also on the dais, I was again listed on the program to speak. However, this time Senegalese PEN had written remarks for me in French, and I stepped over to my nearby colleagues at French PEN to practice.

PEN International Secretary Joanne Leedom-Ackerman addressing Assembly of Delegates at 73rd PEN Congress, July 2007.
To close out this final memory, I share here a portion of my report to the Congress. Each International Secretary and President and Board member and Staff member brings his/her talents, skills and affection to this organization which is held together in part by ideals and friendship. In marking progress, no one diminishes the work that came before. I continue to note in wonder the improbability of an organization of writers connected around the globe in 150 centers in more than 100 countries surviving for a century. With gratitude I recognize those who have come before and kept the organization together and those who come after and add to the bridges and structures or whatever metaphor suits at the time. Here is a brief summary of my journey those years as International Secretary:
As an organization we have grown in the past three years, both in numbers of centers, scope of activity, and size of the Secretariat. We have worked to strengthen the infrastructure of the London office so that it can better assist the centers and can coordinate the international work of PEN. We have put financial systems in place for budgeting and have expanded fundraising, and have established employment procedures and contracts for staff and transparent criteria for our own grant-making.
The Board, which now meets monthly by phone, has worked, along with the Staff and myself, in this process. I want to take this moment to thank the Board whose members work hard on your behalf and each of whom has always said yes when asked to take on a task. I’ve also had the pleasure of working with a wonderful staff, first Jane Spender, who has now retired and sends her best and with the highly qualified team of Caroline McCormick, Sara Whyatt and now Frank Geary and Karen Efford and newer members Tamsin Mitchell and Emily Bromfield…I want to thank former International Secretaries Alexandre Blokh and Terry Carlbom who have always been available when I’ve sought counsel. And I want to thank so many of you in the centers who have helped me in the work and my home center in America for sustained support. Finally we all want to thank Senegalese PEN for its work in putting on this Congress and all the African centers who participated in this effort.
To finance PEN’s growth we have raised funds from new funders and from existing funders, who have signed onto the expanded program for International PEN and have given us larger grants…
I’ve had the pleasure of working with and visiting many of you and your centers over the last three years…One of the greatest pleasures of working with International PEN has been developing friendships around the globe.
PEN is only as strong as its centers. We have been working through our regional program on a one-to-one basis with centers in Africa this year to develop strategic plans. Through the Board we have also been in touch with centers whom we have not heard from in long time to see if they still exist and to find out how we might help them. Through the workshops at the Congresses and in the consultations last year with the whole membership, we have developed for centers a guide to good governance which we will share later at this Congress. Most PEN centers already operate according to the principles of transparent membership criteria, regular elections, rotation in office, and governance by a constitution, but other centers need assistance in this area.
PEN began as a club of writers committed to the ideals which developed over the years. But a club does not mean that qualified writers should be kept out of the work of PEN or that PEN should be an exclusive Academy. There has always been the balancing of PEN as a club and PEN as a nongovernmental organization (an NGO.) Each center chooses its activities, but internationally, PEN operates as an NGO. That is why we have consultative status at the United Nations. Clubs do not receive this status. As an international organization we work to achieve goals related to civil society—the goals of promoting literature and defending freedom of expression. The work of International PEN, through its committees and through the centers and writers who chose to participate in the international work, serves these goals.
This year Caroline and I visited UNESCO several times and are happy to report that UNESCO officials are enthusiastically recommending PEN’s partnership under the framework agreement be renewed for another six-year period. They specifically praised PEN for its “significant modernization.”
At a PEN Congress in 1966 the Mexican novelist Carles Fuentes took note of “the improbable spectacle of 500 writers—conservatives, anarchists, communists, liberals, socialists—meeting not to underline their differences or to enumerate their dogmas, but to bear witness to the existence of a community of spirit while accepting diversity of interests.” That is still what PEN is and what PEN represents to the world.
The theme of this Congress—The Word, The World and Human Values—resonates and was chosen by PEN’s African centers. I am particularly honored to be finishing my term in Africa, for African literature and the literature of African American writers have had a significant influence on my own work as a writer. I’d like to end with a verse from Senegal’s great poet and first President and also International PEN Vice President Leopold Senghor, from his elegy written after the assassination of my countryman Martin Luther King. Senghor’s life offered a kind of bridge in the world. Through his life and his words, he showed how an individual and a writer can in fact enhance human values.
From Senghor’s “Elegy for Martin Luther King”:
“As the Reverend’s heart evaporated like incense and his soul
Flew like a diaphanous rising dove, I heard behind my left ear
The slow beating of the drum. The voice and its sharp breath close to
My cheek said: ‘Take up your pen and write, Son of the Lion.’
“And I saw a vision…”
You must read the poem to see the vision, but I can tell you it is a vision very much in the spirit of PEN.
Next Installment: PEN Journey 46: Wrapping Up
PEN Journey 44: World Journey Beginning at Home
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.
After PEN’s Asia and Pacific Regional meeting in Hong Kong February 2007, I flew to Tokyo for a two-day visit with members of Japanese PEN, along with International PEN board members Eric Lax and Takeaki Hori. We met with Japan PEN’s board, and in the evening I shared a stage and conversation with Mr. Hisashi Inoue, chairman of Japan PEN and one of the country’s well-known playwrights. Part of our discussions explored the possibility of Japanese PEN hosting an International PEN Congress. Only once before, in 1984, was the World Congress held in Japan.

International PEN Board members Eric Lax and Takeaki Hori
Housed in an impressive building in Tokyo, Japan PEN was one of International PEN’s largest and most active centers with one of the more interesting histories. Founded in November 1935 on the eve of a tumultuous period in world affairs, Japan PEN members committed to the PEN ideals of freedom of expression and “one humanity living in peace in one world.” By 1935 Japan had left the League of Nations in the wake of the Manchurian Incident and was moving towards international isolation, a direction that concerned liberal literary figures and diplomats. In this climate International PEN in London, with support from leading novelists, poets and foreign literary figures, reached out and requested that writers in Japan form a PEN Club. Japan’s well-known novelist Toson Shimazaki served as the founding president. As suppression of free speech increased as war in the Pacific broke out and the Second World War advanced, Japanese PEN stayed in limited contact with International PEN in London and provided a unique portal to the world for its writers and citizens during that time.

Japan PEN members at PEN’s 71st Congress in Bled: Furukawa Taeko, Miyakawa Keiko and Yonehara Mari, along with Fawzia Assad (Suisse Romand PEN) Huguette de Broqueville (French PEN) and Celia Balcazar (Colombian PEN) and Takeaki Hori (PEN International Board & Japan PEN)
Personally, I remember the hospitality of Japan PEN members who took me out on the Ginza to toast my birthday as I rounded a decade. I had explained that I needed to fly home that evening, a day early to share the birthday. I still remember the glasses of pink champagne flowing up and down the Ginza, (though I was drinking sparkling water), as my own new decade was heralded, then flying halfway around the world and arriving in time to have another dinner that same night with my husband.
Three years later, in September 2010 Japan PEN hosted the 76th PEN International World Congress in Tokyo, one of PEN’s largest with representatives from 90 centers around the theme “The Environment and Literature—What Can Words Do?”
******
World War II, D-Day, the fall of the Berlin Wall—all were global events in the 20th Century which framed the history that followed for much of the world and stirred both despair and optimism among politicians and citizens and inspired stories and poetry among writers. PEN’s Peace Committee conference in March 2007 settled on three themes: Languages under Threat—Dying Cultures, Reading as a Social Event, and Post-Totalitarian Resistance.

Bled, Slovenia, setting of PEN International Peace Committee meeting, March 2007
In my files I found the keynote paper “Post-Totalitarian Resistance” by Peace Committee Chair Edvard Kovač, a portion of which I quote here. It provokes thought with the kind of open-ended questions that don’t necessarily have answers but can lead to discovery. Contents of PEN’s forums are among its important legacy.
After the fall of the Berlin Wall there was a great deal of hope that the era of totalitarian ideologies was over forever. Fukuyama and others even talked about the end of history. But ideological thinking has settled like sediment in people’s minds and it still persistently, albeit imperceptibly, affects our thoughts, conclusions and decisions.

Edvard Kovač, Chair PEN’s International’s Peace Committee, 2007
The role of the writer is to be vigilant and to recognize a transformation in the rigid thinking that until only recently stifled his creativity and pushed him towards dissidence. Perhaps he will notice that the ‘class struggle’ has been transformed and that out of this transformation the germs of new ideologies are emerging: to the legitimate striving for the creation of a Palestinian state a new anti-Semitism has been attached and alongside the right to the existence of the state of Israel the humane protection of civilian population has simply been forgotten. Recognition of and admiration for Third World culture is fortified by anti-Europeanism while a critical attitude to technological civilization confirms the ethno-centrism of the young states. The spread of democracy is confused with domination of the world market and a critical attitude to processes of globalization is interlaced with anti-Americanism. An emphasis on the need for virility conceals a kind of anti-feminism, while the emancipation of women facilitates a new uniformity. The elements of old totalitarianism which have transformed into foundations of new ideologies are harder to unmask as they appear in the name of anti-ideological principles…
…the demise of totalitarianism does not necessarily equate with critical thinking. The defeat of ideologies only creates the possibility of enlightened thinking. In fact, the desire for quick and simple solutions is even greater in post-totalitarian states. Hence the unbearable lightness of new populisms. If in the past it was politics that fully led the economy, it has now come to a complete turnaround so that the economy is stifling political initiative and economic success is putting a noose around the neck of culture and artistic creativity that cannot be marketed…
How can a writer establish a reasonable dialogue when faced with the new fundamentalisms of all colors and creeds?…this new humanism of the pen, which would once again oppose the violence of the sword (which is also the idea behind PEN’s logo) must create new means of expression. So what is the writer’s language in this new struggle?” —Edvard Kovač, Slovene PEN
There are no simple answers to these observations, but the questions continue to be worth asking in PEN’s forums.
Somewhere in the world during most weeks, if not most days, one of PEN’s 150 centers is holding an event or conference and is at work on behalf of writers. For me, the conferences and literary festivals in 2007 included a visit, along with PEN International Executive Director Caroline McCormick to New York to PEN America’s impressive World Voices Festival with over 100 writers from around the globe. The annual World Voices Festival anticipated and informed the launch of PEN International’s own Free the Word! Festival in London in 2008 and in subsequent countries thereafter.
One of the privileges of serving as International Secretary was visiting centers and members around the world though I couldn’t accept all invitations. I regret missing the celebration of PEN’s Global Library launched by members of Slovak PEN. The Global Library gathered books from PEN members worldwide in multiple languages. I missed a conference on freedom of expression and Kurdish literature and a conference in Georgia arranged by Three Seas Writers and Translators’ and the Georgia Writers Union under the auspices of UNESCO, a frequent funder for PEN gatherings. Other International PEN board members and Vice Presidents often did attend as well as the PEN members.

Visit to UNESCO headquarters. L to R: Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (PEN International Secretary), Eugene Schoulgin (PEN International Board Member), Eric Lax (PEN International Board Member), Homero Aridjis (Mexican Ambassador to UNESCO & former PEN International President), Caroline McCormick (PEN International Executive Director)
Following the World Voices Festival, Caroline and I, along with International Board members Eugene Schoulgin and Eric Lax, met with UNESCO officials in Paris where former International PEN President Homero Aridjis was now Mexico’s Ambassador to UNESCO. The meetings at UNESCO headquarters and with Homero and the US representative to UNESCO were in anticipation of the renewal of PEN’s formal consultative relationship and “Framework Agreement” with UNESCO. In the prior agreement PEN had also been recognized as a Category II organization with ECOSOC (United Nations Economic and Social Council.) These agreements were renewed every six years; the relationship continues to this day.
One country in which PEN and UNESCO were active, but not always with compatible agendas was Turkey. Because UNESCO depended on governments for its funding and PEN frequently criticized the Turkish government for its suppression of free expression, we sometimes walked separate paths in Turkey.
The month after the UNESCO meetings I participated in Istanbul in the Forum on Freedom of Expression, sponsored by that independent organization. Along with dozens of PEN members, I had attended the first Forum on Freedom of Expression in Istanbul in 1997 as Chair of PEN International’s Writers in Prison Committee, and I and other PEN members had spoken at many of the biennial meetings since.

Meeting before Forum on Freedom of Expression in Istanbul. L to R: Novelist Elif Shafak (PEN case at the time), Sara Whyatt (PEN International Writers in Prison Committee Program Director), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (PEN International Secretary), friend, Journalist Nadire Mater (PEN main case), Eugene Schoulgin (PEN International Board Member)
In Ankara, I was hosted at the International Ankara Short Story Days Festival, an initiative which also aspired to get UNESCO support to establish a World Short Story Day. Professor Aysu Erden, Turkish PEN’s international secretary and editorial board member of PEN International’s Diversity Project of the Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee (TLRC) was a champion of the effort. That year the theme was “Preservation of Multiculturalism and Diversity,” a UNESCO focus as well.

Joanne Leedom-Ackerman with Aysu Erden, Turkish PEN board member
In a visit to a large school in Ankara and at a program later that evening, we considered how people and societies bridged differences, how consciousness could change in societies and how literature and stories could play a role. I reflected on the changes during the civil rights movement in the U.S. where I had grown up.
“Many of the stories in my short story collection No Marble Angels are set in the late 1950’s and 60’s in the American South during a time of upheaval in the United States. It was a time when blacks and whites peered at each other over the barriers of history and laws which separated them,” I told both audiences, aware that in Turkey, Kurds often faced discrimination as did Armenians, and the writers who wrote about this discrimination could face time in prison.
That schism is still one of the U.S.’s major national dramas though much distance has been travelled in my lifetime. The abolishment of the laws of segregation and the opening up of opportunity has strengthened U.S. society immeasurably, though there is still a journey to take. It is the closing of the distance between people which has interested me as a writer over the years, whether the distance arises from race or gender or age or simply from the self looking out into the world and seeing an image other than its own.
One of the books that had an impact on me growing up was written by another Texan who literally changed the color of his skin in an attempt to get inside the experience of being black in the South during the time when racial covenants dictated where a person could get a drink of water or sit on the bus or go to the bathroom. John Howard Griffin’s Black Like Me came out when I was a school girl. I don’t remember if I read the book then, or a few years later, but when I read it, the dilemma it posed both shaped and mirrored feelings and questions which were growing in me. The questions were really questions of the human condition: Who am I? And who is that person who is not me and different from me?
For a time I considered these as political questions. I spent much of my youth debating issues of civil rights with family and friends. I located the antagonist outside myself, as some monolith, which for lack of a better description had a handle at the top, a wing on the west and several large rivers running through it. And so I left the state of Texas.
As long as the antagonist was outside in politics, society, and culture, I could separate myself from it. As a journalist in the Northeastern part of the United States, I gathered facts and statistics and social opinions and searched for answers to issues. I wrote articles on segregation and desegregation and integration of institutions in the United States. All the while other stories were building in me that I wanted to write, stories that couldn’t so easily be contained in facts and figures and social theory. I began a journey of my own, not by changing the color of my skin, but by considering experience from the inside out. I began writing fiction—short stories and novels. My writing changed from the journalistic to the consideration of the individual heart, from the objective to the subjective.
What continues to interest me in writing are the shadowy places in the individual heart, those places which keep us from seeing one another. Sometimes the distance between self and other is measured in terms of race, sometimes age, sometimes gender, sometimes culture, sometimes religion, sometimes country of origin. I’m interested in the way people go about making bridges or tearing them down.
To the extent a multicultural society recognizes the human spirit that connects its citizens at the same time valuing the cultural differences among them, the society progresses. Multiculturalism is at the heart of International PEN, which has 144 centers in 101 countries. PEN is committed to dispelling race, class and national hatreds in an effort to champion one humanity living in peace; PEN is also committed to freedom of expression.
Because we are writers, literature is our means of expression. Literature has an important role in bridging cultures. The first glimpse we have of another culture is often through reading. We let our imagination take an author’s images, scenes, and characters and bind them to our own lives. We draw from books wisdom and experience.
Many of the characters in my short stories are struggling to expand who they are and come out of themselves, to reach across to another person, to enter and occupy that space at the back of the house, that dark, vine-covered, musty room where “the other” lives. Entering that space, one raises the shades and opens the doors and windows and glimpses in the face of the other, a reflection of one’s self.
Next Installment: PEN Journey 45: Dakar—The Word, the World and Human Values
PEN Journey 43: Turkey and China—One Step Forward, Two Steps Backward
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.
January 2007 began with an assassination. The Board of PEN International was just gathering in Vienna for the first meeting of the year when board member Eugene Schoulgin got a phone call letting him know that our colleague and his friend Turkish-Armenian editor Hrant Dink, had been gunned down in Istanbul and killed. Many of us had seen Hrant at the PEN Writers in Prison Committee conference in Istanbul in March.
Editor-in-chief of the bilingual Turkish-Armenian newspaper Agos, Dink had long advocated for reconciliation between Turks and Armenians and for Turkey’s recognition of the Armenian genocide early in the century. Dink had received death threats before and had himself been prosecuted for “denigrating Turkishness,” but as with Russian colleague Anna Politkovskaya, Dink’s assassination stunned us all and set off widespread protests in Turkey and abroad. Eventually a 17-year old Turkish nationalist was arrested and convicted, but not before police were exposed posing and smiling with the killer in front of a Turkish flag.

PEN International Board Meeting, Vienna, January 2007. L to R: Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, International Secretary; Jiří Gruša, International President; Caroline McCormick, Executive Director; Judy Buckrich, Women Writers Committee Chair; Elizabeth Norgdren, Finish PEN; Eugene Schoulgin, Norwegian PEN; Franca Tiberto, Search Committee Chair; Sibila Petlevski, Croatian PEN; Britta Pedersen, International Treasurer; Eric Lax, PEN USA West; Mohamed Magani, Algerian PEN; Kata Kulavkova, Translation and Linguistic Rights Chair; Frank Geary, Programs; Karen Efford, Programs.
The work of PEN is, at its heart, personal. It is writers speaking up for and trying to protect other writers so that ideas can have the freedom to flow in society. In league with other human rights organizations, PEN also advocates to change systems that allow attacks and abuse. At times the work can feel ephemeral when the systems don’t change, or make progress only to regress. However, the individual writer abides, and PEN’s connection to the writer stands.
During my tenure working with PEN, Turkey and China have been the two countries that have imprisoned the most writers. For a period both nations appeared to be advancing towards more open societies but soon retreated. In the early 2000’s as Turkey aspired to join the European Union, the country operated as a democracy with a more independent judiciary; fewer writers became entangled in the judicial processes. However, in 2007 the democratic transition in Turkey began to veer off course and has continued a downward spiral towards authoritarianism ever since.
China also promised to become a more open society with the advent of the Olympic Games in 2008. Democracy activists inside and outside of China grew hopeful. In this climate, PEN held an Asia and Pacific Regional Conference in Hong Kong in February 2007; it was PEN’s first in a Chinese-speaking area of the globe. Over 130 writers from 15 countries gathered, including writers from Hong Kong, Taiwan and Macao and many of PEN’s nine Chinese-oriented centers as well as members from Japan, Korea, Vietnam, Nepal, Australia, the Philippines, Europe, and North America.
Both China’s and Turkey’s Constitutions protected freedom of expression in theory, but in practice the protection was lacking. Instead, laws and regulations prohibited content. In Turkey, exceptions included criticism of Ataturk, expressions that threatened “unitary, secular, democratic and republican nature of the state” which in effect targeted issues around Kurds and Kurdish rights. In China, the Constitution noted that “in exercising their freedoms and rights, citizens may not infringe upon the interests of the State, of society or of the collective, or upon the lawful freedom and rights of other citizens.” The state was the arbiter.
The Asia and Pacific Regional Conference in 2007 took place at Po Leung Kuk Pak Tam Chung Holiday Camp at Sai Kung, a scenic seaside area in the New Territories with programs also at Chinese University of Hong Kong and the Hong Kong Foreign Correspondents Club. The theme Writers in the Chinese World celebrated Chinese literature and a dialogue among PEN’s Asian centers and also explored issues of translation, women, exile, peace, censorship, internet publishing, freedom of expression and PEN’s strategic plan.

Asia and Pacific Regional Conference in 2007 at Po Leung Kuk Pak Tam Chung Holiday Camp at Sai Kung, a scenic seaside area in the New Territories. Over 130 writers from 20 PEN centers in 15 countries gathered for the four-day conference.
However, 20 of the 35 mainland Chinese writers who planned to attend were prevented or warned off by government authorities, including the President of the Independent Chinese PEN Center (ICPC) Liu Xiaobo, who later won the Nobel Prize for Peace in 2010 while imprisoned in a Chinese jail. Qin Geng had his permit rescinded and two writers—Zan Aizong and Zhao Dagong—were stopped at the border and denied permission to exit though they had permits. (Two overseas Chinese writers who attended and had other citizenship—Gui Minhai and Yang Hengjun—are now in prison in China and are PEN main cases.)
In addition, the Chinese Communist government banned eight books, including one by Zhang Yihe, an honorary board member of the ICPC who had been invited to speak at the conference but instead was warned not to attend.
China’s promised opening of its society was already contracting, and the restrictions bore a harbinger of events to come both for writers and eventually for Hong Kong. The conference attracted wide press attention with articles in Chinese and English newspapers in Hong Kong, Taiwan and Macao and globally via the BBC and newswire services. Renowned Shanghai playwright Sha Yexin, poet Yu Kwang-chung (Yu Guangzhong) from Taiwan and Korean poet Ko Un, short-listed for the Nobel Prize for Literature, attended. But the restrictions on the mainland Chinese writers cast an ominous shadow and grabbed the largest regional and international headlines.
“PEN has nine centers representing writers in China, Hong Kong, Taiwan and abroad and has great respect for Chinese Writers and Chinese literature,” International PEN President Jiří Gruša told more than 40 reporters at the Hong Kong Foreign Correspondents Club, “but we are very concerned by the restrictions on writers in mainland China to write, travel and associate freely.”
In honor of the absent writers, an empty chair sat on the platform for each session of the four-day conference.

Press Conference at Hong Kong Foreign Correspondents Club, February 2007; L to R: Translator, Journalist Gao Yu (Independent Chinese PEN Center), Jiří Gruša (PEN International President), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (PEN International Secretary)
In 2007 more than 800 writers were under threat worldwide, and at least 33 writers were in prison in China. A number of the attendees at the conference had been imprisoned and been main cases for PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC), including celebrated Korean poet Ko Un and Chinese journalist Gao Yu, both of whom addressed the conference. They knew firsthand the role of the writer in the struggle for freedom, and they knew the support PEN had given, observed one of the conference organizers Yu Zhang, General Secretary of the ICPC, half of whose members lived in mainland China.
“I am no longer afraid of anything,” one Chinese writer unable to attend said in a message to the conference. “Our bodies and our spirits are our own. To speak of ugliness and injustice we have to shout, but our throats are cut when we do.”
“We are willing for some things to be burned in the soil so a new leaf will come,” added another mainland writer in a message to the conference.
“It is important that all writers get together, and all writers protect the freedom of speech and free expression. We must write what’s in our hearts and write as a witness to history,” said Qi Jiazhen, who spent 10 years in a Chinese prison and now lived in exile.
Owen H.H. Wong of Hong Kong’s English-Speaking PEN Center pointed out that Hong Kong was a meeting point of East and West, North and South, Leftists and Rightists and Modernization and Classic writing. He noted that before the 1997 handover, Hong Kong writers saw themselves as writers in exile. Only those born in Hong Kong regarded themselves as Hong Kong writers. Now most publishing houses in Hong Kong were funded by the Communist government, and free expression in Hong Kong was threatened and controlled.
Yu Jie, a Beijing-based essayist and author and vice President of ICPC, spoke at the Foreign Correspondents Club noting that even though he was able to attend the conference and speak to the foreign media, he had not been able to get published in mainland China. For mainland writers, Hong Kong was a place where freedom of expression and freedom of the press still existed, he said. “It’s as if those of us in the mainland have our heads immersed in water and cannot breathe, but Hong Kong allows us to stick our heads above the surface of the water, and for a short time, breathe freely.”
He predicted that the authorities would later “settle the score” with the writers and publishing houses. He was in fact later arrested, tortured and imprisoned for his writing. In 2012 he emigrated to the United States.

PEN International Panel at Asia and Pacific Regional Conference. L to R: Conference organizers included Yu Zhang, (Independent Chinese PEN Center), Caroline McCormick (PEN International Executive Director), Chip Rolley (Sydney PEN)
“Existing in the unofficial nooks and crannies of an emerging civil society in China, ICPC is determined to insist that their country live up to the rights guaranteed in its Constitution,” said another conference organizer, Chip Rolley, Vice President of Sydney PEN. “This continuing work will ensure that there is indeed a turning point for PEN in China and the wider Asia and Pacific region, and that this historic conference will not dissipate like smoke.”
In his keynote address Taiwanese writer and poet Yu Kwang-chung called for “all the writers and the poets across the Chinese world” to strengthen the channels of mutual exchange, and make efforts to find a consensus on basic issues such as the formation of a common national culture (which includes in particular the establishment of joint aesthetic and literary values) in order to “make a valuable contribution to preventing war and maintaining peace.”
Attendees launched a dialogue on literature as well as on networking among PEN’s Asian centers with a regional strategy for freedom of expression and translation. The conference was part of PEN International’s program to develop the regions in which PEN operated by connecting existing writers and PEN centers and also developing new centers in countries starting to open up such as Myanmar/Burma. Often a PEN center was one of the first civil-society organization to set down roots when authoritarian controls began to relax. [A Myanmar PEN Center was established in 2013.]
In a panel on Literature and Social Responsibility panelists noted that free speech and writers’ responsibilities were the basis of social prosperity and that PEN was a bridge between writers and their responsibilities.

Participants at Asia and Pacific Regional Conference from China, Hong Kong, Japan, Korea, Philippines, Vietnam, Nepal, including speaker Yu Kwang-chung (Taiwan) seated in center.
Chen Maiping of ICPC read a message from Zhang Yihe, the mainland novelist who was to have been on the panel but who had been prevented from attending. “There is a saying: human hearts are like water, while people’s favor and loyalty feel as heavy as mountains. During these ten plus days since my books were banned, so many people have shown their concern I have nothing to give in return for their kind support other than to express my gratitude on paper. Writing is my only means of self-expression. Writers have always been prisoners of language and words. It is not an easy affair for me to live, nor can I die in peace. I can only write…In China we talk about ‘literature as a vehicle for the Tao (the Nature, the Way).’ People have talked about this for thousands of years. However, those who have written the best literature are exactly those who never think about their social responsibility. Zhang Bojun [the author’s father who was a scholar and a minister in the Chinese government in the 1950s and persecuted during the 1957 Anti-Rightist campaign in Mao’s Cultural Revolution] was an example of this. In my view his achievements were much greater than many of the contemporary writers, artists and painters. If a writer has too strong a responsibility, he may have no achievements at all.
“For several decades, literature has been tied together with ‘revolution’ and ‘reform.’ I can’t bear such responsibility. I can only recall the past. I do not have such social responsibility tied to ‘revolution‘ and ‘reform.’ I am out of date. There are so many people singing praise for the society, why not allow an old woman like me to sing a little song of my own. I am only a piece of withered leaf. I hope that I can decay quickly so that I may become a new leaf soon. “
Chen Maiping also read “Writing in Anger” by Liu Shu, another mainland writer prevented from attending. “The conflicts between our hearts and reality and an unwillingness to keep silent are the driving forces for my writing. The disgraceful politics have turned us into dissident writers. Chinese dissident writers write in isolation. The marginalized position of dissident writers has marginalized their writing. This is very different from the West. The Eastern people have the ability to suffer and digest their sufferings. This kind of ability enables writers to ignore the reality and to become numb to the suffering of their people. They choose to write only about ‘pleasant things to lighten the load on their hearts.’
“The cruelty of reality fills their lives with ‘submission.’ The writers are swollen and weighed down with humiliations and sufferings; they have lost the anger created by their reality. They have no anger at the past, nor do they imagine a future. They only write about meaningless, shallow and trivial affairs. My anger comes from my refusal to accept and make peace with this reality. I have been detained four times because of my ideas. We puzzle over social phenomena but we long for peace. The way to calm our anger is to write…I must speak for citizens who were screened by the totalitarian society, by the police and the ugly society…we do not want to be silent. Like Lu Xun said, life is ourselves: everybody is responsible for his own life. Our flesh body and our life are in exile in our homeland, until we disappear.”

Women Writers Committee gathering at Asia and Pacific Regional Conference including Chair Judy Buckrich in turquoise in center.
Women participants at the conference focused in addition on the restrictions for women writers in the region.
Qi Jiazhen was imprisoned 10 years and accused of trying to overthrow the government after she inquired whether she could study aboard. She said she had been young and inexperienced and felt guilty and wrong, the same feeling shared by other women. Gender awareness was low in China, she said. She now lives in Melbourne, Australia.
Celebrated mainland journalist Gao Yu confirmed two kinds of prisoners in China—special treatment prisoners & prisoners of conscience. As vice chief editor of an economic weekly with an international reputation, she was a special treatment prisoner. She had treatment when she was sick and had to do little hard manual work because was already 50 and given 7 years in prison. But she never admitted her wrong doing so she didn’t enjoy any pain reductions, she said.

Chinese journalist and PEN main case Gao Yu with translator.
In a panel on Censorship and Self-Censorship, Gao Yu noted that censorship began at school where children learned to protest injustice when not treated fairly. Later in life that grew into resistance of the system. The writer who sought to express truth experienced censorship which could lead to punishment and prison. But that was not as frightening as being silent, she said. The essence of being a writer was to have integrity and speak the truth.
After the conference, a dozen police picked up one participant and took him to a hotel room to find out what the conference had been about. A poet and member of ICPC, he told the police, “To build a ‘harmonious society’ and ‘harmonious culture’ [as President Hu Jintao has called for], writers should sit with writers and not always have to sit with policemen.” He was finally released after hours of interrogation.
One of the more creative campaign tools planned during the conference was spearheaded by a team of PEN Centers in Asia, Europe, North America and Australia. The members developed a digital relay with Chinese poet Shi Tao’s poem June. The poem tracked the path of the Olympic torch across a digital map. Shi Tao was serving a 10-year prison sentence for sharing with pro-democracy websites a government directive for Chinese media to downplay the 15th anniversary of the Tiananmen Square protests. His emails had been turned over to the Chinese government as evidence by Yahoo. His poem commemorated the Tiananmen Square massacre and was translated and read in the languages of PEN’s centers around the world, including in regional dialects as well as in the major languages. Ultimately 110 of PEN’s 145 centers participated and translated the poem into 100 languages, including Swahili, Igbo, Krio, Tsotsil, Mayan. The poem’s journey began on March 30, 2008 in Athens and traveled to every region on the online map, arriving in Hong Kong on May 2 and in June to Tibet where it was translated into Tibetan and the proposed Uyghur PEN center translated it into Uyghur. Finally August 6-8 it arrived in Beijing where it was translated and read in Mandarin. Anyone could click on the map and hear the poem in the language of the country designated.
By the 2008 Olympic Games 39 writers remained in prison in China.
June
By Shi Tao
My whole life
Will never get past ‘June’
June, when my heart died
When my poetry died
When my lover
Died in romance’s pool of blood
June, the scorching sun burns open my skin
Revealing the true nature of my wound
June, the fish swims out of the blood-red sea
Toward another place to hibernate
June, the earth shifts, the rivers fall silent
Piled up letters unable to be delivered dead.
(Translated by Chip Rolley)
Next Installment: PEN Journey 44: World Journey Beginning at Home
PEN Journey 42: From Copenhagen to Dakar to Guadalajara and in Between
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.

Royal Danish Library extension in Copenhagen, dubbed the Black Diamond (Photo by © User:Colin / Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=66870365)
Arriving in Copenhagen in early September 2006, I walked along the waterfront, dodged bicycles and shared coffee and conversation with longtime colleague Niels Barfoed, former President of Danish PEN who had briefly succeeded me as Writers in Prison Chair and was an eminent Danish journalist and writer. We met at the new waterfront extension of the Royal Danish Library, dubbed the Black Diamond because of its imposing black granite cladding and irregular angles. Niels would be moderating a public meeting on Freedom of Expression in the Arab World.
PEN International’s base was broadening in the Middle East and in Africa, both regions where active centers for writers were fragile, but potentially important havens. Danish PEN was hosting a conference with a dozen writers from the Arab-speaking world, including representatives from Egypt, Morocco, Jordan, Palestinian PEN, Tunisia, Lebanon and invited writers from Iraq and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), along with Danish and Norwegian PEN members and International PEN represented by Centers Coordinator Peter Firkin and myself.
The Copenhagen conference had been initiated in part as a response to the Danish cartoons controversy earlier in the year and also as an opportunity to develop PEN’s work and presence in the Middle East. PEN had a few centers in the region and interest from writers in Jordan, Iraq, Kuwait, and Bahrain to form additional PEN centers and a desire to revive PEN Lebanon. Developing PEN centers in these areas was challenging given the politics and conflicts on the ground.
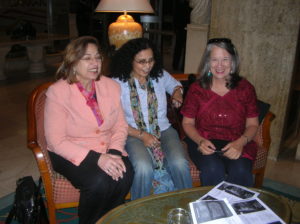
Ekbal Baraka, President Egyptian PEN (left) and Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, PEN International Secretary (right) meeting in Cairo, 2006
The Copenhagen meetings explored common fields of interest among Western and Arab writers, networking among Arab writers and ways in which PEN could assist. Women writers in the Arab world had particular challenges, a discussion led by Egyptian PEN President Ekbal Baraka. Ekbal later became Chair of PEN International’s Women Writers Committee. Algerian PEN and International PEN board member Mohamed Magani offered to host a subsequent meeting in Algiers the following fall, along with a conference on translation. A public event in the evening showcased the work of the visiting writers.
On the final day the public conference on Freedom of Expression in the Arab World moderated by Niels included discussions on Networking in the Cause for Freedom of Media and Opinion and featured renowned Tunisian journalist and human rights campaigner Sihem Bensedrine. A discussion on Access to Information: Implications to Development was addressed by Jordanian journalist Daoud Kuttab and Danish columnist and Danish PEN President Anders Jerichow. Lebanese Writer Elias Khoury and Egyptian journalist and commentator Mona Eltahawy concluded the conference in a discussion on Publication and Powerplay in the Middle East.
The days together resulted in a loose network of these and other Arab writers and eventually led to the opening of additional PEN centers and work in the Middle East. PEN currently has Bahrain, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, and Palestinian centers as well as the Egyptian, Algerian and Moroccan Centers.
******

Anna Politkovskaya, Russian journalist assassinated, 2006
A few weeks after the Copenhagen conference, my phone rang early on Saturday morning October 7, 2006 at my home in Washington, DC. Sara Whyatt, PEN International’s Writers in Prison Committee Director, was on the line. She called to tell me that Anna Politkovskaya, Russian journalist, PEN member who’d visited PEN Congresses and meetings, who’d worked for years reporting on Chechnya—had been assassinated. The report was that Anna had been shot that morning in the elevator of her apartment building in Moscow.
For seven years Anna had been one of the few reporting on the war in Chechnya despite intimidation and violence. She had been arrested by the Russian military and suffered a mock execution; she’d been poisoned while flying from Moscow to the Beslan school hostage crisis and had to turn back to get medical treatment. She had survived many dangerous encounters. But now she had been killed.
The killing of Anna Politkovskaya swept through the news media around the world as well as through the PEN world. We were stunned and deeply saddened and then began our protests and calls for investigation, along with human rights organizations worldwide. PEN honored Anna at its subsequent Congress and meetings and annually held an Anna Politkovskaya lecture on the anniversary of her death to commemorate her fortitude and inspiration.
The work in PEN was a helix of hope and pain and sorrow and hope again.
******

Dakar, Senegal, venue for PEN’s upcoming 73rd World International Congress in 2007
At the end of November Senegalese PEN hosted a meeting with African centers engaged with the planning of PEN’s 73rd Congress to be held in 2007 in Dakar. The meeting included representatives from Egypt, Morocco, Algeria, Guinea, Senegal, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, and Ghana. It was standard practice for International PEN to visit the site of an upcoming Congress to review logistics and budgets and programs in advance, to assist and assure the Congress ran smoothly. The 73rd Congress in Dakar would be only the second time a PEN Center in Africa had hosted a World Congress. In addition to reviewing the facilities at the Meridien hotel by the ocean, the delegation met with the Minister at the Ministry of Culture and Classified Historical Heritage which was supporting the Congress.
At that meeting and throughout the Congress to come, I offered the sentiment I had drafted and memorized in French and still endorse:
“Il n’y a que quelques autres pays dans le monde ou l’ecrivain est plus honore qu’au Senegal.
“There are few countries in the world where the writer is more honored than in Senegal.”
Because Senegal’s founding President Leopold Senghor had been a poet and writer of global distinction, also a Vice President of International PEN, Senegal celebrated literature. “As a national leader, Leopold Senghor left a rich heritage and respect for African culture and writing which we hope to honor by International PEN’s upcoming Congress in Dakar,” I told the Minister.

Karen Efford, PEN Program Officer, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, PEN International Secretary, and Caroline McCormick, PEN International Executive Director, meeting in Dakar. Senegalese PEN members organizing PEN 73rd World Congress included Abdoulaye Racine Senghor, Abdoulaye Fode Ndione, Mamadou Diop Traoré, Seydi Sow, Mbaye Gana Kehe, Alioune Badara Beye, Elie-Charles Moreau, Silcarneyni Gueye, Aissatou Diop
Senegalese PEN hosted our working meetings at its headquarters where the focus was also on regional development. International PEN’s Executive Director Caroline McCormick and Program Officer Karen Efford led a “mapping” or gathering of information with each center on its activities and membership and needs in order to determine how PEN International could assist, especially with fundraising. The Centers also participated in the discussions on the programs and facilities for the July 2007 Congress.
After hours of meetings, we all went to dinner together at the local restaurant. I don’t remember the food, except there were generous plates family style. I remember the atmosphere—the bright blues and reds and yellows in the restaurant, the music, and the laughter after a long day concentrating on budgets, logistics, and translations. The planning meetings were work but also fun with friendships among the writers from the PAN Africa Network with whom I had met on numerous occasions over the past few years.
In my three years as International Secretary, I was impressed by the care of all the host centers for Congresses. The Congress in Senegal would be my last as an officer of International PEN, except for the privilege of attending as a Vice President in the years to come. The operational work and responsibility would be passed on. I had determined not to stand for a second term. I had other responsibilities that had been put on hold for three years, and I had learned it was better to leave a position when everyone wanted you to stay, than to stay too long when people were waiting for you to leave. I needed to return to being a writer and to my family and to the other organizational work I did. So Senegal would be a farewell of sorts for me. It would prove to be a grand occasion, but I am getting ahead of myself…
******
“Does Freedom of Expression Have a Limit?” “Hospitality without Borders.”—those two panels I participated in and moderated at the 2006 Gothenburg Book Fair, Scandinavia’s largest. The International Publishers Association (IPA) and International PEN had been collaborators in selecting the Fair’s theme of Freedom of Expression that year. The Book Fair reflected the Freedom of Expression theme in many of its over 2000 events for the 100,000 visitors. PEN and IPA, along with the International Cities of Refuge Network (ICORN), had an exhibit with a stage where events and seminars took place.
For me, it was a special pleasure to attend the Fair in Sweden where my mentor and predecessor as Writers in Prison Chair Thomas von Vegesack was a respected and now retired publisher. Thomas attended the Book Fair. I noted in my remarks that it was from Thomas I’d learned the difference between having principles and simply talking about principles. Thomas didn’t like “principles,” which meant he didn’t like paradigms of abstractions. Our role—PEN’s role—was pragmatic. It was to help writers in trouble, to be in touch with them and their families so the isolation of imprisonment was broken, to give them support and most of all to figure out where the access was within our PEN centers and within our larger freedom of expression community to pressure governments to spring open the prison doors and also to get protection for writers under death threats. (It was two weeks after the Gothenburg Book Fair that Anna Politkovskaya was assassinated.)
The world had changed since the days Thomas and I had been chair of WiPC. In the late 1980’s and early 1990’s we had all been hopeful that the fall of the Berlin Wall and the fall of the totalitarian governments would ease the situation for writers worldwide, but there were now as many writers as ever under threat. PEN’s casebook listed over 1000. There were more non-state actors. There was also a level of global communication that was only budding in 1993 when Thomas handed over the reins to me. There were new bad guys, and many of the good guys were not as good as they once were. We were in a world where freedom of expression was no longer accepted as an unqualified value.
Yet “the world is still changed by ideas and books, and writers who write them are still the main vehicle for ideas,” I concluded my opening talk.
On the panel “Does Freedom of Expression Have a Limit?” we had no easy answer. We asked if there was a personal and public responsibility to tell the truth, or at least not to lie. And who determined a lie? The responsibility of the writer was to try to find and tell the truth even if truth seemed relative at times. The question arose, who sets the limits on freedom of expression? The State? Society at large? What were those limits and penalties and were they set by fear of attack or violence or censorship?
It was generally agreed that calls for violence such as the killing of another human being set a limit on freedom of expression, especially when this call came from someone who had the power of the state to exercise the threat. An example was the fatwa on Salman Rushdie. The limit should not be on Rushdie but on the Ayatollah and the state that issued the fatwa calling for his death.
Hate speech had a limit when it urged violence as in the case of Radio Rwanda during the genocide against the Tutsis or certain broadcasts during the Balkans wars.
PEN’s Charter contained the elements of the dialectic upon which free societies were based, both the respect for other cultures in an effort to dispel race, class and national hatreds and also a commitment to protect the free and unhampered transmission of thought and ideas.
“And since freedom implies voluntary restraint, members pledge themselves to oppose such evils of a free press as mendacious publication, deliberate falsehood and distortion of facts for political and personal ends,” the PEN Charter concluded.
Democracies flourish only when an exchange of competing, even contradictory, ideas can occur in a battle of ideas, the panel concluded.

Novelist Moris Farhi, former WiPC Chair and PEN Vice President/English PEN
The panel “Hospitality Without Borders,” co-sponsored by ICORN, featured Orhan Pamuk, the Turkish novelist who a month later won the Nobel Prize for Literature, and Moris Farhi, also Turkish but long resident in the UK and member of English PEN. Moris had followed me as Chair of PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee after Niels Barfoed’s brief tenure.

Novelist Orhan Pamuk (Photo credit: © Elena Seibert)
The previous year, Orhan had faced charges of “insulting the Turkish Army and Turkishness” because of his statement in a Swiss newspaper regarding the Armenian genocide and massacre of a million Armenians and 30,000 Kurds in Anatolia in 1919. On the panel Orhan noted how valuable it was for a persecuted writer in his home to know about the possibility of finding refuge in a safe city, even if he didn’t take advantage or was unable to leave his present situation at the time.
Moris, who’d also chaired English PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee, talked about the challenges facing the host city and the community receiving a guest writer. He focused on how to make sure the writer didn’t just disappear from the literary community and the need to focus on translation and publishing strategies for the writer. It was important to help the writer establish new foundations and relationships in a new city.
I recalled the situation of Bangladeshi novelist Taslima Nasreen who had faced death threats and was given asylum in Sweden and awarded the Tucholsky prize. Taslima Nasreen’s was one of the more dramatic cases in my PEN history as she was whisked out of Dhaka in the dark of night and brought to Stockholm by Swedish PEN. That had turned out to be just one stop on a difficult journey into exile.
******
 At the end of 2006, PEN Guadalajara, San Miguel PEN and the Ibero-American Foundation of PEN established a presence for the first time at the 20th Guadalajara Book Fair. The Guadalajara Book Fair was considered the most important publishing event in the Spanish-speaking world, hosting 450,000 visitors and 15,000 book professionals from over 40 countries. Officials of the Guadalajara Book Fair were eager to have a relationship with PEN in order to collaborate and “create and guarantee space in which literature of different languages cohabit supporting the freedom of opinion with words as vehicle of understanding between different nations and cultures,” according to the Coordinator of the Festival events.
At the end of 2006, PEN Guadalajara, San Miguel PEN and the Ibero-American Foundation of PEN established a presence for the first time at the 20th Guadalajara Book Fair. The Guadalajara Book Fair was considered the most important publishing event in the Spanish-speaking world, hosting 450,000 visitors and 15,000 book professionals from over 40 countries. Officials of the Guadalajara Book Fair were eager to have a relationship with PEN in order to collaborate and “create and guarantee space in which literature of different languages cohabit supporting the freedom of opinion with words as vehicle of understanding between different nations and cultures,” according to the Coordinator of the Festival events.
International PEN aspired to have a more robust presence at book fairs globally, but did not yet have the budget or staff. However International PEN supported centers’ activities at book fairs such as at Frankfurt, Gothenburg, and now Guadalajara. I visited the Guadalajara Book Fair as part of this initiative.
PEN Guadalajara and San Miguel and the Ibero-American Foundation of PEN hosted a stand at the Book Fair and offered readings and presentations of books and displayed hundreds of books from PEN members and PEN centers around the globe. On the Book Fair’s program two eminent PEN members, Vice President Nadine Gordimer and former PEN International President Mario Vargas Llosa were featured. Nadine Gordimer participated in a Literary Salon and later had dinner with PEN members. I have no notes from that dinner, but I have fond memories of the outside restaurant in the evening and the hospitality of Guadalajara and San Miguel PEN and the graciousness of Nadine Gordimer.

Photo Left: Meeting at 2006 Guadalajara Book Fair: María Elena Ruiz Cruz, Víctor Sahuatoba, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, Lucina Kathmann, Luis Mario Cerda, Martha Cerda, Moisés Zamora. Photo Right: At dinner: Moisés Zamora, Nadine Gordimer, Martha Cerda, and Joanne Leedom-Ackerman
Martha Cerda, President of Guadalajara PEN, PEN Vice President Lucina Kathmann of San Miguel PEN and I met with Book Fair officials and assured that PEN would have a presence and partnership with the Guadalajara Book Fair in the years to come through its Latin American centers.
The visit to Guadalajara also offered the opportunity to meet with members from several Latin American PEN centers in a preliminary focus on the region and on the “mapping” International PEN would undertake of resources, programs and needs of the Latin American PEN centers before the 2008 Congress in the region.
******
At the end of 2006 PEN’s long time staff member Jane Spender retired. Jane had worked with Peter Day on the PEN International Magazine as an editor; she’d been administrative assistant to the Administrative Secretary Elizabeth Paterson and then became the Administrative Director when Elisabeth retired. She had taken on the role of International PEN Program Director when PEN hired an Executive Director. We all relied on Jane’s intelligence, good humor and patience. Jane and I had spent hours—too many hours we both agreed—toiling over just the right word on several documents. I was especially going to miss working with Jane; I have kept the friendship to this day. To celebrate the past and send her off with good wishes for the future, we surprised her by giving her a bicycle which I rode across the office and presented to her. Friends from International PEN and English PEN all gathered in PEN’s new offices on High Holborn. PEN is about people, and Jane was one of the stalwart ones.

Jane Spender retirement party at PEN offices, 2006. L to R: Sara Whyatt, Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, Jane Spender, Caroline McCormack, Karen Efford, Terry Carlbom, Ursula Setzer, Josephine Pullen-Thompson, Francis King, Peter Day, Gilly Vincent, Jane Spender, Nawal, Karen Efford, Elizabeth Paterson
Next Installment: PEN Journey 43: Turkey and China—One Step Forward, Two Steps Backward
PEN Journey 41: Berlin—Writing in a World Without Peace
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.
I first visited Berlin in the fall of 1990 just after Germany reunited. I was living in London and took my sons, ages 10 and 12, to witness history in the making. I returned on a number of occasions, researching scenes for a book, attending meetings, and visiting German PEN in preparation for PEN’s 2006 Congress. Each time Berlin’s face was altered as the municipalities east and west moved to become one city again.

PEN International’s 72nd World Congress, Berlin, 2006
At the time of PEN’s Congress in May 2006, Berlin was bedecked with water pipes above ground—pink, green, blue, red—before the city buried its plumbing and infrastructure beneath the streets. Portions of the city had the appearance of an amusement park; there were also sections of the Berlin Wall with its colorful graffiti still standing, more as art exhibit than stark barrier to freedom.
“Welcome to a United Berlin” the German PEN President headlined his letter to the 450 delegates and participants for PEN’s 72nd World Congress. The Congress theme “Writing in a World Without Peace” was challenged by the reunification of Berlin and Germany, a historic event which bode well for the prospects of peace and which stood in contrast to the history that had come before. Yet the globe was still in conflict in the Middle East, in Asia and in Latin America where writers were under threat.
“There are countries such as Iran, Turkey or Cuba, where authors are jailed because of their books,” noted International PEN President Jiří Gruša. Resolutions at the Congress addressed the situations for writers imprisoned or killed in China, Cuba, Iran, Mexico, Russia/Chechnya, Sri Lanka, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, and other countries.

Left: Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC) meeting at Berlin Congress. Karin Clark (Chair WiPC) and Sara Whyatt (WiPC Program Director). Right: WiPC Conference in Istanbul: Eugene Schoulgin (Norwegian PEN/PEN Board), Jens Lohman (Danish PEN), Jonathan Heawood (English PEN), Notetaker
Two months before in March, over 60 writers from 27 PEN centers in 23 countries had gathered for International PEN’s Writers in Prison Committee conference in Istanbul where the WiPC planned a campaign against insult and criminal defamation laws under which writers and journalists were imprisoned worldwide. The conference also addressed the recent uproar over the Danish cartoons, impunity and the role of internet service providers offering information on writers, especially in China. A working group formed to support the Russian PEN Center which was under pressure from the Russian government.
Berlin, however, was sparkling and filled with the energy of reunification. “Today, this city—once separated by a Wall most drastically manifesting the division of Germany and Europe—has not only been re-established as the capital of Germany, but has simultaneously turned into a thriving meeting-place between East and West and North and South,” welcomed Johano Strasser, German PEN President. “Here in Berlin, history in all its facets—from the great achievements of German artists, philosophers and scientists to the crimes of the Nazis—has left its mark on the urban landscape.”

Left: German Chancellor Angela Merkel addressing PEN members at 72nd PEN Congress, 2006; Right: PEN International President Jiří Gruša speaking to PEN delegates and members at the Federal Chancellery; front row: German PEN President Johano Strasser, Chancellor Angela Merkel and PEN International Secretary Joanne Leedom-Ackerman. [Photo credit: Tran Vu]
The keynote address by Nobel laureate Günter Grass challenged the conflicts around the globe and the countries engaged in them. “There has always been war. And even peace agreements, intentionally or unintentionally, contained the germs of future wars, whether the treaty was concluded in Münster in Westphalia, or in Versailles,” he said.

Nobel laureate Günter Grass addressing Opening Ceremony of PEN International’s 72nd World Congress in Berlin, 2006 [Photo credit: Tran Vu]
As I sat on the dais on the edge of the stage listening to this renowned German writer, I leaned over to Jiří and said, If there is a standing ovation, I can’t stand. I was concerned. Grass could say and think whatever he wanted, but PEN was a non-political organization. Whatever my views of my country’s foreign policy, I was an American; I was also the mother of a son in uniform. Jiří leaned back to me and said in effect: Don’t worry, I won’t stand either. The speech ended with applause but no ovation, and then everyone got up and went to the next event.
It wasn’t my role to argue with Günter Grass even had the occasion allowed. But it was important that PEN assure the open space for debate existed which it did later in the Congress workshops and programs. PEN was filled with a multitude of points of view among its members; it did not have a litmus test of politics, only a commitment to the free expression of ideas. It offered a wide tent where views could be debated and challenged. Dogmatic political certainties often fell on their own in the alchemy of literature and imagination.

PEN members and delegates from around the world at Opening Ceremony of 2006 PEN Congress [Photo credit: Tran Vu]
Programs at the Congress also featured Nobel laureate and PEN International Vice President Nadine Gordimer and writers from around the world, including former International PEN Presidents Ronald Harwood, and György Konrád, Bei Dao, A.L. Kennedy, Margriet de Moor, Péter Nádas, Per Olov Enquist, Mahmoud Darwish, Duo Duo, Jean Rouaud, Johano Strasser, Veronique Tadio, Patrice Nganang and others. These writers participated in the literary events, including an evening of African literature and one of writers of German literature who had immigrated from abroad to Germany or had non-German cultural backgrounds. Afternoon literary sessions included prominent PEN writers introducing authors of their choice, an afternoon of essays and discussions on the theme Writing in a World without Peace and a lyric poetry afternoon.
PEN’s 85th anniversary coincided with the 60th anniversary of the United Nations. Both organizations had been founded after a World War out of an idealism that arose from desperate times with the hope that the future could be better than what had just transpired. “Both organizations were founded on a belief in dialogue and an exchange of ideas across national borders,” I noted in my address to the Assembly of Delegates. “When U.N. members were writing the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the framers consulted, among other documents, PEN’s Charter.”
PEN also had a history with the city of Berlin, where PEN members had gathered in 1926 for the first international meeting of importance held in Berlin after World War I. At that Berlin Congress tensions had arisen among old and young writers, writers from the west and the east, and debate had flared about the political versus the nonpolitical nature of PEN. The debate that stirred in Berlin in part led to the framing of PEN’s Charter the following year.
Since those early days, PEN had grown in size beyond what the founding writers might ever have imagined. After the 2006 Berlin Congress, with the addition of centers in Jamaica, Uruguay, and Pretoria, South Africa, PEN had 144 centers in 101 countries in almost every time zone. The PEN world didn’t sleep. Someone, somewhere was always awake doing something. Through its centers PEN International participated in at least a dozen conferences around the world each year, including meetings of its standing committees. PEN thought globally but worked locally.
Berlin—with its own alterations and progress—proved a fitting location for the presentation of International PEN’s new Three-Year Plan. For the past decade, since the 75th Anniversary at the Congress in Guadalajara, PEN International had been in an organizational reformation. It now had a governing structure with a global Board that participated in decision-making; it had revised its Constitution and Rules and Regulations; it had developed a budget, increased its funding, and recently moved its offices into Central London to a larger space with cheaper pro rata rent and an elevator, which had meaning for anyone who had climbed the steep four (or five?) flights to PEN’s old offices. The staff size had also increased, and PEN had hired its first Executive Director, Caroline McCormick Whitaker, former Development Director from the British National History Museum.

International PEN Board meeting preceding 72nd PEN Congress in Berlin, May 2006. L to R: Eugene Schoulgin (Norwegian PEN), Judith Rodriguez (Melbourne PEN), Kata Kulakova (Chair Translation & Linguistic Rights Committee), Sylvestre Clancier (French PEN), Sibila Petlevski (Croatian PEN), Chip Rolley (Chair Search Committee), Karen Efford (Program Officer), Caroline McCormick Whitaker (Executive Director), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (PEN International Secretary), Jiří Gruša (International PEN President), Peter Firkin (standing—Centers Coordinator), Eric Lax (PEN USA West), Jane Spender (Programs Director), Judith Buckrich (Women Writers Committee Chair)
Because British charitable tax law had changed, the opportunity had also arisen to unite International PEN and the International PEN Foundation into one charitable organization: International PEN, Ltd, a step that would provide the legal framework and protection for the organization and PEN’s name, would limit personal financial liability of the Board and attract a wider funding base. At the Berlin Congress, resolutions and approval were endorsed for this step which would be finalized the following year at the 2007 Congress in Dakar.
Caroline Whitaker took the Assembly of Delegates through the Three-Year Plan which had been developed after widespread consultation with PEN centers and the Board. She acknowledged that PEN couldn’t do everything that everyone wanted right away, that it was necessary to focus resources even as PEN developed more resources.
The Plan, which had grown out of all the discussions and preceding plans, concentrated on PEN’s three missions: to promote literature, to protect freedom of expression and to build a community of writers. “International PEN will work regionally to connect the activity of its many Centers around the globe on these issues,” Caroline told the delegates.

All PEN’s Standing Committees met at Berlin Congress—Writers in Prison Committee, Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee, Women Writers Committee and Peace Committee [Photo credit: Tran Vu]
In helping to develop PEN’s centers, the Three-Year Plan recommended International PEN focus on one region at a time, beginning with Africa where the 2007 PEN Congress would be held. International PEN would assist in programming and fundraising for development of PEN’s African Centers. The next regional focus would be Latin America, where PEN’s 2008 Congress was to be held. This rolling focus would allow the limited international staff to plan strategically. Regular daily work would still continue for the needs of centers in all regions.

PEN members met in workshops at 72nd Berlin Congress. Topics: PEN in the World—Global Issues; Education; the Strategic Plan; Centers; Networks and Partners; Asia and Central Asia; Middle East; Africa; Europe and Americas [Photo credit: Tran Vu]
As International PEN’s work had taken me across the globe that year, I’d come to see that PEN and its members formed a kind of intricate net which helped hold civil society together, the kind of sturdy net used on hills to prevent landslides. In a way that is what PEN members did around the world. They helped prevent literary culture and languages and freedom of expression from slipping away by both their active programming and their defensive actions
At the 1926 PEN Congress in Berlin International PEN’s President John Galsworthy and PEN’s founder Catherine Amy Dawson Scott had their voices recorded and preserved in a project of the German state. Galsworthy read a page from his Forsyte Saga. According to Dawson Scott’s journal, she recorded the following: “Even as individuals become families and families become communities and communities become nations, so eventually must the nations draw together in peace.”
It was a worthy, if not yet realized goal, but at least in PEN we had a global family.

Mayor’s reception for PEN members and participants at 72nd World Congress in Berlin, May 2006 [Photo Credit: Tran Vu]
Elections at 2006 Congress:
International PEN President: Jiří Gruša was re-elected for further 3-year term.
International PEN Board: Cecilia Balcazar (Colombian Center) and Eugene Schoulgin (Norwegian PEN re-elected to the Board)
Vice Presidents: Toni Morrison (American PEN) and J.M. Coetzee (Sydney PEN) elected Vice Presidents for service to literature and Gloria Guardia (Panamanian Center) for service to PEN
Women Writers Committee: Judith Buckrich (Melbourne Center) re-elected as Chair
Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee: Carles Torner (Catalan PEN) stood down as Vice Chair, replaced by Josep Maria Terricabras (Catalan PEN)
Next Installment: PEN Journey 42: From Copenhagen to Dakar to Guadalajara and in Between
PEN Journey 38: PEN’s Work On the Road in Kyrgyzstan and Ghana
PEN International celebrates its Centenary in 2021. I’ve been active in PEN for more than 30 years in various positions and now as an International Vice President Emeritus. With memories stirring and file drawers of documents and correspondence bulging, I am a bit of a walking archive and have been asked by PEN International to write down memories. I hope this personal PEN journey will be of interest.
There have been a number of conferences and a few Congresses in PEN I’ve regretted not being able to attend. One was the Women’s Committee conference June 2005 in Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan right after the 71st Bled Congress. As International Secretary, I have notes and reports from that conference. Nine years later in the fall of 2014, PEN held its 80th World Congress in Bishkek, a Congress I did attend. The Women Writers Committee led the way for International PEN into Central Asia. Later in 2005 members of the Women Writers Committee also met at the International PEN conference in Ghana which I did attend.

Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan, site of PEN International’s Women Writers Meeting in June 2005 and Accra, Ghana, site of PEN International’s African conference and also meeting of African women writers, November 2005.
First, Bishkek: The President of Bishkek PEN Vera Tokombaeva was concerned about the circumstances of writers in Central Asia since the breakup of the Soviet Union. She suggested to the new Women Writers Committee (IPWWC) chair Judith Buckrich that PEN hold a women writers meeting in Bishkek. Many of the institutions which had enabled writers to publish had vanished, and the status of women in the region had grown worse. Young writers from Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan and Tajikistan who were members of the PEN center were troubled by the decrease in the number of women working creatively. Only a handful were left.

PEN Women Writers Committee Chair Dr. Judith Buckrich and International PEN Board member Judith Rodriguez (Melbourne PEN)
Bishkek PEN did a study highlighting the problem. Central Asian women writers were struggling with poverty, it said, and literature was no longer published unless self-published with limited distribution.
“Women writers are now mostly on their own. They have fallen into a cultural vacuum,” the conference proposal noted. “They are not in contact with colleagues outside their own country and know nothing of the state of culture in the world. In the meantime the global community has begun to pay attention to Central Asia because its difficult geopolitical situation could lead to the rise of violent, ultra-religious and fundamentalist ideologies into the area. And it is partly the lack of modern local literature that makes the region a breeding ground where alien ideologies can take root among young people. Flourishing modern literature could be the means to disseminate democratic ideas and social awareness.”
International PEN raised funds for the conference whose theme was “Women and Censorship.” Women from Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan as well as from Finland, Norway, Switzerland and Australia gathered. The discussion focused on the access to education for women, access to literature and the formation of support groups and publishing cooperatives within and outside the region and ways to overcome censorship and self-censorship. The group addressed external pressures on what women should write and considered ways and means to access funding for women writers.
Attendee Kristin Schnider, President of Swiss German PEN, noted, “Following the discussion on the main topic, women and censorship in Central Asia, I learned just how hard it is for the strong and determined women I met to overcome censorship and self-censorship within their societies…First and foremost a woman is perceived as a mother and wife, tending the family. So much so that women feel they are confronted with the choice between being either creative or getting married. Women are not supposed to enter politics…[and] if women insist on writing they are supposed to stick to detective stories or romantic topics.”
In a discussion “The Situation in Central Asia: Women and Society and Economic Censorship,” moderator and documentary film maker Dalmira Tilepbergenova from Kyrgyzstan, noted: (translated from Russian)
“Patriarchy foundations have always been strong in Asia…My disclosing of gender inequality by the example of cinematograph is not casual. Because firstly cinematograph is a corporative sort of creative work and thus the problem of relations between men and women shows very clear and strikingly there. Second, I as a film director have to constantly deal with the problem of my work. Since Kyrgyzstan became independent, our cinematograph has passed through the period of its clinical death to its reestablishment. New names have already appeared and new films have been shot. But strange relations between our cinematograph and gender policy have existed up to now. Unwillingness of men to see women in the spheres usurped by men occur…instinctively. And this instinct is as strong as the instinct of self-preservation. Firstly, when the woman is engaged on an assisting job position in our cinematograph, everything seems to be all right. But as soon as the woman shows a desire to make films independently, the friendly atmosphere of men around her turns into syndicate of plotters. Men at once start to blame the woman for her excessive ambitions, incompetence, and uselessness. Men also criticize her private life. The woman’s desire to make films is considered as diagnosis of having deficit of sex.”
IPWWC Chair Judy Buckrich of Melbourne PEN reported the Bishkek conference was “a fantastic opportunity,” and said the committee had already begun planning for a meeting of women writers on the African continent to follow the Senegal PEN Congress in 2007. “The meetings are important in expanding the horizons of PEN to women who are not members of PEN but who PEN supports as part of its belief to support writers in difficult circumstances,” she noted.

Women Writers meeting at 2005 PEN Ghana conference including Veronica Uzoigwe (Nigerian PEN), Zeinab Koumanthio Diallo (Guinean Center), Ekbal Baraka (Egyptian PEN), Muthoni Likimani (Kenyan PEN), Kristin Schnider (Swiss German PEN), Caroline McCormick Whitiker (PEN International Executive Director), Jane Spender (PEN International Programs Director), Joanne Leedom-Ackerman (PEN International Secretary/American PEN)
In December 2005 International PEN’s conference in Accra brought together 36 writers, a number of them women, from 13 of PEN’s 17 African Centers to prepare for the 2007 Senegal Congress. Supported by UNESCO and hosted by Ghanaian PEN, the conference aim was to begin developing a plan for sustained programs and collaboration among the African centers and to select a theme for the Congress. While PEN Senegal would act as the host center, the World Congress was a joint effort of PEN’s PAN African Network. African members of the Women’s Committee held an additional meeting to address the challenges facing women writers in Africa and to plan for the larger IPWWC conference in 2007.
In preparing for the Ghana conference, I returned to the shelves of African literature I’d read years before and pulled some of the books which first took me to Africa before I ever arrived on the continent—Ama Ata Aidoo’s No Sweetness Here, Ayi Kwei Armah’s Fragments, Charles Mungoshi’s Waiting for the Rain. In my address to the conference, I included a quote from Ghanaian writer Kofi Anyidoho’s prose poem Akofar only to discover when I arrived that Kofi Anyidoho was on the program.

Speaking Ghanaian Professor and poet Kofi Anyidoho, seated Frankie Asare-Donkoh, Secretary PEN Ghana
From Akofar:
Words are birds. They fly so fast too far from the hunter’s aim. Words are winds. Sometimes they breeze gentle upon the smiles our hearts may wear for joy; they fan the sweat away from fever’s brow; they lull our minds to sleep upon the soft breast of earth. Yet soon too soon words become the mad dreams of storms. They howl through caves through joys into shrines of thunderbolts. They leave a ghost on guard at memory’s door. Therefore gently…gent-ly…Akofa, gen-t-ly…Take care what images of life your tongue may carve for show at the carnival of weary souls.”
The poem spoke to the themes and mission of PEN and the gathering of writers who understood that words transport over time and place and history, that words cross borders and have the power to connect us to each other and to ourselves. It is words, shaped into images and ideas, that survive wars and famine and political unrest if we are vigilant and protect them and circulate them and translate them.

Top to Bottom: Zeinab Koumanthio Diallo (Guinean PEN), Frankie Asare-Donkoh (Ghanaian PEN), Veronica Uzoigwe (Nigerian PEN)
I also quoted from Ghanaian poet Ayi Kwei Armah’s Fragments:
“Where are you going,
go softly.
Nananom,
you who have gone before,
see that this body does not lead him
into snares made for the death of spirits.
You who are going now,
do not let your mind become persuaded
that you walk alone.
There are no humans born alone.
You are a piece of us,
of those gone before
and who will come again.
A piece of us, go
and come a piece of us.
You will not be coming,
when you come,
the way you went away.
You will come stronger,
to make us stronger,
wiser,
to guide us with your wisdom.
Gain much from this going.
Gain the wisdom
to turn your back on the wisdom
of Ananse.
Do not be persuaded you will fill your stomach faster
if you do not have others’ to fill.
There are no humans who walk this earth alone.”
The poem reflected the aspiration of PEN and the meeting among participants who, as writers, often did work alone, yet understood we were all part of a larger community. For any community of letters to thrive and survive, the freedom of the individual writer had to be protected.
At that time in Africa over 230 writers in 34 countries were listed as PEN cases, excluding Egypt, which was counted in the Middle East, though the President of Egyptian PEN also attended the meeting. The large majority of cases were journalists arrested as critics of the authorities or as whistleblowers on corruption. Journalists also ran afoul of the “insult laws” which were on the books in 45 of the 53 African countries. Because of the difficult state of publishing in Africa, journalists were the group of writers with realistic possibilities of being published. Countries of most concern then were the Democratic Republic of Congo, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gambia, Libya, Somalia, Tunisia and Zimbabwe, none of which had active PEN centers, though a Somali-speaking PEN center did exist in London, and Zimbabwe PEN had existed but was inactive with its President poet Chenjerai Hove having to live in exile. (Today there are PEN centers in Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gambia, and Tunisia though the situation in some of the countries remains problematic.)
The Network of African Freedom of Expression Organizations (NAFEO) had formed just two months before the conference with 33 freedom of expression organizations attending a press freedom conference in Ghana. The aims of the network were similar to PEN’s whose Writers in Prison Committee would interact and assist when the network began to function.
The attendees at the Ghana conference shared experiences of their PEN centers, particularly in providing writing and reading programs in schools. Ghana PEN had a robust program in the schools as did other centers. The delegates agreed that the goals and work of PEN in Africa should include expanding freedom of expression, helping to lower barriers to publishing and disseminating African literature, cultivating new voices and increasing access to literary creation. The means to achieve these goals were part of the discussion, including cultivating new voices by working with youth writing clubs, bolstering recognition and excellence in literature by awarding literary prizes. Delegates planned for these discussions to continue among the African PEN Centers, facilitated when possible by International PEN. They also planned to expand the ideas and work at the 2007 PEN Congress.

Writers and visiting students at 2005 PEN International Conference in Accra, Ghana. African PEN Centers attending conference: African Writers Abroad, Algeria, Egypt, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Malawi, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somali-Speaking, South Africa, Uganda and Zambia as well as American and Swiss German and International PEN facilitating and note taking.

Ghana PEN organizers Frankie Asare-Donkoh, General Secretary and Frank Mackay Anim-Appiah, President with PEN International Secretary Joanne Leedom-Ackerman
During the Ghana conference the possible theme for the 2007 Congress was debated and discussed, including:
—Literature and the Environment/ Literature and Ecology
—Literature and Emancipation (women, political, financial)
—Freedom of Expression and Conflict Prevention
—African Writing in a New Age, In and Out of Africa
—The Role of Literature in the Creation of Peace (with sub-themes “The crisis of reading and readership” and “Literature for children”)
—Writers Role in Peace Building in Africa and World & Literature
—Literature and the Oral Tradition (with the subtheme of the environment)
—The Writer’s /Literature’s Role in Peace-building in Africa and the World
—Literature of Exiles/ Exile Literature
—The Roles of Literature and Publishing
—The Word, the World and Human Values
—Challenge of African Literature Today
—Being a Writer in Africa
—Writer in Age of Globalization (cultural diversity)
—Survival of Literature in New Millennium
—African Writing in New Age: In and out of Africa
—Writers and Prevention of Conflict
—Writers in Their Role in Encouraging and Promoting Literacy in Africa (Responsibility and Role of Writer)
—Literature and Conflict management in Africa and the World
—Freedom of Expression and Global Diversity
—Writers in a World in Crisis (diversity, literacy etc)
The theme finally agreed for the 73rd PEN World Congress in Dakar was: The Word, The World, and Human Values.

Elmina Castle, built in 1482 as Portuguese trading settlement, became principle holding prison for slave trade on Cape Coast, Ghana for three centuries.
The highlight of the conference was a long road trip to Cape Coast (also known as the Gold Coast), where the first European (Portuguese) explorers arrived in the 1400s. The Portuguese built the Castle of Elmina there which still stands on the rocks above the sea. In this new/old land the Portuguese discovered gold and also began acquiring human beings to trade for European goods. British, Dutch, Danish, Prussian, and Swedish traders soon followed and built other forts along the coast. Elmina Castle was turned into a prison for men and women who were sent shackled through “the door of no return” into slavery. From this point, as well as from Gorée Island off the coast of Dakar, Senegal, the slave trade flourished for centuries as European and other traders sold men and women and goods into the Caribbean and North and South America.

“Slave Exit to Waiting Boats” in Elmina Castle, Cape Coast, Ghana; Kadija George, President of African Writers Abroad Center standing in front of a “door of no return.” The back of her shirt reads: “Literature is the most beautiful of countries.”
The ghostly white fort of Elmina with its iron-barred cells with peep holes to the ocean facing west and the crashing surf on the rocks silenced us as we moved through these portals of history. The several hour ride back to the city was much quieter than our impatient journey to the Coast.
In Tanzania an exchange between poet and audience in the oral and performed poetry often begins:
“I give you a story.”
Audience: “I give you another.”
“I came and I saw.”
Audience: “See so that we may see.”
This power to see and invoke, to enter the rhythm of the human heart and dance there for a time with another as partner is what literature does and what PEN celebrates and tries to protect.
Next Installment: PEN Journey 39: Spiritus Loci—Literature as Home


